Phone
Consular Issues
Phone
Uzbekistan news
We recommend
A New Chapter in Uzbekistan–EU Relations: Why the EPCA Matters
📅 06.11.2025
On 24 October 2025, Uzbekistan and the European Union signed the Enhanced Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (EPCA) — a comprehensive framework that culminates negotiations launched in February 2019 and initialled in July 2022. More than a ceremonial milestone, the EPCA codifies a strategic upgrade in our relationship with the EU. It is broad in scope — nine titles, 356 articles, and 14 annexes — and practical in ambition: to align our cooperation with the realities of a rapidly changing world economy while reinforcing the rule-of-law foundations of sustainable development at home.
The agreement’s timing is revealing. Uzbekistan’s recent balanced, multi-vector foreign policy and people-centred reforms — strengthening the rule of law, expanding public administration openness, and advancing market reforms — have laid the necessary groundwork. These steps in human rights and governance have increased international confidence, enabling a rules-based partnership with Europe. The EPCA is both a vote of confidence in Uzbekistan’s reform trajectory and a tangible roadmap to deliver measurable outcomes.
Economically, the EPCA offers a clear pathway for integration and growth. It promotes approximation to EU norms on technical regulations, product safety, and sanitary and phytosanitary measures. The agreement is designed to reduce non-tariff barriers, simplify border procedures, and make our exporters more competitive in the EU market. It encourages joint ventures and industrial clustering, extends agro-processing and manufacturing value chains, and supports energy efficiency and industrial modernisation. In short: more trade, more investment, and more quality jobs at home.
Human capital is an equally central pillar. The EPCA expands cooperation across education, science, skills development, and public health. It encourages joint university programmes, faculty and student exchanges, and research grants — mechanisms that accelerate knowledge transfer and help align our skills base with the demands of a digital and green economy. The spillovers are immediate and tangible: better public services, higher productivity, and new career pathways for our young people.
The rule-of-law dimension is another strategic gain. Deeper cooperation on judicial reform, anti-corruption, data protection, and cybersecurity increases predictability for investors and protections for citizens. The agreement’s chapter on foreign and security policy expands dialogue on conflict prevention, crisis management, non-proliferation, and export controls. This cooperation supports regional stability, which is essential for long-term growth.
Connectivity is the backbone that makes these ambitions feasible. Through synergies with the EU’s Global Gateway initiative and the Trans-Caspian Transport Corridor, the EPCA supports logistics hubs, border modernisation, and greener infrastructure. Better connectivity means lower trade costs, faster delivery times, and diversified export routes — practical levers for competitiveness. It also enables cooperation on water management, climate adaptation, and resilient energy systems — strategic priorities for a land-linked Central Asian economy.
Critically, the EPCA opens structured avenues for collaboration on critical raw materials needed for the green and digital transitions. This builds on the EU-Uzbekistan memorandum of understanding signed in 2024. It creates opportunities to upgrade domestic standards, attract responsible investment, and join higher segments of global value chains, while maintaining environmental and social safeguards.
Beyond the text, the joint statement issued at the signing underscores a shared commitment to the UN Charter and to the principles of independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity — principles that guide our positions in international fora. It also welcomes the outcomes of the EU–Central Asia Summit, including plans for a Central Asia–EU Economic Forum and a Trans-Caspian Connectivity Investors Forum in Tashkent in 2025. In short, the EPCA is embedded in a wider, forward-looking regional agenda.
In practical terms, success requires implementation of three clear priorities: coordinated institution building, enhanced business support, and transparent, data-driven tracking. These will ensure commitments translate to outcomes.
First, institutional coordination. Translating commitments into outcomes requires a whole-of-government mechanism with clear mandates, timelines, and dashboards. A national EPCA coordination council, supported by technical working groups, should steer approximation to EU standards, monitor progress, and troubleshoot bottlenecks.
Second, business enablement. Firms need guidance to navigate new standards and opportunities. An 'EU Helpdesk' for exporters and investors would offer practical advice on certification, rules of origin, and compliance. This would turn legal text into business practice. Expanding the capacity of testing, inspection, and certification bodies will further reduce transaction costs and speed market entry.
Third, open, data-driven delivery. Customs and trade facilitation should be fully digitised through single-window systems and interoperable data exchange. Regular public reporting on milestones — such as education partnerships, financed projects, and adopted standards — will sustain credibility and invite feedback from business and civil society.
The EPCA also aligns with Uzbekistan’s WTO accession path by encouraging market-based reforms and transparent, rules-based trade. As reforms deepen, our economy will see more diversified exports, stronger investor protections, and a more competitive domestic market. These outcomes raise household incomes and expand opportunity.
This agreement is ambitious by design. Ambition alone is empty; execution alone is stagnant. The EPCA combines both — setting a high bar and supplying the means to reach it. By acting decisively, we turn this framework into a catalyst for inclusive growth, institutional maturity, and global credibility.
Ultimately, the EPCA is more than a diplomatic success; it is the engine for Uzbekistan’s reform agenda. By linking citizen welfare, business competitiveness, and international engagement, the EPCA puts us on a path to fundamental transformation. The critical task ahead is to deliver on this promise and make the Uzbekistan-EU partnership impactful and enduring.
