Phone
Consular Issues
Phone
Uzbekistan news
We recommend
Uzbekistan–Turkiye: From Trade to Expanded Economic Engagement
📅 29.01.2026
Economic cooperation between Uzbekistan and Turkiye is carried out within the framework of signed bilateral agreements and established intergovernmental mechanisms, and is supported by regular high-level contacts. In addition, Uzbekistan and Turkiye cooperate within the framework of the Organization of Turkic States.
In 2023, the President of the Republic of Turkiye paid an official visit to Uzbekistan, during which the Uzbekistan–Turkiye Business Forum was held. As a result of the visit, a substantial package of intergovernmental and commercial agreements was signed, covering key sectors of the economy with a total value of around $10 bn.
In June 2024, the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan paid an official visit to Turkiye. During the visit, a meeting of the High-Level Strategic Cooperation Council was held, resulting in the signing of an important package of agreements, protocols, and roadmaps aimed at further expanding trade, economic, and investment cooperation.
Mutual trade between Uzbekistan and Turkiye operates under a most-favoured-nation regime, and a Preferential Trade Agreement has also been signed.
Turkiye is among Uzbekistan’s leading trade and economic partners, ranking 4th in terms of total trade turnover and imports, and 5th in terms of Uzbekistan’s exports.
In 2025, Turkiye’s share in Uzbekistan’s foreign trade turnover amounted to 3.7%, including 3.4% of exports and 4.0% of imports.
Dynamics of Bilateral Trade
Over the period 2017–2025, bilateral trade between the two countries increased by 1.9 times and reached $3.0 bn by the end of 2025. Exports to Turkiye grew by 1.3 times to $1.1 bn, while imports from Turkiye increased by 2.8 times to $1.9 bn.
At the same time, annual growth rates of imports from Turkiye consistently exceeded export growth rates, resulting in a widening trade deficit to –$751.6 mn.
Uzbekistan’s exports to Turkiye in 2025 comprised the following categories: industrial goods (copper products, yarn, etc.) amounting to $511.4 mn (45%); miscellaneous manufactured articles (mainly precious metal products) at $152.3 mn (13.4%); chemical products (polymers, fertilizers, etc.) at $124.3 mn (11%); machinery and transport equipment at $80.1 mn (7%); food products (dried fruits and nuts) at $63.0 mn (5.5%); petroleum products (gasoline, gas oil) at $36.6 mn (3.2%); non-food raw materials at $18.0 mn (1.6%); as well as services, primarily transport services, at $149.9 mn (13.2%).
Imports from Turkiye in 2025 were dominated by the following categories: machinery and transport equipment at $674.6 mn (35.7%); chemical products at $408.9 mn (21.7%); industrial goods at $390.2 mn (20.7%); miscellaneous manufactured articles at $136.2 mn (7.2%); food products at $94.6 mn (5.0%); petroleum products (lubricating oils) at $30.2 mn (1.6%); non-food raw materials at $30.1 mn (1.6%); and services at $117.4 mn (6.2%).
Investment Cooperation
The two countries have signed an Agreement on the Promotion and Reciprocal Protection of Investments. As of 1 January 2026, 2,137 enterprises with Turkish capital operate in Uzbekistan, accounting for 11.8% of all active enterprises with foreign investment. Of these, 496 are joint ventures and 1,641 are wholly owned by Turkish investors.
Total direct investments and loans from Turkiye to Uzbekistan’s economy over 2017–2025 amounted to $9.0 bn, including $2.6 bn attracted in 2025 alone.
Turkish capital continues to expand its presence in Uzbekistan, primarily in priority sectors such as energy, manufacturing, agriculture, and construction.
In particular, investments in the power sector are linked to the construction by the Turkish company Cengiz Enerji of a 240 MW thermal power plant in Tashkent Region and a similar 220 MW plant in Syrdarya Region.
Prospective Areas of Economic Cooperation
An analysis of Turkiye’s import structure indicates opportunities to increase Uzbekistan’s exports to Turkiye, particularly in product categories that Uzbekistan already supplies to global markets. These include polymers (Turkiye’s imports amounting to $2.8 bn), copper wire ($1.4 bn), fertilizers ($1.1 bn), legumes ($1.0 bn), zinc ($857 mn), copper tubes ($360 mn), textile products, particularly T-shirts and undershirts ($373 mn), knitted fabrics ($158 mn) and other manufactured goods.
Promising areas for cooperative engagement between Uzbekistan and Turkiye include manufacturing industries – especially textiles, electrical engineering, and machinery – chemical industry, agriculture, healthcare, education, as well as projects aimed at preserving and promoting cultural heritage. There are also prospects for joint infrastructure projects, including the construction of water treatment facilities.
In agriculture, particular attention is paid to the selection and cultivation of domestic pistachio varieties and the development of pistachio farming. Agreements have been reached on implementing joint research projects focused on cultivation techniques and adaptation.
A significant emphasis is placed on expanding cooperation in education, including the involvement of Turkish lecturers and specialized professionals in educational initiatives in Uzbekistan, experience exchange, and human capital development.
At the same time, areas of cooperation in healthcare are being discussed, focusing on the development of primary healthcare, the introduction of medical insurance systems, sector digitalization, improvement of service quality, and modernization of the pharmaceutical industry.
Tourism has been identified as a separate and promising area of cooperation. Currently, 12 hotels in Uzbekistan operate with the participation of Turkish partners, along with more than 100 joint restaurants, reflecting sustained interest by Turkish businesses in the country’s tourism sector.
In 2025–2026, with the support of Turkish investors, 11 hotel projects with a total value of $167.9 mn are planned in Bukhara, Samarkand, Jizzakh, Fergana, and Tashkent regions.
Transport connectivity is also expanding significantly. The number of weekly flights between Uzbekistan and Turkiye has increased from 62 in 2023 to 106 at present, creating additional conditions for the growth of mutual tourist flows and the expansion of travel routes.
A key initiative in tourism is the “Million + Million” programme, aimed at attracting at least one million tourists to each country. The programme envisages a further increase in flight frequency and the expansion of tourist routes between Uzbekistan and Turkiye.
Conclusion
In recent years, there has been steady growth in bilateral trade, investment volumes, the number of enterprises with Turkish capital, and the breadth of economic cooperation.
At the same time, Uzbekistan’s exports to Turkiye are still dominated by raw materials and intermediate goods used in Turkiye’s industrial sectors. Against this background, the key task for the coming years is to move from a “raw materials–finished goods” trade model toward the formation of joint production chains with higher value added.
In this context, Turkiye can play a role for Uzbekistan not only as one of its principal trading partners, but also as a contributor to Uzbekistan’s industrial development and to the expansion of its participation in global value chains.
Edvard Romanov
Center for Economic Research and Reforms
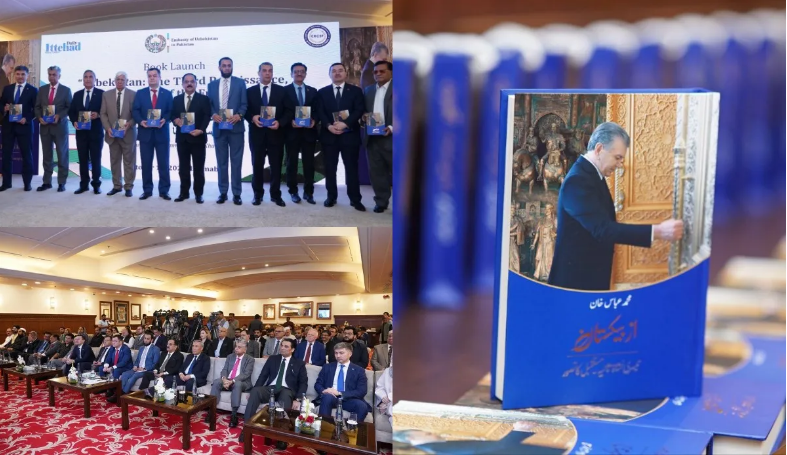
Pakistan hosts presentation of the book – “Uzbekistan: Third Renaissance – Concept of the Future” in Urdu
📅 06.11.2025
A presentation of the literary and publicistic collection “Uzbekistan: Third Renaissance – Concept of the Future” was held in Islamabad, written in Urdu by renowned Pakistani journalist and author Muhammad Abbas Khan, explores Uzbekistan’s modern development vision and reform agendat.
