Узбекистан и страны Балтии объединяют усилия в борьбе с коррупцией
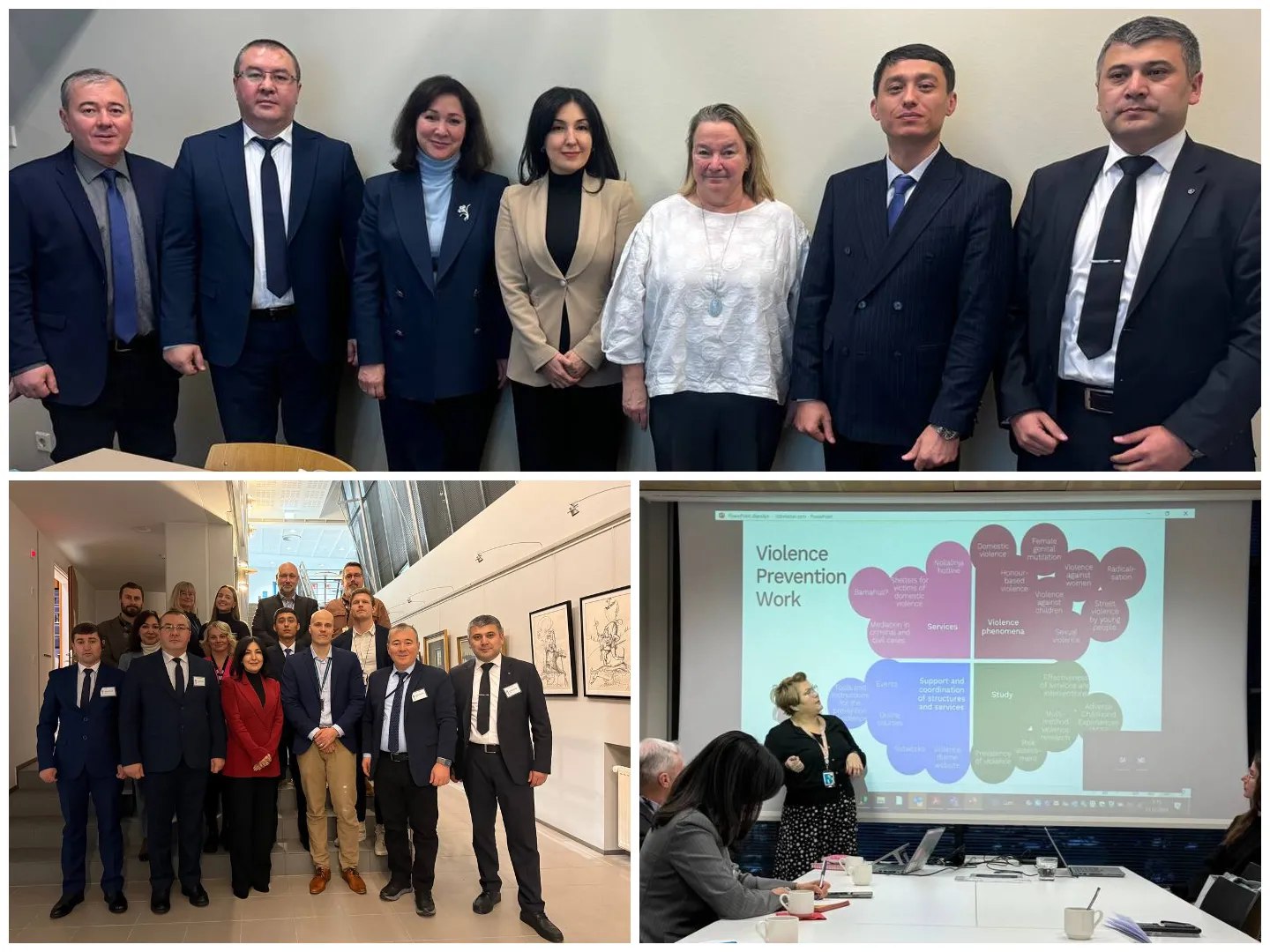
15.07.2025РИГА, 15 июля. /ИА «Дунё»/. Делегация Узбекистана во главе с директором Агентства по противодействию коррупции Акмалом Бурхановым посетила Латвию и Литву с целью укрепления двусторонних связей и определения новых перспективных направлений сотрудничества в сфере борьбы с коррупцией, сообщает корреспондент ИА «Дунё».