By Eldor Tulyakov,
Executive Director, Development Strategy Centre, Uzbekistan
The “Sharq Taronalari” XIII International Music Festival PRESS RELEASE Samarqand City August 26-30, 2024
📅 08.08.2024
Under the auspices of UNESCO, the “Sharq Taronalari” XIII International Music Festival will be held from August 26 to 30 in the ancient and unique city of Samarkand, known as “The Pearl of the Earth.”
“Sharq Taronalari” is considered one of the largest festivals in Central Asia. The main objectives of the festival are to promote the achievements in national music art to the wider public, to preserve and develop the cultures and traditions of nations, to support talented youth in the fields of music and singing, and to expand international creative ties while promoting the ideals of peace, friendship, and mutual tolerance.
Established in 1997 and held for the first time, the “Sharq Taronalari” International Music Festival welcomed musical groups and performers from 31 countries; by 2019, the number of participating countries had increased to 75 during the XII “Sharq Taronalari” festival.
The XIII International Music Festival “Sharq Taronalari”, scheduled for August 26-30, 2024, is expected to be attended by more than 300 representatives from about (As of August 1, 62 countries have expressed their desire to participate in the festival, and applications for participation in the festival continue to arrive these days) 70 countries.
As of today, “Sharq Taronalari” has taken its place among the famous festivals not only in Central Asia but on a global scale. This is vividly evidenced by the increasing number of participants and the countries expressing desire to participate each year, alongside the growing level of the program’s quality.
The following program is planned for the XIII International Music Festival “Sharq Taronalari”:
On August 26, a solemn opening ceremony of the XIII International Music Festival “Sharq Taronalari” will be held in the city of Samarkand.
On August 27-28, an International Scientific and Practical Conference on the theme “Music Culture of Eastern Peoples: Principles of Creative Convergence in the Processes of Globalization” is scheduled, expecting the participation of musicologists, scientists from research centers, professors and teachers from musical higher education institutions, and researching doctoral and master’s students.
From August 27-29 (at 7:00 PM), a competition will be held among the participants of the XIII International Music Festival “Sharq Taronalari,” where the performances will be evaluated by an International Jury in two directions:
Professional (classical) level of folk music and song;
Music and song created by modern composers.
For reference. (Order No. 354 of April 25, 2019, on the approval of the regulations for the holding of the “Sharq Taronalari” International Music Festival (lex.uz))
To evaluate the performances of the competition contestants, an International Jury consisting of no less than seven members will be formed by the Organizing Committee.
The Jury will include highly qualified foreign and local musicologists, renowned artists, composers, and representatives from organizations of international art festivals in foreign countries.
During the evaluation process, the national identity of the songs, the harmony and meaning of the lyrics, the level of the performer’s skills, cultural attire, and stage movement will be the main criteria for the competition.
For the performance, a live ensemble of no more than 12 musicians will be allowed to participate.
The performances of the competition participants will be evaluated by the International Jury in two directions:
Professional (classical) level of folk music and song;
Music and song genres created by modern composers.
Winners of the competition will be awarded diplomas, statuettes, and cash prizes in the following amounts by the Organizing Committee:
“Grand Prix” — 10,000 US dollars;
1st place (in each genre) 2 x 5,000 — 10,000 US dollars;
2nd place (in each genre) 2 x 3,500 — 7,000 US dollars;
3rd place (in each genre) 3 x 2,000 — 6,000 US dollars;
The “Grand Prix” will not be awarded if no worthy candidate is found according to the decision of the International Jury.
According to the decision of the International Jury, only the “Grand Prix” prize will not be shared; the cash prizes for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd places may be shared.
Participants who took part in the competition but did not win will receive a diploma of participation in the “Sharq Taronalari” International Music Festival.
Winners of the competition must participate in the concert program of the solemn closing ceremony of the “Sharq Taronalari” International Music Festival.
Participants who have won the competition (laureates) cannot participate in this competition in the following years but may be invited to the festival as honored guests. Participants who participated in the competition and did not place are entitled to participate in the next competition.
Participants recognized by the organizers, creative unions, foundations, and independent jury members and fans will be awarded special diplomas and cash prizes of 500 US dollars in categories such as “Youngest Participant,” “Best Participant Recognized by Fans,” “Best Instrumental Music Performer,” and other nominations.
Each participant of the festival will receive a certificate of active participation in the “Sharq Taronalari” International Music Festival.
Note: Participants who have won the competition (laureates) cannot participate in this competition in the following years but may be invited to the festival as honored guests. Participants who participated in the competition and did not place are entitled to participate in the next competition.
On August 30, the solemn closing ceremony of the “Sharq Taronalari” XIII International Music Festival will take place in Samarkand, where the winners will be announced and awarded.
List of winners (festivals I and XII) at the “Sharq taronalari” International Music Festival from 1997 to 2019List of award winners at the “Sharq taronalari” I International Music Festival.