The collection offers a comprehensive analysis of the essence, spiritual foundations, and global significance of Uzbekistan’s vision for a New Renaissance — the foundation of the country’s Third Renaissance — under the leadership of President Shavkat Mirziyoyev. The book elaborates on the concept advanced by the Head of State, tracing its historical roots and outlining its relevance for the future of human civilization. The author emphasizes that this vision draws inspiration from the legacy of Uzbekistan’s great ancestors and seeks to unite the principles of modern development, enlightenment, and humanism, serving as a bridge between the nation’s rich intellectual past and its forward-looking aspirations.
The collection also highlights the shared initiatives and common aspirations of the leaders of Uzbekistan and Pakistan to advance major transport and communication projects linking Central and South Asia. According to the author, these efforts represent the revival of the legendary Silk Road. The book not only describes the sweeping reforms and modernization taking place in Uzbekistan, but also emphasizes that the development path of the “New Uzbekistan” may serve as an inspiring model for Pakistan and the wider Eastern world.
The presentation ceremony brought together members of Pakistan’s government and parliament, representatives of the diplomatic corps accredited in Islamabad, prominent scholars, analysts, public figures, and media representatives. Attaullah Tarar, Federal Minister for Information & Broadcasting of Pakistan, attended the event as the guest of honour.
The presentation opened with the national anthems of Uzbekistan and Pakistan, followed by a video highlighting the nine years of Shavkat Mirziyoyev’s leadership as a President of Uzbekistan.
The event commenced with welcoming remarks by Alisher Tukhtaev, Ambassador of Uzbekistan to Pakistan. In his address, the Ambassador emphasized that, under the leadership of President Shavkat Mirziyoyev, Uzbekistan has entered an era of openness and creative transformation.
He noted that over the past nine years, the country has implemented comprehensive reforms across the socio-economic, political, educational, and cultural spheres. As a result, Uzbekistan’s Gross Domestic Product has doubled, reaching 115 billion US dollars; exports have risen to 26 billion dollars; and foreign investments have exceeded 130 billion dollars. Thousands of new enterprises have been established, reflecting the dynamic pace of development and modernization.
It was noted that relations between Uzbekistan and Pakistan have been elevated to the level of a strategic partnership, with the establishment of the High-Level Strategic Cooperation Council. Direct air connections now link Tashkent with Islamabad and Lahore, while collaboration in the fields of education and culture continues to expand rapidly.
Particular attention was given to the Trans-Afghan Railway Project — recognized as a strategic initiative aimed at strengthening peace, mutual trust, and economic connectivity across the region, effectively reconnecting Central and South Asia.
Ambassador Alisher Tukhtaev expressed his sincere gratitude to the author of the featured work, Muhammad Abbas Khan, and to the management of “Daily Ittehad” publishing house for their contribution to the creation and publication of the book. He emphasized that this work will make a valuable contribution to fostering friendship and solidarity between the peoples of Uzbekistan and Pakistan.
In turn, Tahir Farooq, head of “Daily Ittehad” publishing house, expressed his satisfaction with the publication of the book “Uzbekistan: Third Renaissance – Concept of the Future”.
“This book is not merely a compilation of facts about Uzbekistan”, - he noted, - but an important work that vividly reflects the ongoing processes of reform and renewal in the country. It is not a collection of speeches or a translation of another author’s work, but the result of five years of observation and analysis by Muhammad Abbas Khan. His insights carry great significance for understanding Uzbekistan’s contemporary path of development. The book also serves as an important historical document of the new era unfolding in Uzbekistan”.
In his address, Attaullah Tarar, Minister for Information and Broadcasting of Pakistan, highlighted the deep historical ties between the peoples of Uzbekistan and Pakistan, noting that the land of Uzbekistan has produced eminent figures of the Timurid dynasty, including the distinguished scholar and statesman Zahiriddin Muhammad Babur. The Minister emphasized that the region connecting Central and South Asia has always been a vital part of the Great Silk Road, and that Uzbekistan’s contemporary policy under the leadership of President Shavkat Mirziyoyev is focused on revitalizing this historic corridor of cooperation.
Concluding his speech, Minister Attaullah Tarar reaffirmed the readiness of Pakistan’s Ministry of Information and Broadcasting to extend full support in promoting the book and the “Third Renaissance” initiatives advanced by President Shavkat Mirziyoyev to the Pakistani public.
In his address, author Muhammad Abbas Khan discussed the process of writing the book, the ideas it conveys, and its principal objectives. According to the author, the work is based on his research, observations, and personal impressions, providing an objective account of Uzbekistan’s ongoing processes of renewal and development.
“I have had the opportunity to directly observe the profound transformations taking place in Uzbekistan, the reforms being implemented under the leadership of President Shavkat Mirziyoyev, and the policies aimed at fostering an open society, enhancing human dignity, and advancing education and enlightenment, along with their tangible results. Today, Uzbekistan is experiencing a period of awakening. The concept of the Third Renaissance, being realized in Uzbekistan, serves as an example of a universal experience grounded in confidence in the future, scientific and spiritual renewal, and policies for the development of human potential”, - said Muhammad Abbas Khan.
The book “Uzbekistan: Third Renaissance – Concept of the Future” is expected to serve as a unique resource for familiarizing the Pakistani public with Uzbekistan’s new historical path of development, while further strengthening the cultural and spiritual bonds between the two nations.
UZBEKISTAN – A HOMELAND OF TOLERANCE AND SOLIDARITY
📅 22.09.2025
If the greatest gift given to human is life, then, without a doubt, the highest goal that humanity has always strived for is peace and harmony. That is why we always wish each other peace and tranquility, health and well-being.
Uzbekistan has always been a place of tolerance, harmony and friendship. Representatives of different nationalities and peoples living on the same land, drinking water from the same river, sharing happiness and sorrow together, have coexisted side by side for centuries. No wonder that such expressions as “Tolerant Uzbekistan!” and “Generous Uzbek people” have appeared.
In a multinational and multi-confessional state, interethnic consent and interfaith harmony are important factors that create a solid foundation for stability and development, determining its prospects.
One of the main factors why our country is rapidly developing today, fruitfulness of reforms and steady growth of the people’s well-being is that representatives of more than 130 nationalities and peoples, 16 religious confessions live together in our country as a single people of Uzbekistan.
The fundamental basis of reforms in this direction is that our Constitution stipulates that the Republic of Uzbekistan ensures a respectful attitude towards languages, customs and traditions of the nationalities and peoples living on its territory, and creates conditions for their development.
Today, education in schools is conducted in 7 languages, creating conditions for pupils of different nationalities to receive education in their native language. National television and radio channels broadcast in 12 languages, and newspapers and magazines are published in 14 languages, creating equal conditions for everyone to receive information in their native language.
Representatives of different nationalities and peolpes living in our country, as the single people of Uzbekistan, contribute to the development of our country with their active and selfless work, nowadays about 5 thousand representatives of 35 nationalities work in the state civil service.
In particular, 12.7 percent of our deputies in the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis, which are considered the country’s political institutions, and 11.2 percent in local Kengashes, are representatives of different nationalities and peoples. There is no limit to such achievements, we observe that interethnic harmony and solidarity are reflected in every aspect of society.
The President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev considers the ethnic diversity that has existed on the land of our country since ancient times as a unique social phenomenon and pays special attention to the preservation and further strengthening of harmony between nationalities, peoples and confessions. As a result of the wise policy of the head of our state, based on the principles of prudence, humanism and justice, national unity is growing stronger in our country, and our precious and beloved Motherland is becoming a place of peace, friendship and mutual respect, where human dignity and happiness reign.