В рамках визита состоялись двусторонние встречи с директором “Transparency International Latvia” Кристой Асмусой и заместителем руководителя Бюро по предотвращению и борьбе с коррупцией Латвии Янисом Розе. В ходе встреч стороны выразили обоюдную заинтересованность в продолжении эффективного сотрудничества и расширении масштабов реализуемых совместных проектов.
В частности, на встрече с директором “Transparency International Latvia” обсуждались вопросы разработки эффективных стратегий противодействия коррупции, улучшения позиций Узбекистана в Индексе восприятия коррупции, обеспечения открытости и прозрачности государственных органов в этой сфере, а также повышения потенциала институтов гражданского общества.
На встрече с заместителем руководителя Бюро по предотвращению и борьбе с коррупцией Латвии состоялся обмен опытом по вопросам антикоррупционной экспертизы нормативно-правовых актов и их проектов, а также крупных строительных проектов. Стороны также обсудили практику оценки коррупционных рисков и мониторинга процессов государственных закупок.
Важно отметить, что Агентство по противодействию коррупции Узбекистана и Бюро по предотвращению и борьбе с коррупцией Латвии в 2022 году подписали Меморандум о взаимопонимании. В рамках этого документа осуществляется сотрудничество в сферах укрепления двусторонних связей в борьбе с коррупцией, обмена передовым опытом и информацией, повышения квалификации кадров, а также организации учебных мероприятий, семинаров и тренингов по вопросам профилактики коррупции.
В ходе встречи с директором Службы специальных расследований Литвы Линасом Пернавасом была подчеркнута значимость проводимых в Узбекистане реформ и роль международного сотрудничества в сфере противодействия коррупции. Стороны также отметили важность обмена опытом с Литвой для его адаптации и применения в национальной практике.
На встрече были обсуждены вопросы двустороннего сотрудничества в области профилактики коррупции, оценки коррупционных рисков и повышения квалификации кадров.
По итогам встречи был подписан Меморандум о взаимопонимании между Агентством по противодействию коррупции Узбекистана и Службой специальных расследований Литвы, создающий основу для дальнейшего развития сотрудничества в борьбе с коррупцией.
Подписание Меморандума стало важным шагом к укреплению международного сотрудничества Узбекистана в сфере противодействия коррупции. Ожидается, что реализация положений Меморандума будет способствовать обмену опытом, внедрению передовых практик и, как следствие, повышению эффективности антикоррупционных мер и улучшению позиций Узбекистана в международных рейтингах.
The Constitution of Uzbekistan: a foundation for modern statehood and human dignity
28.11.2025The 33rd anniversary of the adoption of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan is a momentous occasion for the nation. For the first time in our independent statehood, a Constitution adopted through the will of the people stands as a cornerstone of modern governance. It embodies the rich experience of national state-building, addresses pressing societal and administrative challenges, and presents a carefully considered strategy for the relationship between the individual, society, and the state amidst complex global geopolitical developments. In essence, the renewed Constitution reflects our irreversible commitment to democratic reforms in both state governance and human rights.
Our Basic Law defines the path of national development, ensures that reforms remain irreversible, and serves as the guiding framework for the country’s statehood model.
The anniversary is not only a celebration but also an opportunity to reflect on the Constitution’s role in daily life and its unmatched significance in safeguarding human dignity and justice. The President’s directive on celebrating Constitution Day at a high level reinforces this, highlighting the deep legal, moral, and strategic importance of the Constitution in modern society.