1997 Position held Full name Country Awards
(US)
Gran pri Simara Imanova Azerbaijan 10.000
1-place Munojat Yo'lchiyeva Uzbekistan 5000
Shannu Khurana India 5000
2-place Se Liin China 3500
Shahrom Noziriy Iran 3500
3-place Aleksandr Samojikov Russia 2000
B.Ganbat Mongolia 2000
Ramazan Stamgaziyev Kazakhstan 2000
Special Jury Prize Turkmenistan music group "Neksiya" automobile
Egyptian national music ansam
UNESCO trophy
Afganistan music group
List of awards at the “Sharq taronalari” II international music festival. 1999
Gran pri Nasiba Sattorova Uzbekistan 10.000
1-place Muhammad Omon Saudi Arabia 7000
Yun Kong Son Korea 7000
2-place “Lashari” ensemble Georgia 5000
Jaspinder Narula Xonim India 5000
3-place Olim Boboyev Tajikistan 2000
Ustod Ali Hamidxon Pakistan 2000
List of awards at the “Sharq taronalari” III International Music Festival. 2001
Gran pri - - -
1-place Alim Gasimov Azerbaijon 7000
Sohibjon Niyozov Uzbekiston 7000
Abdunabi Ibrohimov Uzbekiston 7000
2-place “Lashari” ensemble Georgia 5000
Madkhushri Ramsonder Badaltjavhariy India 5000
3-place Milliy musiqa ensemble Greece 3000
Nohide Tokguz Turkey 3000
Special Jury Prize "Altay" group Russia 1000
"Музыканты" group Kyrgyzstan 1000
Festival organizing committee trophy "Angan al-Shabab" group Egypt Maxsus mukofot
List of awards at the "Sharq taronalari" IV International Music Festival. 2003
Gran pri "Uranhay” ensemble Russia (Tuva Republik) 10.000
1-place Dilnura Mirzaqulova Uzbekiston 7000
Fozil Jamshidiy Iran 7000
2-place Ozoda Ashurova Tajikistan 5000
Zabit Nabizade Azerbaijan 5000
3-place Milliy musiqiy ensemble Afganistan 3000
An'anaviy musiqiy ensemble Bangladesh 3000
UNESCO trophy Abduhoshim Ismoilov Uzbekiston 1000
Musiqiy ensemble India 1000
Roman Kehman Israil 1000
List of awards at the “Sharq taronalari” V International Music Festival. 2005
Gran pri - - -
1-place Aygun Biylar Azeribajan 7000
Nodira Pirmatova Uzbekiston 7000
2-place "Viulan" group Italy 5000
Kuwait Academy of music string instrument ensemble Kuwait 5000
Urna Chahar Tuhchi Mongolia 5000
3-place Korean music group South Korea 3000
Shilpakala Academy musical group Bangladesh 3000
"Nazaret" Orchestra Israil 3000
Special Jury Prize National Brass Band Egypt 2000
UNESCO Special Prize musical group led by Hanif Nabizoda Afganistan 1500
List of awards at the “Sharq taronalari” VI international music festival. 2007
Gran pri Kuwait Music Institute group Kuwait 10.000
1-place South Korean music institute group South Kora 7000
2-place "An-Nil " national musical instrument group Egypt 5000
Music group Italy 5000
3-place "Ratang" group Keniya 3000
"Seri Maharani Gazal" group Malasia 3000
China National Youth Center Group China 3000
YUNESKO sovrini Youngest participant Arzu Aliyeva Azerbaijan 2000
List of awards at the “Sharq taronalari” VII international music festival. 2009
Gran pri Honored Artist of Turkmenistan Lale Begnazarova Turkmenistan 10.000
1-place Gochag Askerov Azerbaijan 7000
People's artist of Uzbekistan Matluba Dadaboyeva and ensemble of folk instruments Uzbekistan 7000
2-place "Vinalog" rok-pop group South Korea 5000
"Shem Tov Levi" ensemble Israil 5000
3-place Ensemble of folk instruments of the State Institute of musical arts Kuwait 3000
Laura Molika Italy 3000
Special Jury Prize "Kunsu" opera artists China
"Borte" group Mongolia
"Big Mountain" group US
Musiqiy group India
"Shilpakala" national ensemble of the Academy of music Bangladesh
List of recipients at the “Sharq taronalari” VIII international music festival. 2011
Gran pri "Park Jong-Vuk va Park Jonguk" South Korea 10.000
1-place "Dunhuang nude vords" China 7000
"Aysva" Lithuania 7000
2-place "Lider" musiqiy group Russia 5000
"Sato" musiqiy group Uzbekistan 5000
"Ovoi mehriboni" music group Iran 5000
3-place "Talilema" Madagascar 3000
"Chvenburebi" Georgia 3000
"Galkinish" group Turkmenistan 3000
UNESCO Special Prize Ilyos Arabov Uzbekistan
Jivan Gasparyan Armenia
Nazeket Teymurova Azerbayijan
For his contribution to the development of National Music "Huk Mongol" Mongolia
"Dror" Israil
"Yorqin ijrolar"
"Varsi brazers" India
Fan recognition "Hidden Dragen" Japan
Samarkand City Hall Award Afghanistan Institute of Arts team
Registan award of Samarkand regional government Xurshed Ibragimov Tajikistan
Special Jury Award "Bogʻ aro" Uzbekistan
List of awards at the “Sharq taronalari” IX International Music Festival. 2013
Gran pri Rashmiya Agarval India 10.000
1-place "Sadoi Pamir" group Afganistan 7000
"Lanaya" group Burkina Faso 7000
2-place "Pentan" group Great Britain 5000
"Sarihyun Gayageum Byungchangdan" group Republic Of Korea 5000
National opera and drama theatre team China 5000
3-place Abror Zufarov Uzbekistan 3000
"Chikuyusha" group Japan 3000
Catch-pop String-strong Austria 3000
Special award winners Sanam Marvi Pakistan
Galit Giat Israil
Taul Triini Estonia
Nadi Singapura Singapore
Salomat Ayapov Karakalpakstan
Sedar Hills US
"Sharq taronalari" List of awards at the X international music festival. 2015 < BR >
Gran pri "Jiangsu" women's orchestra China 10.000
1-place "Shamisenʼ group Japan 7000
2-place Chelm Poland 5000
Silver Sepp Estonia 5000
3-place "Quelite" Costa Rica 3000
UNESCO Special Prize "Ayqulash yulduzlari" Uzbekistan 1500
Samarkand City Hall Award Didgori Georgia
Samarkand regional government award "EVA" ensemble Bulgaria
Special Jury Award Afrikan voice JAR
Festival Direction award" Sharq taronalari Birjan Baziljanov Kazakhstan
Ministry of culture and Sports Award "Sedaa" Mongolia
Special awards Pung Ryu Republic Of Korea
Lingua Franca ansambli Greece, Cyprus
"Baxshi" trio Turkmenistan
"Laus Nova" group Italy
Yulduz Turdiyeva Uzbekistan
"Buta" team Azerbaijon
Ucell Communications special award Modern Maori Quartet New Zenland
List of awards at “Sharq taronalari” XI international music festival.