As the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev emphasized in his speech at a meeting with deputies of the chambers of the Oliy Majlis, representatives of political parties and the public on May 8, 2023: “Our main wealth is our great multinational people, who consider Uzbekistan their only Motherland. The highest duty of each of us is to carefully preserve, like the apple of our eye, the priceless treasure — interethnic friendship and harmony that have taken hold in our beloved country”.
Indeed, in New Uzbekistan, interethnic and interfaith harmony, and mutual understanding based on loyalty to the spiritual heritage of ancestors, educating the younger generation in the spirit of tolerance, respect for national and universal values and patriotism, have become one of the most important priorities of state policy.
Large-scale reforms implemented in all spheres of public life at the initiative of the head of state also marked new milestones and initiatives in the field of interethnic and interfaith relations.
In this sense, the Decree of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On measures to bring to a new stage the strengthening of national harmony and relations with compatriots abroad”, adopted on March, 2025, and the Resolution “On measures to effectively organize the activities of the Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan on Interethnic Relations and Compatriots Abroad” bring work in this direction to a qualitatively new level.
In accordance with these documents, the Committee on Interethnic Relations and Compatriots Abroad of the Republic of Uzbekistan was created on the basis of the Committee on Interethnic Relations and Friendly Cooperation with Foreign Countries under the Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
The main tasks of the Committee were defined as the harmonization of interethnic relations, strengthening friendship, harmony, tolerance and unity in society, the formation of a single civil identity, strengthening the involvement of all nationalities and ethnic groups in national development, promoting the preservation of the national identity of compatriots abroad and mobilizing their social and economic potential for the development of our homeland, as well as promoting the prevention and identification of factors that negatively affect interethnic harmony.
Also, the fact that it is planned to develop draft concepts of state policy in the field of ensuring national unity and strengthening relations with compatriots abroad indicates that work in this direction will be consistently continued.
First of all, as an important element in ensuring national unity, special attention is paid to preservation of culture, language, customs, values and traditions of all nationalities and peoples living in Uzbekistan, and transmission to the younger generation
As is known, the role of national cultural centers is very important in the systematic implementation of work in this direction. Today, there are 157 national cultural centers in our country. Their activities are constantly supported by the state. Based on the President’s initiatives, starting in 2021, state subsidies will be allocated for the operation of these centers and their implementation of activities aimed at popularizing culture, language, customs, values and traditions.
For national cultural centers operating in the regions, premises have been allocated in the “Houses of Friendship”, where they use these places absolutely free of charge. Also, in the building of the Committee on Interethnic Relations, located in the center of Tashkent, all conditions have been created for the work of 27 national cultural centers of the republican and city level.
In particular, the construction in July of this year next to the building of the Committee on Interethnic Relations of the Pavilion of National Cultural Centers is a unique symbol of national harmony, where national houses of 22 nationalities were built, became a great gift from the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan to national cultural centers. This pavilion can safely be called a place of national harmony.
The grand opening of the pavilion of national cultural centers took place as part of the Friendship Festival, which was held throughout our country from July 25 to 31 this year, in honor of Peoples’ Friendship Day, celebrated on July 30.
The event was attended by members of the Senate of the Oliy Majlis and deputies of the Legislative Chamber, representatives of ministries and departments, the public, and the media, guests from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and China, as well as heads and employees of diplomatic missions of 30 states and international organizations in Uzbekistan.
The participants of the event assessed the construction of this pavilion as a unique event, emphasizing that it opens up another wonderful opportunity for the nationalities and peoples living in Uzbekistan to preserve and develop their culture, customs and traditions, fully reflects the large-scale reforms carried out in our country in the sphere of interethnic harmony and national unity, and serves as a platform for mutual cultural exchange.
Akiko Fujii, UNDP Resident Representative in Uzbekistan, who took part in the event, noted that she highly appreciates the respect and attention to various nationalities and peoples in Uzbekistan, and she considers the opening of the pavilion of national cultural centers to be truly attention to the person, and a progressive idea.
Thanks to the strong political will of our President, special attention is paid to close cooperation with compatriots living abroad. One of such projects is the Uz Global Think forum. This project is being implemented in the form of an ongoing dialogue between compatriots living abroad — representatives of expert and scientific circles — with the aim of creating business platforms, exchanging opinions on issues such as the socio-economic development of society, environmental sustainability and quality education.
A platform is also being created for the exchange of opinions among compatriots abroad about individuals in academic circles, their life path, successes and recommendations that will serve the development of New Uzbekistan.
In addition, in order to further increase the contribution of compatriots abroad to the economic power of the New Uzbekistan, following the example of the UNDP program “Knowledge Transfer through Compatriots Abroad”, work is underway to transfer human capital, which will contribute to ensuring innovative socio-economic development and environmental sustainability.
The “Graduates from Uzbekistan” program is being developed, which will unite and support compatriots who graduated from foreign educational institutions, and live and work in foreign countries.
All these tasks serve the further development of Uzbekistan with the participation of compatriots abroad.
One of the most important human freedoms is undoubtedly freedom of conscience. The adoption in 2021 of a new version of the Law “On Freedom of Conscience and Religious Organizations” was another important step towards institutional strengthening of freedom of conscience in our country. This law further strengthened the principles of tolerance and created a solid legal basis for the activities of all faiths.
Today, 2,361 religious organizations belonging to 16 confessions operate freely in Uzbekistan. Of these, 2,164 are Islamic, 197 are non-Islamic: 180 Christian, 8 Jewish, 7 Baha’i, as well as a Buddhist temple, a Krishna center, and an interfaith Bible society. In 2017–2024 there were registered 108 new religious organizations. New mosques, Christian churches and temples were built, and existing ones were renovated. This is a practical confirmation of respect for all faiths.
At the same time, we have every reason to say that the adoption of the Law “On the Concept of Ensuring Freedom of Conscience of Citizens and State Policy in the Religious Sphere in the Republic of Uzbekistan” on February 25 of this year has become the most important event in the life of society.
The concept will serve the multinational and multi-confessional people of Uzbekistan to realize the interests of society as a whole, to ensure its harmonious coexistence based on equality, social justice and unity.
This year, on September 10-13 the II International Forum “Dialogue of Declarations” was held in Tashkent and Samarkand.
In May 2022 the first forum “Dialogue of Declarations” was held in Tashkent, Samarkand and Bukhara over five days. Leading scientists from a number of foreign countries, as well as representatives of local authorities and religious organizations took part in the forum. The Bukhara Declaration adopted following that conference was subsequently recognized as an official document at the 76th session of the UN General Assembly. This confirms the importance of the Uzbek model for the formation of a tolerant society consisting of people of different nationalities, religions and beliefs.
The regular holding of the forum “Dialogue of Declarations”, the participation of influential foreign and international participants in it testifies to the high recognition in the world of Uzbekistan’s policy aimed at ensuring freedom of religion and interfaith harmony. In addition, the II Forum confirms Uzbekistan’s commitment to the principle of openness, development of an atmosphere of religious magnanimity and tolerance, in order to bring interfaith dialogue to a higher level of values. We are also convinced that this conference will serve as a unique platform for the exchange of best practices in ensuring peaceful coexistence of peoples and representatives of different faiths.
I would like to conclude the article with the following words from the festive greetings of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev on the occasion of July 30 – Peoples’ Friendship Day:
“In the current extremely dangerous situation, when various conflicts on national and religious grounds continue in different regions of the world, we will continue to work to further strengthen our greatest wealth — peace and stability, an atmosphere of mutual respect and harmony in our country — based on the idea of a united Uzbekistan, educating young people as holders of national and universal values, knowledge, professions, deepening the principles of inclusiveness.
We are mobilizing all our forces and capabilities for the reliable protection of the rights and interests of representatives of all nationalities and faiths who are proud to be citizens of Uzbekistan, as well as our compatriots abroad, everywhere, in accordance with the requirements of our Constitution and laws”.