In today’s rapidly changing world, a country’s competitiveness, the effectiveness of governance, and the protection of human rights depend on constitutional norms and institutional mechanisms that meet contemporary needs. The revised Constitution embodies such modern legal approaches. It articulates principles such as human dignity, liberty, equality, social justice, popular sovereignty, and the rule of law, and establishes practical mechanisms for implementing these principles.
The Constitution’s impact extends to all sectors, uniting them under a single socio-legal system aimed at the overarching goal of ensuring human well-being. It serves as the foundation for consistent and sustainable reforms, from strengthening democracy and civil society to protecting entrepreneurship and expanding social protection. Positive changes in healthcare, education, science, culture, and sports all reflect the practical outcomes of these constitutional principles.
The core of these tasks is to convey the philosophy of the renewed Constitution, endorsed by the people, to every layer of society. It recognizes human dignity as the highest value, strengthens social solidarity, elevates legal culture, and unites the efforts of citizens to consciously and responsibly shape their future as a modern state founded on the rule of law – all under the noble ideal: “For the Motherland, for the Nation, for the People!”
The scholarly community and mentors in constitutional law play a crucial role in this process. Every academic study, legal insight, and educational initiative deepens public understanding of the spirit and essence of constitutional norms.
Practical mechanisms are also advancing these goals. For instance, “Law School” (“Huquq maktabi”) mobile application, developed under the President’s 24 May 2024 decree, enables citizens to acquire legal knowledge independently, conveniently, and in a modern format. With nearly 66,000 registered users, 32 educational courses, and over 33,000 users having completed courses and obtained certificates, the application is a clear sign of growing public interest in legal literacy. It is an effective, modern tool for strengthening legal culture, ensuring the rule of law, and enhancing citizens’ legal knowledge.
Tashkent State University of Law plays a vital role in educating the younger generation. Its faculty have developed “Foundations of State and Law” textbooks for students in grades 8–11, based on the revised Constitution, which help students understand its spirit and essence and develop practical skills to apply it in everyday life.
Ultimately, understanding the Constitution’s place in our lives and ensuring that its provisions are applied in all areas requires active civic engagement, a high level of legal culture, and steadfast commitment to the rule of law. The Constitution is more than a legal document; it is the moral benchmark of national development and the foundation that strengthens citizens’ trust in the state and society’s confidence in the future. Respecting it is not only a constitutional duty but also a civic responsibility in building the New Uzbekistan.
Ikhtiyor Bekov
Head of Constitutional Law Department,
Tashkent State University of Law
Professor of Law, DSc.
Third Renaissance: Center of Islamic Civilization as a strategy for Spiritual and Intellectual Advancement of New Uzbekistan
12.03.2026Human history demonstrates that every great advancement is built upon intellectual and spiritual foundations. Today, a project emerging from the heart of Central Asia is drawing global attention for its scale and significance - Center of Islamic Civilization is not merely an architectural landmark, but an intellectual bridge connecting the past, present and future of the region.
The anticipated opening of the complex in March 2026 has already attracted the attention of leading international publications and organizations, recognizing it as one of the most significant cultural projects of the New Uzbekistan.
The foundation for the project was laid in 2017, when President Shavkat Mirziyoyev introduced the initiative at the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly. At that time, Leader of Uzbekistan emphasized the need to show the international community the true humanistic essence of Islam - enlightenment, peace and creation. This was not only a political statement but also a program for returning to the roots of a land that for centuries served as a cradle of science and culture.
The emergence of this monumental project coincides with a global need for spiritual transformation. In an era where Islamophobia and radicalism are spreading across different parts of the world, Uzbekistan has proposed a model to confront these challenges through science and education.
Today, this vision has materialized in a majestic complex covering ten hectares in the historic center of Tashkent. Its 65-meter azure dome and four golden gates symbolically represent the unity of all regions of Uzbekistan. Across every line of the building, architectural traditions of the Timurid era are harmoniously integrated with modern technological solutions.