Gran pri Sohib Poshazoda Azerbaijan 10.000
1-place Mohichehra Shomurodova Uzbekistan 7000
"Keosong"people's artistic collective South Korea 7000
2-place Kyrgyz artistic team Kyrgyzstan 5000
Litwa artistic team Litwa 5000
3-place "Nagesh" artistic team Iran 3000
Indonesia artistic team Indonesi 3000
Turkish artistic team Turkey 3000
List of recipients at the “Sharq taronalari” XII International Music Festival.
Gran pri Mehrinigor Abdurashidova Uzbekistan 10.000
1-place "Qomuzchilar" duet Kyrgyzstan 5000
Parviz Gasimov Azerbaijon 5000
2-place "Archabil" group Turkmenistan 3500
"Xatan" group Mongolia 3500
3-place "Ayarxan" group Russia 2000
"Badaxshon" group Tajikistan 2000
Azizjon Abduazimov Uzbekistan 2000
Ulugʻbek Elmurodzoda Uzbekistan 2000
Note: The Ministry of Culture https://t.me/madaniyatvazirligi you can get more information on the official Telegram page based on the hashtag #Sharq_taronalari
On May 28-29, the Prime Minister of Italy will pay an official visit to Uzbekistan
📅 27.05.2025
The principle of “New Uzbekistan - a social state” implies comprehensive support for the population
📅 29.07.2024
Social policy in our country contains a wide range of issues on poverty alleviation, job creation, and support for socially vulnerable groups of the population. Investments in human capital are both a contribution to the social and economic sectors of the country's development. Moreover, according to a study by the Institute of Macroeconomic and Regional Studies under the Cabinet of Ministers of Uzbekistan, improving the quality of human capital leads to an increase in the inflow of foreign direct investment by 0.51 percent.
Article 1 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan in the new wording, adopted following the results of the national referendum, once again confirmed the commitment and orientation of the state to care for its citizens from the first days of their birth, regardless of their social status. It should be noted that the state did not come to this principle immediately, as the domestic social policy was formed step by step, i.e. in the process of long negotiations, permanent compromises and economic opportunities.
The enshrinement in the Constitution of the statement that Uzbekistan is a sovereign, democratic, law-based, social and secular State increases its social obligations.
It should be noted that a social state in the general sense guarantees quality education, qualified medical care, comprehensive support for families, children, women, the elderly and persons with disabilities, provides housing and employment for those in need, creates safe working conditions and reduces poverty.
All of the above-mentioned state guarantees began to be reflected in the last decade of our country, which entered the world history as New Uzbekistan.
First, the Strategy of Action on Five Priority Areas of Development of the Republic of Uzbekistan in 2017-2021 and the Strategy for the Development of New Uzbekistan for 2022-2026 identify as priority tasks: building a humane state by elevating human honor and dignity and further developing a free civil society; turning the principles of justice and the rule of law into a fundamental and necessary condition for the country's development; accelerating the development of the national economy and ensuring high growth rates; carrying out the development of the country's economy; and ensuring the development of the national economy.
Secondly, the Ministry of Employment and Poverty Reduction has been established, the Ishga Markhamat monocenters have been launched, the “iron” “women's” and “youth” notebook systems have been set up, one hundred percent pensions are paid to working pensioners, the Social Protection Strategy of the Republic of Uzbekistan has been approved, and the problem of poverty in the country has been recognized. Moreover, the post of assistant khokims has been introduced, who are responsible for poverty reduction, developing entrepreneurship, organizing jobs and increasing the incomes of citizens. Most importantly, a new system of caring for the population has been created.
President Shavkat Mirziyoyev chaired a video conference call on May 15, 2023 to discuss measures to reduce poverty and provide employment. Following the recognition of the existence of poverty in the country, a system to reduce it was introduced. At the beginning of last year, all districts in Uzbekistan were divided into five categories and given differentiated benefits based on the pace of socio-economic development. As a result, one million people have been lifted out of poverty.
Thirdly, education and medicine are the most important and comprehensive social spheres. In order to accelerate reforms and improve efficiency in these sectors, relevant project offices have been established.