Kakhramon SARIEV,
Chairman of the Committee
on Interethnic Relations and Compatriots Abroad
of the Republic of Uzbekistan
Linguistic Analysis of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan’s 2026 State of the Nation Address
📅 02.01.2026
The analysis covers the key thematic and semantic emphases of the President’s speech, the structure of core concepts and their interrelations, priority directions of state policy, as well as the strategic benchmarks for the country’s socio-economic development in 2026.
On 26 December 2025, President Shavkat Mirziyoyev delivered his Address to the Oliy Majlis and the people of Uzbekistan. Experts of the Center for Economic Research and Reforms (CERR) conducted a linguistic content analysis of the President’s speech.
The analysis was carried out using modern linguistic methods and is aimed at identifying semantic priorities, key concepts and their connections. A word cloud and diagrams were also prepared to visually demonstrate the priority directions of state policy.
Analysis (from the original language)
In total, the President used 9,135 words in his Address. The creation of a word cloud made it possible to visualize the most significant themes and gain a deeper understanding of the priorities and directions of the country’s socio-economic development.
Figure 1. Most frequently used words in the President’s Address (26.12.2025)
The linguistic analysis showed that the most frequently used key words included “mahalla” – 49 times, “aholi” (population) – 35 times, “iqtisodiyot” (economy) – 28 times, “bozor” (market) – 26 times, “loyiha” (project) – 25 times, and “technology” – 22 times (Fig. 1).
Words such as “ta’lim” (education), “natija” (result) and “daromad” (income) were each used 20 times; “tadbirkor” (entrepreneur) and “sanoat” (industry) – 19 times each; “suv” (water) – 18 times; “elektr” (electricity) and “hudud” (territory) – 17 times each; “yoshlar” (youth), “infratuzilma” (infrastructure) and “qurilish” (construction) – 16 times each.
The analysis of two-word expressions showed that the phrase “Markaziy Osiyo” (Central Asia) was used eight times; “aholi daromadi” (household income), “qishloq xo‘jaligi” (agriculture) and “yangi bosqich” (new stage) – seven times; “yangi texnologiyalar” (new technologies) and “Toshkent shahri” (city of Tashkent) – six times each. Expressions such as “Davlat xizmatlari” (public services), “xorijiy investitsiya” (foreign investment) and “yangi tizim” (new system) were used five times, while “dual ta’lim” (dual education), “ish o‘rni” (jobs), “viloyat markazlari” (regional centers) and “tuman byudjeti” (district budgets) were used four times each.
Among three-word combinations, the most frequent expressions included “the next five years” – nine times; “based on dual education” – four times; and “water-saving technologies” and “water, electricity” – three times each.
Thus, the analysis shows that at the core of state policy are the mahalla, public welfare, and the transition to a new stage of development based on economic and technological transformation, with clearly defined strategic objectives for the next five years.
Thematic structure of the speech
The diagram below shows the distribution of the speech’s vocabulary by key directions, where the content is grouped into nine main thematic blocks.
The diagram clearly demonstrates that technological development and human interests, implemented at the level of the mahalla, are at the center of state policy. The ultimate goal of all reforms is to ensure public welfare through sustainable economic growth (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Distribution of words by thematic areas in the structure of the speech
Interconnection of development directions
The analysis highlights key words that demonstrate the interconnection between various directions of Uzbekistan’s state policy in the coming years.
The transition of the economy to a technological and innovation-based growth model is a central element of state policy and implies a shift away from a raw-materials model toward high-tech industry. This direction is closely linked with such concepts as “investment,” “technology,” “market,” and “product.”
The block on economic growth and welfare reflects the key outcomes of reforms, including the increase of the economy to $145 bn and a twofold reduction in poverty over the past three years. It is directly associated with the concepts of “population,” “economy,” “mahalla,” and “services.”
The social foundation of reforms is built through the development of the mahalla and social solidarity. This direction is associated with “mahalla,” “youth,” “society,” and “values.”
Structuring vocabulary by thematic areas shows that the core of the President’s speech is technological modernization of the economy and a human-centered governance model based on the “mahallabay” system.
It emphasizes the interconnection between economic growth, improvement of public welfare and the development of local infrastructure, as well as priorities such as strengthening human capital, expanding employment and increasing the efficiency of public administration.
Figure 3. Interconnection of development directions
Among the highlighted semantic blocks are also tasks related to stimulating domestic demand, developing the housing and tourism sectors, modernizing the transport system, increasing productivity in agriculture and introducing water-saving technologies.
Special emphasis is placed on the “green” agenda, including the development of renewable energy, expansion of the “Yashil Makon” (“Green Space”) initiative, and strengthening resilience to climate risks.
In the foreign policy dimension, the analysis highlights Uzbekistan’s openness, strengthening of good-neighborly relations, and integration into the global economic system.
The linguistic analysis confirms that the idea at the core of the President’s speech is built around the triad “inson qadri – mahalla – farovonlik” (human dignity – mahalla – welfare), where the goal of reforms is sustainable growth, improved quality of life, and the further strengthening of Uzbekistan’s position.
Ilyos Rabbimov, CERR
CERR Public Relations Service
For inquiries, please contact:
(78) 150 02 02 (417)
Improving Efficiency and the Rational Use of Energy Resources
📅 22.01.2026
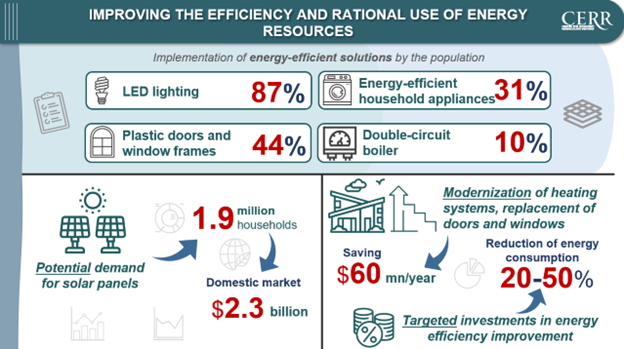
A study conducted by the Center for Economic Research and Reforms has revealed a large-scale transition of Uzbekistani households to energy-saving technologies. The widespread adoption of energy-efficient solutions has enabled nearly 90% of households to implement at least one measure to reduce energy costs.
One of the key changes has been the widespread adoption of energy-efficient solutions at the household level.
The most common practice has been the installation of LED lighting. Overall, 87% of households have switched to LED lighting. In some regions, such as the Republic of Karakalpakstan and Khorezm, Navoi, and Tashkent regions, this figure exceeded 90%.
A total of 44% of households improved the thermal insulation of windows and doors through the installation of plastic structures, with particularly high activity in Kashkadarya (84%), Bukhara (69%), and Khorezm (54%) regions.
Additionally, 31% of households purchased energy-efficient household appliances, with the highest shares observed in Jizzakh (60%), Navoi (59%), and the Republic of Karakalpakstan (54%).
There is also growing interest in the use of renewable energy sources. More than half of owner households expressed satisfaction with the results and interest in expanding generation capacity.
The analysis indicates that potential demand for solar panels among the population amounts to approximately 1.9 million households, opening prospects for the formation of a domestic market valued at over $2.3 bn.
At the same time, a share of consumption through less efficient heating sources remains, including outdated gas boilers and solid-fuel stoves.
Potential for Improving Building Energy Efficiency
According to estimates, insulating the exterior walls of apartment buildings, modernizing heating systems, and replacing doors and windows could yield savings of more than $60 mln per year.
According to the World Bank, similar potential exists in social facilities, healthcare institutions, preschools, and public schools. Targeted investments to improve the energy efficiency of these facilities could reduce energy consumption by 20–50%, equivalent to a reduction of up to 7.1 bn kWh per year.
Thus, the measures being implemented in Uzbekistan to enhance energy efficiency serve as an important driver of economic growth.