Center embodies a balance of religion and science. Its main pillar, reflecting the rich architectural traditions of Ulugh Beg Madrasah, is adorned with a calligraphic inscription of the first revealed verse of the Qur’an, “Iqra” (“Read in the name of your Lord”), symbolizing the pursuit of knowledge as the highest spiritual duty of every individual.
The centerpiece of the exhibition is the 7th-century Uthman Qur’an, a unique sacred relic inscribed by UNESCO in the “Memory of the World” Register.
The architectural concept of the complex impresses not only with its grandeur but also with its full compliance with contemporary urban planning and environmental sustainability standards. Every element of the project - from the foundation to the dome - has been constructed with respect for historical heritage and designed for longevity. The landscaped grounds surrounding the complex transform it into more than a scientific center, creating a spacious cultural and educational zone accessible to both city residents and international visitors.
The exhibition concept of the Center fundamentally departs from that of traditional museums. Built upon the principle endorsed by Shavkat Mirziyoyev, “Civilization – Personalities – Discoveries”, it does more than present historical facts; it immerses visitors in a living intellectual innovation. The exhibition is organized chronologically: the pre-Islamic period, the First and Second Renaissance and New Uzbekistan - forming the foundation of the Third Renaissance.
A special feature is the “Wall of Civilizations”, which showcases humanity’s intellectual progress as a continuous process. It illustrates how the discoveries of great figures from each era - including Al-Khwarizmi, Al-Farghani, Ibn Sina, Al-Biruni, and Mirzo Ulughbek - are directly linked to modern high technologies.
The extensive use of VR and AR technologies, holograms, and artificial intelligence enables the Center to “bring to life” unique 9th-century manuscripts, digitally reconstruct the original appearance of ancient observatories and transport past discoveries into the digital realm.
This large-scale integration of digital technologies positions the Center as a museum of the future. Through smart systems, visitors not only receive visual information but can virtually interact with great scientists and participate in their laboratory experiments. The “1001 Inventions” Laboratory, designed for children, sparks early interest in engineering and natural sciences. Center thus evolves beyond a repository of knowledge, becoming an interactive educational platform that nurtures the nation’s intellectual potential.
Shavkat Mirziyoyev, President of Uzbekistan, has repeatedly emphasized that the true strength of a nation lies in its memory and cultural roots. He instructed that museum exhibitions be enriched with authentic examples of national heritage and that the rarest artifacts preserving the spirit and history of the Uzbek people be returned to the homeland.
In fulfillment of this noble vision, a delegation led by Firdavs Abdukhalikov, Director of the Center of Islamic Civilization and a special commission of scholars, Orientalists and art historians, conducted large-scale research. One of the Center’s most important tasks is the repatriation of national cultural heritage scattered abroad; in recent years, systematic cooperation has been established with prestigious auction houses and private collectors for this purpose.
Thanks to these efforts, more than a thousand unique manuscripts and artifacts have been returned to Uzbekistan. The World Society for the Study, Preservation and Promotion of the Cultural Heritage of Uzbekistan (WOSCU) has also transferred numerous unique artworks from Transoxiana and Khorasan to the Center's collection.
Scientific expeditions and diplomatic missions organized by the Government of Uzbekistan have facilitated the creation of facsimile copies of manuscripts preserved in major museums and libraries worldwide. This process underscores that the rich cultural heritage of the Uzbek people is not only the legacy of Central Asia but also an integral part of the Islamic world and human civilization. Each repatriated treasure symbolizes the determination of the New Uzbekistan to restore its cultural identity.
The Center of Islamic Civilization is conceived not merely as a museum, but as an active scientific and educational platform. It provides comprehensive facilities for researchers, including a library housing over 200,000 volumes, restoration laboratories, a calligraphy school, and digital archives. Center also hosts offices of prestigious international organizations - including ICESCO, IRCICA and OCIS (Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies) - highlighting its role as a major hub for scientific and educational engagement.