Undoubtedly, investment in human capital is the best contribution to the future. In this regard, unprecedented reforms have been carried out in the area of continuous improvement of the system of continuous quality education and training of qualified personnel. As a result, preschool education coverage has increased from 27 to 74 percent, 11-year compulsory schooling has been resumed, the workload of school teachers has been optimized, and forced labor has been abolished.
Changes in the higher education system in recent years have also shown significant positive results. As a result, enrollment in higher education has increased from nine to 42 per cent, and the number of higher education institutions has grown from 77 to 212.
Our country pays great attention to the medical sphere, which directly affects the quality of life. Over the past seven years, the financing of the health care system has increased from 5.9 trillion to 33.5 trillion soums, i.e. six times. Hospitals are being equipped with modern equipment and new facilities are being built. In order to bring medicine closer to the people, on-site screening examinations are being conducted.
It should be noted that Uzbekistan is working on targeted support for socially vulnerable segments of the population. This is evidenced by the addition of a new wording to article 57 of the Constitution on State measures aimed at improving the quality of life of socially vulnerable categories, creating conditions for their equal participation in public and State life with other citizens, and expanding their opportunities to independently provide for their basic living needs.
One of the main innovations is article 42 of the Basic Law, which states that the minimum wage shall be determined taking into account the need to ensure a decent standard of living. From December 1, 2023, the minimum wage is equal to 1.05 million soums, while the cost of consumer expenditures is set at 568 thousand soums per person per month.
In addition, according to the Presidential Decision “On measures to further improve the system of social services and assistance to the population” of September 28, 2023, a new system of social assistance by the employees of the social service centers “Inson” of the National Agency for Social Protection has been introduced in 28 districts (cities) on a pilot basis since October 15 last year. The employees are responsible for keeping records and register of lonely, elderly and disabled persons in need of care, which helps to develop a plan of individualized social services by taking into account the degree of need for care. At the same time, assistance to the lonely elderly included in the Unified Register of Social Protection is provided on the basis of a contract.
President of Uzbekistan: The time has come for a new generation of diplomats – those who achieve concrete results and firmly defend the interests of Uzbekistan in the international arena
📅 22.01.2026
The Head of State identified priorities for updating the activities of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and foreign diplomatic missions
On January 15, an expanded meeting was chaired by President Shavkat Mirziyoyev on the activities of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and diplomatic missions abroad, reports Dunyo IA correspondent.
Opening the session, the Head of our state noted that the meeting is taking place amid sharp geopolitical changes in the world and increasing threats to the sovereignty of states. In this regard, the need to critically assess current foreign policy activities and move to a renewed format for organizing the work of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and foreign diplomatic missions was emphasized.
President noted that 2025 had been a productive year for the country's foreign policy. During the year, high-level visits were made to 26 foreign countries, and for the first time in recent history, visits to Uzbekistan were organized by the leaders of a number of countries. Multilateral dialogues in the “Central Asia Plus” format became productive. In recent years, strategic partnerships have been established with 11 countries, bringing the total number to 19, and allied relations have been built with Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, and Tajikistan.
– As a result of an open, pragmatic, thoughtful and proactive foreign policy, Uzbekistan is consistently strengthening its position as one of the global centres of peace and diplomacy, – emphasized President.
Since 2017, 16 new diplomatic missions and consulates have been opened abroad, bringing their total number to 60, and the number of countries with which diplomatic relations have been established to 165. There has also been an increase in the number of staff and salaries of employees of embassies, consular offices, representative offices to international organizations and employees of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
At the same time, a fundamental question was raised as to whether all diplomatic missions are making full use of the opportunities provided.
– In the current environment, an ambassador is not just a person who conducts political dialogue. An ambassador is a state representative who attracts investment and technologies, opens new export markets, launches transport and logistics corridors, increases tourist flows, creates conditions for legal labor migration and, most importantly, protects the rights of our citizens, - emphasized President.
In this regard, it was noted that key performance indicators for ambassadors should include the volume of export revenues from the countries of residence, growth in tourist flows and the effectiveness of organizing legal labor migration.
Particular emphasis was placed on the need to increase exports and investments by strengthening economic diplomacy.
As part of bilateral and multilateral events in 2025, agreements were signed on investment projects and trade contracts totaling $160 billion. For the first time in history, foreign trade turnover exceeded $80 billion, exports reached $33,5 billion, and foreign investment exceeded $43 billion. Exports to 75 countries increased by almost $4,5 billion.
In view of this, the ambassadors have been tasked with expanding export deliveries to the Middle East, Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as implementing specific projects in the fields of industry, agriculture, the chemical industry, the textile industry, greenhouse farming, and the service sector. At the same time, it was noted that Uzbekistan's products remain insufficiently recognized in certain markets.
It was noted that the growth of logistics costs has a negative impact on the competitiveness of domestic products. In this regard, the need to diversify transit routes, optimize logistics chains, and develop additional proposals to reduce transportation costs when entering European markets was indicated.
In the agricultural sector, tasks have been set for researching and implementing water-saving technologies, modern agricultural technologies, and innovative greenhouse solutions. Along with this, measures have been outlined to expand export markets for chemical industry products, bring domestic manufacturers up to international standards and requirements, and organize specialized exhibitions and presentations.
The need to intensify trade and economic cooperation with the African continent as one of the promising new export destinations has been emphasized. To this end, a clear roadmap is to be developed with the participation of relevant ministries and foreign diplomatic missions.