CERR Public Relations Sector
Tel.: (78) 150 02 02 (417)
Uzbekistan – Turkey: The Practical Phase of Cooperation in the Forestry Sector
📅 29.01.2026
Today, one of the priority areas of state policy in Uzbekistan is focused on expanding forested areas, increasing green coverage, mitigating the negative impacts of climate change, and ensuring environmental sustainability. In order to achieve effective results in these areas, studying advanced foreign experience and adapting it to the country’s climatic conditions is of particular importance. In this context, the participation of a delegation of representatives of the Forestry Agency under the National Committee on Ecology and Climate Change of Uzbekistan in a training and practical seminar organized during their visit to the Republic of Turkey in October 2025 was of significant importance.
The seminar, organized in cooperation between the Forestry Agency and the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry of the Republic of Turkey, enabled participants to familiarize themselves with Turkey’s experience in forest establishment, restoration, ecological classification, and sustainable forest management. In particular, on the first day of the seminar, Turkish specialist Ahmed Yalvach delivered a detailed presentation on modern approaches applied in the development of forestry.
Within the framework of the practical visit, Turkey’s advanced experience in establishing and managing nurseries, creating forests using the “terrace” method in mountainous areas, developing “green belts” around cities, and establishing green public parks in urban and district areas was studied.
In addition, members of the delegation closely examined the activities of nurseries operated by the Seydikemer and Gökova Forestry Departments located in Muğla Province. Notably, the Seydikemer nursery, established in 1983, covers an area of 144 hectares and has an annual production capacity of 1.5 million seedlings. The Gökova nursery, occupying more than 61 hectares, stands out with its capacity to produce up to 7 million seedlings per year.
It was emphasized that special attention to seed collection, storage, and laboratory analysis in these nurseries allows the production rate of high-quality seedlings and saplings to reach 90–95 percent. Participants studied the practical experience of Turkish specialists in establishing mother plantations, caring for seedlings and saplings, and grafting techniques.
The delegation members were also introduced to the use of greenhouses, in vitro laboratories, modern equipment, and mechanisms for managing seasonal work processes. The experience-sharing activities were conducted in an atmosphere of open dialogue and professional cooperation.
In conclusion, cooperation between Uzbekistan and Turkey in the forestry sector has acquired a practical dimension, contributing to the adoption of advanced practices, enhancement of specialists’ capacity, and the formation of a sustainable ecological environment in Uzbekistan. The knowledge and skills gained within the framework of this cooperation will play an important role in further improving the national forestry system.
A New and Technological Approach to Elections Begins
📅 26.07.2024
The Central Election Commission held a meeting and a series of events today, July 26th. The primary agenda item was the preparation and high-level accomplishment of the upcoming elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies in full compliance with the Constitution and laws.
According to Article 128 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan, elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies are scheduled to take place on the first Sunday of the third ten-day period of October in the year their term expires. Considering that the term of the deputies of the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies ends in 2024, the elections will be held on October 27th of this year, and the election campaign will begin on July 26th, as decided by the Central Election Commission.
These elections mark a significant departure from the past, taking place in a new socio-political environment as stipulated by our Constitution. The meeting underscored the unique features of these elections, which include:
- For the first time in Uzbekistan's history, the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis elections will be conducted using a mixed electoral system, combining majoritarian and proportional systems. This significant change will see seventy-five deputies elected directly through the majoritarian system, where voters vote for specific candidates. The remaining seventy-five deputies will be elected based on votes cast for political parties under the proportional system.
- One of the most significant advancements is the full digitization of election commissions' activities at all levels and their interactions with participants in the election process. This development significantly reduces bureaucracy, time, and document handling in election procedures, ushering in a new era of efficiency in our electoral system.
- Our election legislation has been fundamentally improved to align with advanced democratic standards. These improvements include introducing a new system for election bodies led by the Central Election Commission and requiring political parties to ensure that at least 40% of their candidates for deputy positions are women. Additionally, a candidate must receive a relative majority of votes to be elected. If a candidate gets more votes than other candidates in their respective electoral district, they will be elected without needing a repeat vote.
- The elections are taking place in conditions of significantly strengthened parliamentarianism and the powers of representative bodies at the local level, as established by the Updated Constitution. Specifically, the absolute powers of the Legislative Chamber have increased from 5 to 12, and those of the Senate from 12 to 18. The parliament's oversight functions over the activities of executive, judicial, law enforcement agencies, and special services have been expanded. The institution of hokims leading local Councils of People's Deputies is being abolished. To enhance the role of representative bodies in resolving important state issues, 33 powers previously held by hokims have been transferred to local Councils.
The meeting underscored the significance of these elections as a vivid example of democratic state-building in our country and an essential means for citizens to exercise their constitutional rights to vote and be elected to democratic state bodies. The elections will involve the election of 150 deputies to the Legislative Chamber, 65 members to the Senate, 65 deputies to the Jokargy Kenes of the Republic of Karakalpakstan, deputies to 208 district (city) Councils in the regions and Tashkent city, with around 30,000 candidates and nearly 90,000 trusted representatives actively participating. Over 120,000 election commission members and more than 70,000 citizens and international observers are expected to participate in the election process.
Considering the important role of elections in state life and with the aim of widely engaging citizens in this process, the Central Election Commission announced that the elections will be held on October 27th under the slogan “My Choice—My Prosperous Homeland.”
The 'E-Saylov' information system is a key tool in making the election process more transparent and accessible. It facilitates around 60 interactions between election commissions, political party candidates, observers, and the media entirely electronically. Integrated with other electronic platforms, the system automates many procedures in the election process without human intervention. This system forms an extensive database of nearly 400,000 participants in the election process, including election commission members, candidates, and observers. Around 32,000 participants will professionally use the information system, which includes communication through 40 types of SMS notifications.
For citizens, the "E-Saylov" information system introduces several conveniences in obtaining election-related information. Specifically, it provides statistical data on voters and polling stations, information on candidates for various elections, and interactive maps to learn about candidates and their biographies.
The meeting emphasized that the "E-Saylov" information system represents a new level of technological advancement and transparency in elections.
It was also noted that according to Article 37 of the Election Code, political parties have the right to nominate candidates for deputies to the Legislative Chamber and local Councils.
To participate in the elections, political parties must have been registered by the Ministry of Justice at least four months before the announcement of the election campaign and collect at least 40,000 signatures supporting their participation.
Additionally, the meeting approved a calendar plan to ensure that the activities related to conducting the elections are carried out step-by-step within the timelines specified by election legislation. The Central Election Commission, as an impartial and independent constitutional body, will take all necessary measures to prepare for and conduct the upcoming elections in full compliance with national legislation and international election standards, ensuring the process is open and transparent.
A Press Center has also been established under the Central Election Commission.
Central Election Commission
of the Republic of Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan and Finland: An Economic Partnership Built on Technology and Trust
📅 06.11.2025
Historical Background
The history of Uzbek - Finnish relations dates back to the early 1990s, when Finland became one of the first countries to recognize the independence of the Republic of Uzbekistan - on 30 December 1991. Just two months later, on 26 February 1992, diplomatic relations were officially established, marking the beginning of a new chapter based on mutual respect, trust, and a shared commitment to technological progress.
The first high-level visits in 1992 laid the foundation for political dialogue. During that year, Uzbekistan took part in the signing ceremonies of the OSCE Helsinki Final Act and the Paris Charter. In October of the same year, Finnish President Mauno Koivisto paid an official visit to Tashkent, further consolidating the partnership. Since then, cooperation between the two countries has developed steadily across political and economic spheres.
Legal and Institutional Framework
Today, the legal framework governing Uzbek-Finnish relations comprises eight active documents, including two interstate and six intergovernmental agreements. These include the 1992 Agreements on Mutual Protection of Investments and on Trade, Economic, and Technological Cooperation, as well as treaties on air and road transport (1996 and 1997) and agreements on avoiding double taxation and on customs cooperation.