More than 1,500 specialists from over 40 countries contributed to the project. International experts, including Khaled El-Enany, have described the Center as a “unique civilizational complex, integrating a next-generation museum, advanced research infrastructure, a modern library, national and international archives on the history of Central Asian civilizations, digital humanities technologies and an extensive network for global scientific and cultural collaboration”.
President of Finland, Alexander Stubb, referred to the Center as an intellectual hub of the modern world, likening it to historical institutions such as the Bayt al-Hikma, Academy of Ma’mun and Ulugh Beg Madrasah, which once shaped the development of science.
At the Congress “Central Asia: Shared Spiritual and Educational Heritage – Shared Future”, Center was visited by five presidents, becoming a symbol of collective regional pride. The event also brought together more than 300 scholars and cultural figures from Central Asian countries and Azerbaijan.
In February 2026, new reports from Paris further bolstered the project’s global prestige. The International Committee of the “Prix Versailles” included Center of Islamic Civilization in Tashkent in the list of the “World's most beautiful museums of 2026”.
This recognition is further reinforced by the inclusion of the Center of Islamic Civilization in authoritative international publications and rankings, such as “Smithsonian Magazine”, “BBC Travel”, “BBC History” and “National Geographic”. This places it alongside the world’s major museum initiatives, including the “Lucas Museum of Narrative Art” (Los Angeles), “National Geographic Museum of Exploration” (Washington, D.C.) and “London Museum” (London).
Such acclaim significantly enhances the Center’s scientific and tourism potential, transforming it into a must-visit global landmark. These achievements vividly demonstrate the creative potential of New Uzbekistan and its innovative approach that meets international standards.
It is no coincidence that the Center’s opening coincides with the Holy month of Ramadan. It was in 2018, during this blessed month, that the first stone of this grand project was laid. Now, eight years later, Center of Islamic Civilization will open its doors, becoming a vital symbol of the revival and preservation of Islamic cultural heritage for future generations.
In recent years, Uzbekistan has adopted more than 3 thousand normative acts aimed at comprehensive support for business
22.06.2024Business rights are a priority of the New Uzbekistan
Since 2017, Uzbekistan has put forward cardinal, unexpected and favorable changes for entrepreneurs. The peculiarity of these changes is that they were aimed at reducing the control functions of the state and opening the way to the free conduct of business. All barriers that hindered entrepreneurs at that time were gradually eliminated.
Liberalization of punishment against entrepreneurs, elimination of possibilities of unjustified interference in their activities, strengthening of close diplomatic ties with foreign countries, simplification of export-import procedures - all this gave a powerful impetus to the development of business environment and motivated entrepreneurs to develop and actively expand their business without obstacles.
In particular, all types of unscheduled inspections and counter-inspections of the activities of business entities, including criminal cases, were canceled. A mechanism of putting forward a moratorium on inspections conducted in the activities of entrepreneurs was introduced, which is actively used to this day.
The measure of criminal punishment in the form of deprivation of the right to carry out entrepreneurial activities was abolished.
Since 2017, the Business Ombudsman, created on the initiative of the head of state himself, has been functioning effectively. Reporting to the President, it makes proposals to improve the business environment in the country and remove various obstacles to the development of entrepreneurship.
Uzbekistan is not resting on its laurels. The country has set itself big goals - to bring the share of the private sector in GDP to 80% and the share of the private sector in exports to 60% by 2027.
The president's dialog with entrepreneurs is the key to solving many problems
It is important for every entrepreneur to be listened to in case of difficulties or obstacles in his/her activity. This is especially important if the problem requires the intervention of government officials.
Obviously, in the conditions of economic development of the state there are problems that create difficulties for business. They require prompt intervention from the highest authorities in order to prevent stagnation in the development of this or that industry, as well as to give an impetus for further development.
Such a peculiar impetus was the dialog of entrepreneurs with the President, which is held annually, and entrepreneurs have the opportunity to communicate directly with the head of state.