It was noted that ambassadors should be directly interested in finding promising projects, attracting them, and implementing them in practice. In this regard, it was decided to introduce financial incentives for ambassadors who bring specific investment or export projects to a logical conclusion.
Criticism was levelled at the insufficient realisation of existing potential in a number of areas. In particular, it was noted that opportunities to attract international grants are not being fully exploited. It was noted that with closer and more systematic interaction between ministries, industry leaders, and ambassadors, it would have been possible to attract an additional $200-300 million in grant funds last year.
As noted, international organizations and donor countries announce grant programs worth approximately $200 billion annually. In this regard, the task has been set to implement a unified, systematic and effective approach to working with grants.
In addition, the need to take concrete measures, together with the ambassadors to the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Switzerland, China, Japan and Singapore, to attract leading foreign universities ranked in the top 100 worldwide as partners of Uzbek higher education institutions was emphasized.
It was noted that cooperation between regions and diplomatic missions in expanding foreign economic relations is still insufficient. The need for active participation of regional governors, together with ambassadors, in the systematic promotion of export-oriented products of the regions and in facilitating the entry of local enterprises into foreign markets was emphasized.
Providing Uzbek citizens with legal and high-paying jobs abroad was identified as another priority area. The expansion of the geography of organized labor migration was noted, while it was pointed out that in a number of countries, work in this area is not sufficiently effective and relevant instructions were given in this regard.
It was emphasized that embassies and consulates should actively protect the rights and legitimate interests of citizens and provide qualified legal assistance in each specific case. The task has been set to abandon "office diplomacy", strengthen work in the field and establish direct dialogue with compatriots.
In the field of tourism, the need to further strengthen the role of ambassadors, introduce new approaches to promoting the country's tourism and cultural potential, make effective use of visa-free regimes and attract international outsourcing companies has been identified.
Issues related to expanding foreign policy ties, high-quality and timely preparation of high-level visits, retraining of diplomatic personnel, and the formation of a reserve of promising specialists were also discussed.
The intensification of foreign information policy and the improvement of the country's international image through systematic work with foreign media and the implementation of special media projects were identified as priority tasks.
The need to update the Concept of foreign policy of the Republic of Uzbekistan, review its priority areas, and define clear tasks for protecting national interests and strengthening the country's position in the international arena was emphasized.
As the President noted, the new concept should comprehensively reflect long-term strategic goals, the logic of internal reforms as well as national interests in the areas of economic diplomacy, security, investment, exports, transport and logistics, water and climate issues.
In order to give proper recognition to the achievements of diplomats, it was proposed to establish the honorary title of “Honored Diplomat of the Republic of Uzbekistan".
At the end of the meeting, President Shavkat Mirziyoyev emphasized: “The time has come for a new generation of diplomats – those who achieve concrete results and firmly defend the interests of Uzbekistan in the international arena”.
In the course of the session, reports and proposals of our ambassadors abroad were heard.
Dunyo IA
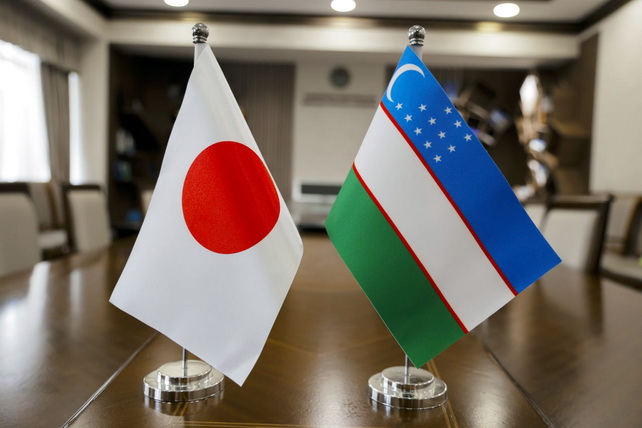
Partnership for Future Generations
📅 22.12.2025
Despite the 6,000-kilometer distance between Tashkent and Tokyo, the official visit of President of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev to Japan on December 18-20 elevated Uzbek-Japanese relations to a qualitatively new level of expanded strategic partnership for future generations.
Uzbekistan’s relations with Japan have deep historical roots. For centuries, Samarkand served as one of the key centers of the Great Silk Road, while Nara, the ancient capital of Japan, was its eastern gateway. Trade and the exchange of knowledge along the Great Silk Road, including between Uzbekistan and Japan, played a significant role in the development of international commerce and cultural interaction, forming lasting cultural bridges between civilizations. Today, Samarkand and Nara are twin cities.
Since Uzbekistan gained independence, reliable and stable relations of mutually beneficial cooperation have developed between Uzbekistan and Japan. Since the establishment of diplomatic relations, Japan has been one of Uzbekistan’s key technological and investment partners.
Economic cooperation dynamics
The most dynamic growth in economic cooperation has taken place in recent years, following the launch of comprehensive economic reforms in Uzbekistan. The Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO), the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) play an important role in advancing Uzbek-Japanese economic cooperation.
Cooperation with JICA has, in recent years, reached the level of strategic partnership. The value of the project portfolio has exceeded $8 billion, and additional initiatives worth more than $3 billion are under consideration in areas such as healthcare, energy, transport, education, industry, and other sectors. During the visit, new agreements were signed with JICA concerning the development of economic zones, agriculture, supply of medical equipment, and support for entrepreneurship, as well as the launch of a special economic zone for Japanese investors, to be developed in line with Japanese models and standards.