New initiatives reflecting the modern stage of partnership are under consideration - such as a draft agreement on visa exemption for holders of diplomatic passports, a memorandum on cooperation in environmental protection, and a protocol on consultations between the foreign ministries.
Cooperation Priorities: Technology, Ecology, and Innovation
Finland, recognized globally as a leader in innovation, sustainable development, and green technologies, serves as a valuable model for Uzbekistan in its transition toward a digital and energy-efficient economy.
In 2017, a business delegation of nine Finnish companies specializing in engineering, agribusiness, telecommunications, and logistics visited Uzbekistan to participate in the AgroWorld Uzbekistan international exhibition. This visit gave new impetus to direct business-to-business engagement.
In April 2019, Tashkent hosted a delegation led by Mikko Koiranen, Deputy State Secretary of Finland for Foreign Economic Relations. The delegation included 29 representatives from leading companies and organizations - such as Nokia Siemens Networks, ABB, Wärtsilä, Uponor Infra, Tikkurila, ISKU, and Airbus Defense and Space. Discussions focused on implementing Finnish technologies in Uzbekistan, joint energy and raw material processing projects, and opportunities in smart cities and water management.
Later, in November 2019, Antti Koskelainen from the Finnish export credit agency Finnvera visited Tashkent, marking an important step toward deeper financial and investment cooperation. Meetings with the Ministry of Investment, Industry and Trade, the Ministry of Finance, and the Agency for State Asset Management addressed mechanisms for crediting and insuring Finnish export operations in Uzbekistan.
Trade: A Threefold Growth in One Year
Economic cooperation between Uzbekistan and Finland continues to expand. The two countries enjoy Most-Favored-Nation trade status, and regular meetings of the Joint Intergovernmental Commission on Trade, Economic, and Scientific-Technical Cooperation (five sessions to date, the latest held in Tashkent in February 2023) ensure a dynamic dialogue.
Trade turnover has shown remarkable growth in recent years: from USD 48.45 million in 2020 to USD 151.7 million in 2024 - an increase of over threefold. This upward trend reflects intensified business ties and growing interest among Finnish companies in the Uzbek market.
Investment and Business Cooperation
Finland is viewed in Uzbekistan not only as a trading partner but also as a source of innovation and investment. Currently, 14 enterprises with Finnish capital operate in Uzbekistan - four joint ventures and ten with 100% foreign ownership - active in sectors such as electronics, software, energy, agriculture, food processing, chemicals, and telecommunications equipment.
Finnish businesses are showing strong interest in renewable energy, waste recycling, eco-construction, water management, and sustainable agriculture. Uzbekistan, in turn, offers attractive conditions for investors - tax incentives, developed industrial infrastructure, and access to a 75-million-strong Central Asian market.
Finland’s Economic Potential: Opportunities for Partnership
Finland is one of Europe’s most advanced and innovative economies, known for its high living standards, sound macroeconomics, and strong industrial base. In 2024, its GDP exceeded USD 320 billion, with GDP per capita around USD 58,000. The economy is well-balanced, with services accounting for over 70%, industry 27%, and agriculture 2.5%. Inflation remains one of the lowest in Europe - around 3% - ensuring a stable and predictable business environment.
For Uzbekistan, cooperation with Finland opens wide-ranging opportunities for industrial, investment, and technological partnership, including:
- Energy: joint projects in renewable energy, smart grids, and energy storage; development of solar panel and wind equipment manufacturing.
- Water and Environment: Finnish expertise in water purification, waste processing, and efficient water management, particularly relevant for agriculture and urban infrastructure.
- Engineering and Electronics: creation of joint ventures in industrial equipment, automation systems, and telecommunications.
- Construction and Green Materials: Finnish participation in energy-efficient building projects, production of eco-friendly insulation and finishing materials, and smart home systems.
- Education and Science: joint engineering and IT education programs, establishment of research laboratories, and introduction of dual education models based on Finnish experience.
- Agro-Industry: cooperation in precision farming, agricultural digitalization, and production of eco-friendly export-oriented goods.
Finland’s experience in sustainable development and digital transformation makes it a strategic partner for Uzbekistan’s “green economy” agenda and industrial modernization. At the same time, Uzbekistan - with its abundant natural resources, young workforce, and expanding domestic market - offers Finnish companies favorable conditions for localization and regional expansion.
A Look Ahead
The partnership between Uzbekistan and Finland goes beyond traditional economic cooperation. It stands as an example of how innovation and sustainability can form the foundation of long-term, mutually beneficial relations. Joint projects in digitalization, green energy, and education are paving new avenues for the exchange of expertise, technologies, and investments.
Finland regards Uzbekistan as a reliable partner in Central Asia, while Uzbekistan views Finland as a strategic ally in advancing its “smart growth” model and building a knowledge-based economy.
The synergy between Finland’s pragmatic northern experience and Uzbekistan’s dynamic eastern development creates a powerful foundation for further strengthening bilateral relations - grounded in trust, innovation, and mutual respect.
In Uzbekistan, the share of non-state media exceeds 60%
📅 22.07.2024
In the modern world, freedom of speech and information is a key element of a democratic society.
Uzbekistan is actively moving towards strengthening the constitutional rights of citizens in this important area, striving to create favorable conditions for the free exchange of information and development of the information society.
The country remains firmly committed to further improving the system of ensuring human rights, freedoms and legitimate interests. The efforts made by the country's leadership in this direction are holistic, sustainable and irreversible.
The following key aspects of state policy in areas of obtaining and disseminating information:
Firstly, creating conditions for free expression of opinions, independent and safe work of the media. Freedom of speech and press are fundamental principles of a democratic society. Uzbekistan strives to ensure pluralism of opinions and prevent any form of censorship, which contributes to the development of an open and informed society.
For this purpose, the necessary legal frameworks have been formed and are being improved in accordance with international standards and recommendations. To date, the country has adopted more than 10 relevant laws, among them - “On guarantees and freedom of access to information”, “On the openness of the activities of public authorities and management”, “On the media”, “On the principles and guarantees of freedom of information” , “On the protection of the professional activities of a journalist”, “On informatization”, etc.
Under Uzbek legislation, journalists are guaranteed personal inviolability in the performance of their professional duties and may not be prosecuted for publishing critical material.
In addition, to further liberalise media activities and ensure the rights of journalists, in 2018, the legislation clarified the legal status of journalists and guarantees of freedom of journalistic activity, as well as the procedure for accreditation of foreign media representatives in the country in accordance with modern requirements.
Mechanisms have also been established for government support of the mass media (provision of privileges on taxes, other compulsory payments and tariffs, preferences, provision of government subsidies, grants and social orders, as well as social support for editorial staff).
The consistent expansion of conditions and opportunities for media outlets is also reflected in their quantitative characteristics. From 2016 to date, their total number has increased by 49 per cent, reaching 2,200. At the same time, the total share of non-state media in the country is over 60%. Alongside traditional media, online publications are also developing rapidly, the number of which has reached 716, and their audience is steadily growing.
It is important to note that in 2023, a number of issues of ensuring freedom of information were enshrined at the level of the country’s Basic Law. Thus, the new version of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan, adopted at a national referendum, outlines guarantees for the state to ensure free activity of the media, as well as responsibility for interference in the work of the media.
Another main difference of the new version of the Constitution in terms of freedom of information is the specification of the legal conditions under which restrictions on the search, receipt, use and dissemination of information can be introduced.
Similar provisions were identified in the Basic Law earlier, but were not detailed, which could lead to ambiguous interpretation and be used to unjustifiably restrict the rights of citizens.
The 2023 amendments establish that restrictions can only be imposed on certain grounds and only to the extent necessary. This represents a significant step forward in ensuring that restrictions on the right to seek, receive and disseminate information are transparent, legal and proportionate. These measures help strengthen the rule of law, protect the rights and freedoms of citizens and increase public confidence in government institutions.