The opportunity to be heard is given to every entrepreneur in every region of the country through meetings. After analysis and generalization, the most relevant and justified proposals are submitted to the head of state for appropriate decisions. In addition, the proposals and complaints of hundreds of entrepreneurs are listened to on a day of open dialog.
Over the past three years, more than 33 thousand appeals and proposals were received from entrepreneurs during the open dialogs. As a result of the dialogs, more than 150 initiatives were put forward to remove obstacles in the development of entrepreneurship, as well as its further development.
In particular, if we analyze the initiatives put forward after the 2021 Dialogue, the reforms were aimed at mitigating the effects of the pandemic, extending tax and customs exemptions and granting deferral of taxes and mandatory payments.
The 2022 Dialogue stood out for the support of business representatives on various fronts, starting with tax reforms such as reducing VAT percentages to 12 percent, shortening the VAT refund period to 7 days, and introducing a flat tax rate of 4 percent instead of the current sales tax ranging from 4 percent to 25 percent.
In addition, the mechanisms for ensuring the rights of entrepreneurs have been expanded by introducing a procedure for canceling the decision to allocate land plots or property only in court.
As a result of the dialog, another problem that worried entrepreneurs was eliminated, concerning the application of higher tax rates due to the non-use of an empty building or land plot. This mechanism was not only canceled, but also debts of entrepreneurs in the amount of 2 trillion soums formed as a result of payment of taxes at the increased rate were written off.
Last year, as a result of the dialog, the mechanisms of financing entrepreneurship were radically revised, the Business Development Bank was established, and tax reforms aimed at protecting the rights of entrepreneurs were introduced.
It has become a tradition for entrepreneurs to look forward to the date "August 20 - Entrepreneurs' Day" every year. It is on the eve of this day that new initiatives to support business are announced in the course of dialog.
Digitalization of business protection as a guarantee to ensure unjustified interference in the activities of entrepreneurs
One of the topics of most concern to entrepreneurs is the topic of inspections. In this area, it is important to ensure the protection of entrepreneurs.
Digital monitoring of inspections conducted in the activities of entrepreneurs by state bodies is carried out by the Business Ombudsman.
The information system "Unified State Control" allows registering inspections carried out in the activities of entrepreneurs, their results, as well as filing complaints in case of violations by the inspecting authorities.
State bodies are prohibited from conducting inspections without registering them in this system. Otherwise, this will serve as grounds for administrative liability.
In order to ensure the transparency of inspections and the rights of business entities, the new system "Unified State Control" provides full access for business entities as well.
Thus, in the new system "Unified State Control" a number of functions have been added, such as the Electronic Book of Registration of Inspections, which provides full oversight of inspections by the Authorized Body.
In order to combat corruption and illegal inspections in the system "Unified State Control" was made an electronic database of all officials with the right to conduct inspections This in turn eliminates the possibility of falsification of data of the certificate with the right to conduct inspections. Entrepreneurs can check the data of the special license of inspectors and in case of non-compliance with the system have the right not to allow them on their territory.
Moreover, registers of state control functions and mandatory requirements have been compiled for business entities, which provides an opportunity to familiarize with the control functions of state inspections and mandatory requirements in relation to them.
As a result of the introduction of the "Unified State Control" system, it has become much easier for the Authorized Body to identify facts of offenses in the state control.
Strategy "Uzbekistan - 2030" - prospects for business development in the future
Uzbekistan does not stop at what has been achieved. Rapid steps to further support the business sphere are also enshrined in the Strategy "Uzbekistan - 2030".
Efficient use of local raw material base and development of industry based on advanced technologies, consistent transfer of monopolistic spheres to market principles, increasing the share of private sector in the economy, creating the most favorable conditions for free activity of entrepreneurs are still a hot topic.
In addition, full digitalization and simplification of the tax system is planned, as well as the creation of equal opportunities for all entrepreneurs to make the official sector preferable and more profitable than illegal activities.
For this purpose, a simplified and compact legislative system will be created, convenient for the population and business entities.
Dilmurod Kasimov,
authorized to protect the rights and legitimate interests
business entities