Cooperation with JBIC is also developing dynamically. Today, the total project portfolio with the bank exceeds $5 billion in sectors such as petrochemicals, energy, telecommunications, infrastructure, and light industry. During the visit, discussions focused on preparing new projects and improving the effectiveness of existing initiatives worth over $10 billion.
Trade relations are also growing dynamically. Between 2017 and 2024, Uzbekistan’s trade turnover with Japan more than doubled, increasing from $166.2 million to $388.5 million. In 2024, growth accelerated, rising by 64.1% compared with 2023, from $236.8 million to $388.6 million. More than 90% of imports from Japan consist of machinery and equipment, while Uzbekistan’s exports to Japan are dominated by services and chemical fertilizers, as well as fruit and vegetable products, textiles, radioactive elements, and jet fuel.
Investment cooperation is expanding as well. Over the past eight years, the number of Japanese enterprises operating in Uzbekistan has increased tenfold, while the combined project portfolio has exceeded $20 billion. Leading Japanese companies such as Sojitz, Toyota Tsusho, Sumitomo, Itochu, Kyoto Plaza, Balcom, and Shikoku Electric are actively operating in Uzbekistan, implementing major projects in energy, geology, tourism, infrastructure development, IT, and other sectors.
For example, Sojitz Corporation is implementing projects including the construction of a combined-cycle power plant in Syrdarya region, a multidisciplinary hospital, a new international airport in Tashkent, and a wind power plant. During the visit, support was expressed for the company’s plans to modernize medical clinics and educational facilities, create a transboundary “green” energy corridor, upgrade gas compressor stations, and participate in establishing a special economic zone for Japanese investors.
Sumitomo Corporation is constructing two solar power plants and energy storage systems in Samarkand region, with a similar wind-power-based project also planned in the Republic of Karakalpakstan. During the visit, the President of Uzbekistan proposed adopting a Cooperation Program with the corporation through 2030.
Uzbekistan has longstanding cooperation with ITOCHU Corporation in mechanical engineering, geology, and infrastructure. Long-term agreements have been reached on the export of critical minerals to Japan. During the visit, new areas of cooperation were discussed, including water purification, automotive manufacturing, modernization of air traffic control systems, as well as implementation of public-private partnership projects in the social sphere.
JOGMEC, together with ITOCHU Corporation, is developing uranium deposits in Navoi and Kashkadarya regions. During the visit, plans by these companies to develop precious-metal deposits at promising sites in Uzbekistan were also reviewed and approved.
Negotiations and outcomes of the visit
During the negotiations, the sides discussed further deepening of the strategic partnership between Uzbekistan and Japan, covering all areas of interstate cooperation. The importance of strengthening existing cooperation formats, including parliamentary friendship groups, economic cooperation committees, and sectoral mechanisms in priority areas, was emphasized.
During the talks between President Shavkat Mirziyoyev and Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi, a number of priority areas for advancing strategic partnership were identified, including green energy and industrial decarbonization, information technology, critical minerals, cooperation in mechanical engineering, modernization of healthcare, and tourism infrastructure.
To implement more than $12 billion worth of new cooperation projects prepared for the visit, the President of Uzbekistan proposed establishing a joint investment platform. Plans were also announced to create a special economic zone in Samarkand region based on Japanese standards and practices, as well as to scale up the “One Village – One Product” program implemented jointly with Japanese partners. It was proposed to hold the first Uzbekistan-Japan Regional Forum in Samarkand next year.
At the meeting between the President of Uzbekistan and Japan’s Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry Ryosei Akazawa, an agreement was reached to develop an action plan to further strengthen business cooperation with the active involvement of JETRO and the Japan Association for Trade with Russia and NIS (ROTOBO).
A key element of the visit was the President’s meeting with leading representatives of Japanese business. The President emphasized that in recent years cooperation between Uzbekistan and Japan has acquired a qualitatively new character. Whereas Japanese companies previously mainly participated as contractors, today they are actively investing in Uzbekistan’s economy, establishing joint ventures, participating in management, transferring technologies, and contributing to human capital development. “As a result of these qualitative shifts, Japan has become one of Uzbekistan’s key economic and technological partners,” the President stressed.
Based on these assessments, priority areas for further cooperation with Japanese business were outlined. These include ensuring energy resilience and advancing the green transition, development of renewable energy sources and storage systems, and reducing the carbon intensity of Uzbekistan’s economy. Particular emphasis was placed on deep processing of critical minerals and establishing full value chains.
Promising areas also include the development of mechanical engineering and industrial equipment to build a modern high-tech industrial economy. Special focus was placed on advancing information technologies, including the implementation of artificial intelligence and digitalization programs.
Another important direction is the creation of modern special economic zones designed to become centers for high-tech, export-oriented industries and platforms for industrial cooperation through automation and digital control systems.
Concluding his speech to the business community, President Mirziyoyev emphasized that Uzbekistan regards Japan not only as an investor, but as a strategic partner in building the industry of the future.
The main outcome of the visit was the signing by President Shavkat Mirziyoyev and Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi of the Joint Statement on Expanded Strategic Partnership for Future Generations, which elevates Uzbek-Japanese relations to a fundamentally new level. A wide package of agreements was also adopted in education, healthcare, environmental protection, water management, transport, urban development, tourism, agriculture, and disaster-risk reduction.