A new provision has also been introduced into the country's Constitution guaranteeing free access to the Internet. Thus, the state at the constitutional level confirms its obligations to create all the necessary conditions for this, including in the context of supporting the processes of active digital transformation of the country and expanding the range of online services provided to the population.
Secondly, ensuring unhindered and equal access to information, including strengthening the accountability of government bodies to society. This includes expanding access to data on the work of government agencies and socially significant information in general. Availability of information allows citizens to be better informed, make informed decisions and actively participate in public life.
Openness and transparency in the activities of government agencies remain one of the key indicators of the effectiveness of the system of public control, ensuring continuous dialogue between the state and citizens, minimizing bureaucracy and combating corruption. It is the full implementation of this aspect that will reflect the principle laid down by the Head of State: “It is not the people who serve the state bodies, but the state bodies should serve the people”.
The work carried out by the Republic of Uzbekistan in this regard is becoming increasingly systematic. Thus, in addition to the current Law on Openness in the Activities of State Authorities and Government Bodies, a number of normative acts have been adopted since 2018 and up to the present time aimed at radically improving the work of the press services of State bodies and raising the status of press secretaries to the level of deputy head of department.
Increased requirements were set for the heads and employees of information services of state bodies, including timely and comprehensive coverage of key events and decisions within the work of their departments, as well as prompt response to requests from journalists and the public.
At present, the combined staff of the press services of ministries and departments includes 778 press secretaries and more than 500 employees.
In addition, the Agency of Information and Mass Communications, together with the press secretaries of government agencies, has created a mechanism for promptly responding to citizens' appeals, as well as critical and widely discussed news items in the media. As part of this work, more than 10,000 responses and expert opinions on the identified materials were published in the media, social networks and messengers.
The new version of the Constitution also obliges public bodies to act in a transparent and open manner. This means that all significant decisions and actions of public institutions must be publicly justified and documented. Authorities are obliged to publish regular reports on their activities and inform the public about important initiatives and programmes.
In 2021, in accordance with the Presidential decree, the possibilities of public control over the activities of government agencies were expanded. A list of socially significant information to be published as open data was approved, government bodies and organizations developing data, as well as the procedure for their publication were clearly defined.
The practice of determining indicators of openness and assessing it based on advanced international standards has been successfully introduced. The corresponding national Openness Indexes were published for 2022 and 2023.
At the same time, in 2022, liability was established for violating the legislation on the openness of the activities of public authorities and management, including for non-disclosure of socially significant information, failure to comply with the deadline and procedure for publication, or falsification of information.
Thirdly, protecting the rights of citizens to privacy and personal data. In the era of digital technology and big data, government policy is aimed at ensuring the security of citizens' personal information and preventing its misuse. This includes the development and implementation of legal regulations and technical solutions to protect personal data.
These issues are regulated by the relevant Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On Personal Data” dated July 2, 2019. In particular, it regulates the need to ensure the collection, systematization and storage of personal data of citizens of the Republic of Uzbekistan in the country in order to suppress the risks and threats of their leakage and misuse.
At the same time, it should be noted that the new version of the Constitution also enshrines the right to protection of personal data as a personal right of the individual. Consequently, their processing is allowed only with the consent of the individual. From now on, the Basic Law creates a direct possibility for citizens to demand correction of inaccurate data and destruction of data collected illegally or no longer having legal grounds, i.e. to realise the established international practice of the so-called ‘right to be forgotten’.
Such amendments are designed to promote the protection of privacy, increase trust in data processing systems, reduce risks and abuse, develop the digital economy and comply with international standards. Together, these measures create the conditions for a more transparent, secure and sustainable society in the digital age.
At the same time, the development of the population's information literacy remains an important factor in the formation of an effective and self-regulated national media environment against the background of various global challenges. The need to meet the needs of citizens for quality content and improve critical thinking skills has been repeatedly emphasised by the President of Uzbekistan.
The relevance of this task is confirmed by the fact that disinformation is recognised as one of the main short-term global threats, according to an expert report by the World Economic Forum. In addition, a long-term study of media consumption in Central Asia, conducted by the United States Agency for International Development and the non-governmental organisation Internews, shows an increase in the share of citizens in Uzbekistan who lack basic skills in working with information on the Internet (from 3% in 2021 to 25% in 2023).
Uzbekistan continue the country's course of strengthening openness and to develop fruitful and constructive international co-operation in the area of freedom of speech and the press with a view to turning the media into a real ‘fourth estate’. This will certainly create the necessary conditions for the creation of an informed, safe and progressive society ready to meet the challenges and opportunities of the digital age.
Aziz Yengalychev,
Chief Researcher at the Institute for Strategic and Regional studies under the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan
The text of the article is in Uzbek!
📅 25.07.2024The text of the article is in Uzbek!
Uzbekistan’s electoral transformation: embracing technology for a stronger democracy
📅 30.07.2024
Uzbekistan's upcoming elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis (Parliament) and the Councils of People's Deputies, scheduled for October 27th, are not just a routine event. They mark a significant milestone in the nation's democratic journey, introducing groundbreaking changes that promise to transform the electoral landscape. The recent meeting of the Central Election Commission unveiled several key innovations that will ensure greater efficiency, transparency, and inclusivity, making these elections a matter of global interest.
For the first time in the nation's history, the Legislative Chamber elections will employ a mixed electoral system, combining majoritarian and proportional representation. This change means that voters will elect seventy-five deputies directly, while another seventy-five will be chosen based on party votes. This system aims to create a more balanced and representative legislature, enhancing democratic legitimacy and ensuring a broader spectrum of political voices.
One of the most notable advancements in Uzbekistan's electoral system is the full digitization of election commission activities. The introduction of the 'E-Saylov' information system is a significant leap forward, revolutionizing the election process. This digital platform not only streamlines the process, reducing bureaucracy and document handling, but also ensures a smoother, more efficient, and transparent electoral experience. It automates interactions between election commissions, political parties, candidates, observers, and the media, providing real-time statistical data, candidate information, and interactive maps. This technological leap empowers voters with unprecedented access to essential election-related information, making the electoral process more inclusive and transparent.
Inclusivity is another cornerstone of these elections. New election legislation requires political parties to ensure that at least 40% of their candidates are women, a progressive move towards gender equality in political representation. This requirement not only aligns Uzbekistan with advanced democratic standards but also enriches the political discourse by incorporating diverse perspectives.
The elections are taking place in a context where the updated Constitution has significantly enhanced the powers of parliament and representative bodies. The Legislative Chamber's powers have increased from 5 to 12, and the Senate's from 12 to 18. Parliament's oversight functions over executive, judicial, law enforcement, and special services have also been expanded. Additionally, the leadership of local Councils of People's Deputies by hokims (governors) has been abolished, transferring 33 powers previously held by hokims to local Councils to increase their role in resolving critical state issues.
The slogan "My Choice—My Prosperous Homeland" not only captures the spirit of these elections but also reflects the unwavering commitment of Uzbekistan's leadership to democratic state-building and citizen empowerment. With over 120,000 election commission members, 70,000 citizens, and numerous international observers participating, the elections are set to be a transparent and inclusive process, further demonstrating this commitment.
In conclusion, Uzbekistan is setting a remarkable precedent with its upcoming elections by embracing technological innovation and inclusivity. These initiatives will undoubtedly pave the way for a more prosperous and democratic future, showcasing Uzbekistan’s dedication to advancing democratic principles and practices.
Eldor Tulyakov,
The Executive Director,
Development Strategy Centre (Uzbekistan)
Address by the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev at the second "Central Asia – Germany" summit
📅 17.09.2024
Distinguished heads of delegations!
I am sincerely glad to greet you all. I would like to echo the words of gratitude to the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, H.E. Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, for the warm welcome and excellent organization of our meeting.
I am grateful to the distinguished Federal Chancellor of Germany, H.E. Mr. Olaf Scholz, for his commitment to expanding the multifaceted partnership with the countries of our region.
Our first meeting in Berlin and today's summit reaffirm shared intention to continue an open and constructive dialogue and our focus on achieving concrete practical results.
We are interested in holding regular meetings in this format, with setting up the mechanisms for expert review and implementation of the initiatives put forward.
Distinguished Federal Chancellor!
We highly value Germany's firm and unwavering support for the ongoing democratic transformations and socio-economic reforms in our countries, partnership and integration in Central Asia.
I would like to highlight that our multifaceted relationship has deep historical roots.
In the 18th century, the great composer of the Age of Enlightenment Handel created one of his greatest works – the opera "Tamerlane" – in just 20 days.
The great poet and philosopher Goethe dedicated a number of his famous works to our ancient cities - the centers of civilization.
I would like to mention another historical fact.
At the beginning of the 20th century, a group of talented, progressive young people from Central Asia studied at the leading German universities and subsequently made a great contribution to the promotion of the enlightenment ideas and socio-economic development of our region.
I would like to emphasize that today we see Germany as one of our important partners in achieving national goals of sustainable development.
Let me briefly highlight the profound and fundamental changes that have taken place in Central Asia in recent years.
We have established an open and productive dialogue and are independently addressing many issues related to borders, water, energy, trade and transit.
Recently, the Sixth Meeting of the Heads of State of the region was held here in Astana.
The international stance of the region is strengthening, cooperation with the leading countries via "Central Asia Plus" format is expanding.
The volumes of trade turnover, investment, freight transport and tourist travel by our citizens have increased many-fold.
We are discussing major regional projects in green energy and the development of transport communications.
We are exchanging experience and technologies, creating modern industrial and agricultural enterprises, and introducing financial instruments to stimulate cooperation projects.
Most importantly, we clearly understand that the future of our region, its security and sustainable development depends solely on our political will and efforts.
We sincerely welcome the interest of our European partners, first of all Germany, as the main initiator and driving force behind the promotion of EU strategies and multilateral cooperation programmes with our countries.
We are preparing to hold another summit in Uzbekistan in the format of "Central Asia - European Union" next year, having defined the investment in the future of the region as the main topic of the agenda of the meeting.
Dear colleagues!
Conflicts and wars, the overall global instability and unpredictability, sanctions policy, increased protectionism and many other factors are causing extremely negative impact on our countries and are becoming a serious test to the implementation of national programs and reforms.
Earlier, during our talks in Samarkand, I shared with Chancellor Scholz my high expectations from today’s meeting.
In this regard, I would like to outline our vision of the main directions for developing cooperation with Germany in Central Asia.
First. We highly value the establishment of a strategic regional partnership between Central Asia and Germany, which meets the common interests of maintaining stability, ensuring sustainability and prosperity of the region.
We consider it appropriate to adopt a long-term Concept for the development of our partnership with program activities in priority areas.
In order to develop this document, we propose to consider the possibility of establishing the “Central Asia – Germany” Forum of Analytical Centers. We are ready to hold its first meeting next year in Khiva - one of the region’s historic cities where a large community of German Mennonites used to live.
We also assign an important role to the annual meetings of the heads of the foreign ministries of our countries in preparing the agenda of our summits.
Second. Investment and technological partnership with the leading German companies.
I would like to note that the portfolio of ongoing and promising projects in Uzbekistan with the participation of German companies exceeds 20 billion Euros.
This includes energy, chemical and extractive industries, machine building, textile and food industry, agriculture, transport and logistics, production of construction materials.
The leading German companies, such as Siemens, Linde, BASF, MAN, Claas, Henkel, Knauf and many others are among our partners, which have invested about 6 billion euros into Uzbekistan’s economy in recent years.
Today we will have the opportunity to discuss long-term plans with the representatives of the German business.
In this regard, I have a number of specific proposals:
– developing a "road map" for expanding investment and technological cooperation between the Central Asian countries and Germany;
– participation of the leading German companies and banks in the implementation of joint projects in the special economic and industrial zones being created in the border areas, as well as large infrastructure projects of regional significance;
– launching of a permanent business dialogue platform – “Central Asia-Germany” Council of Investors and Entrepreneurs. We are ready to hold its first meeting next year in Uzbekistan within the Tashkent Investment Forum;
– study of the possibility of adopting a multilateral intergovernmental agreement on promotion and protection of investments.
Third. Partnership in critical raw materials based on the introduction of advanced German knowledge and technologies.
As it was mentioned our region is abundant in mineral resources.
The German Mineral Resources Agency and German companies could become our key partners in this area.
Here, we are referring to the geological survey projects, intensive exploration, processing and production of products with high added value, as well as arrangement of shipments to Germany and other EU countries.
Uzbekistan is ready to take part in the joint implementation of such projects in neighboring countries.
The technical assistance from Germany and European institutions in implementing the Digital Mapping Program of Critical Minerals and Rare Earth Metals in our region holds promising opportunities.
We also believe it is important to establish a reliable legal framework for such cooperation.
Fourth. “Green” energy. In recent years, all our countries have been actively developing solar, wind and hydropower, modernizing thermal power plants and networks, and promoting green hydrogen projects.
We propose to consider launching an Energy Dialogue between Central Asian countries and Germany, involving energy ministries, companies, operators, scientific organizations, design institutes and industry experts.
We are interested in preparing a Comprehensive Capacity Building Program for specialists in the low-carbon economy with the German technical assistance.
Fifth. Joint response to climate change.
Experts predict that the Central Asian region will remain most vulnerable to the effects of global warming. The rise in average temperatures will be twice as high as the world average.
We are grateful to the German side for launching the second phase of the “Green Central Asia” program, assistance provided for the implementation of environmental projects.
We are also interested in the following:
- implementation of joint educational programs and scientific exchanges at the Central Asian University of Environmental and Climate Change Studies;
- adoption of cooperation programs for the introduction of German water management technologies, modernization of irrigation systems, conservation of biodiversity and training of environmental specialists.
We support and are ready to take an active part in the practical implementation of the initiative of the German Chancellor to create a Central Asian Nature Partnership.
Sixth. The biggest barrier to deepening our partnership is the lack of transport connectivity, including land and air.
We count on Germany’s support in engaging European institutions in the development of alternative transportation corridors connecting Central Asia with Europe.
We propose to hold a joint Ministerial Conference next year on improving the transit capacity of such routes.
Dear heads of delegations!
The exhibition of cultural and historical heritage of our region last year at the Neues Museum in Berlin once again demonstrated the need for regular organization of such events.
Over several months, more than half a million of residents and guests of the German capital city enjoyed the exhibition.
We propose to adopt a Joint Plan for Cultural Activities in our countries, consider the possibility of holding Central Asian Art and Film Days in major cities of Germany, and establish cooperation between museums.
In the field of scientific and educational exchange, it is important to launch a platform for partnership among leading universities,
to develop programs aimed at expanding cooperation in the field of dual education, to train German language teachers with the involvement of the Goethe Institute and other German organizations.
The high interest of our youth in learning German is evidenced by the victory of an Uzbek schoolgirl at the World Olympiad held this summer in Göttingen.
Dear colleagues!
We believe it is important to continue close cooperation with Germany in the fields of combating terrorism, extremism and cybercrime, preventing radicalization of youth.
The security situation in Central Asia is inextricably linked with the processes taking place in Afghanistan.
We believe it is important to prevent the aggravation of the humanitarian crisis in this country, which is left alone with its own challenges.
In this regard, we are ready to cooperate with Germany and other European partners in the implementation of joint projects aimed at involving this country into regional economic cooperation and training personnel, including girls and women, in skills that are on-demand for the peaceful life in Afghanistan, at the Educational Center located in the border town of Termez.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize that Uzbekistan is interested in untapping the potential of Germany’s multifaceted cooperation with the Central Asian region.
I am confident that today’s meeting will serve to further bringing our countries and peoples closer and fill our strategic partnership with concrete projects and programs.
Thank you!