Expanding cooperation potential
Against the backdrop of Uzbekistan’s ongoing technological transformation and innovative development, there is substantial potential to further expand economic cooperation with Japan in trade, investment, and scientific-technical exchange. The agreements reached during the visit form a solid foundation for advancing cooperation to a qualitatively new level.
According to the Center for Economic Research and Reforms, Uzbekistan has significant untapped export potential with respect to Japan. Promising export categories include copper and copper products, textile and apparel goods including home textiles, aluminum and aluminum products, fruits and nuts, as well as electrical equipment and devices.
Japan’s experience in developing innovation clusters may serve as a valuable model for Uzbekistan. In this context, promising areas include the creation of joint venture funds and startup accelerators, support for technology transfer, and commercialization of scientific developments.
Japan’s experience in smart agriculture and agricultural education is also highly relevant for Uzbekistan. Cooperation in this area offers opportunities to modernize agriculture, increase water efficiency, boost productivity, and implement sustainable farming practices.
Thus, the President’s visit to Japan has already become an important driver in deepening and expanding economic cooperation between our two countries, contributing to fuller realization of partnership potential, modernization of Uzbekistan’s economy, and strengthening the presence of Japanese business in Uzbekistan. The strengthened strategic partnership will improve quality of life and broaden opportunities for future generations.
Nozimjon Ortikov,
Center for Economic Research and ReformsINTERNATIONAL DAY OF PARLIAMENTARISM: SIGNIFICANCE, CHALLENGES, AND PROSPECTS IN THE GLOBAL DEMOCRATIC AGENDA
📅 27.06.2025
- 2021 - "I say 'yes' to youth in parliament!";
- 2022 - "Civic participation at the heart of parliamentary democracy";
- 2023 - "Parliaments for the planet" (environmental sustainability);
- 2024 - "Parliamentary diplomacy: building bridges for peace and mutual understanding."
- ensuring equal participation in decision-making at all levels of the parliamentary structure;
- institutional transformation of parliaments into gender-sensitive bodies with equal conditions and support mechanisms;
- systematic combating of gender-based violence and discrimination, including forms of political pressure and violence in the public sphere.
Uzbekistan’s Inclusive Turn: Solutions at the Level of Each Mahalla
📅 29.01.2026
On 23 January, under the chairmanship of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan, a videoconference meeting was held on the key tasks of poverty reduction and employment provision for 2026. In terms of both substance and the framing of issues, the meeting marked a turning point in the evolution of the country’s social policy.
The relevance of transitioning to a new model
The results of the reforms demonstrate a transition to the next stage of social policy. For the first time, poverty reduction has been placed in direct dependence on outcomes at the level of individual mahallas.
This shift is a consequence of the socio-economic results achieved. By the end of 2025, the national economy grew by 7.7%, significantly above the forecast level of 6.5%. GDP exceeded $147 bn, reaching approximately $3,900 per capita. Growth rates in all sectors surpassed those of 2024. Foreign investment reached $43 bn, while exports amounted to $33.8 bn. Inflation declined from 9.8% to 7.3% in 2025.
Sustained economic growth ensured a significant increase in budget revenues, which were consistently directed toward addressing social issues, reducing poverty, and developing mahallas. As a result, in 2025 income sources were provided for 5.4 mn people, and 330,000 families were lifted out of poverty. Unemployment declined to 4.8%, while the poverty rate fell to 5.8%.
As overall poverty indicators decline, its geography is changing. Poverty is becoming localized, concentrated, and heterogeneous. Nearly one-third of low-income households and around one-fifth of the unemployed are concentrated in a limited number of mahallas, which necessitates a transition to a new model.
Against this backdrop, the primary indicator becomes the outcome achieved at the level of each mahalla. The persistence of poverty or unemployment indicates that measures require further calibration.
Accordingly, for the first time at the national level, a systematic classification of all territories by poverty level was conducted. Based on 20 criteria, 37 “difficult” districts and 903 “difficult” mahallas were identified, home to around 120,000 poor families and approximately 155,000 unemployed citizens. At the same time, work to shape the image of a “New Uzbekistan” has also begun in an additional 33 districts and 330 “difficult” mahallas.
A distinctive feature of the new approach is that “difficult” territories are viewed as points of structural transformation. For each mahalla and district, comparative advantages are assessed, including economic, agricultural, industrial, logistics, or service-related strengths.
Individual development programmes for mahallas are being formulated. Practice shows that even in the most vulnerable areas, ensuring stable access to water and electricity, basic infrastructure, and integration with markets can multiply household incomes.
In the current year, territorially targeted development becomes the main instrument for achieving the stated goals, as clearly articulated by the President.
Infrastructure as an economic asset
A particular emphasis in the new model is placed on revising regional policy priorities. As noted by the President, residents and entrepreneurs in “difficult” districts and mahallas primarily expect improvements in roads, water supply, and electricity provision, rather than an expansion of tax incentives.
Concentrating resources on a limited number of problem territories allows infrastructure investment to be transformed from general budget spending into an instrument of targeted socio-economic impact. In 2026, $1.6 bn will be allocated for regional infrastructure development, of which $990 mn will be directed to “difficult” districts and mahallas.
At the same time, transfers from the republican budget to local budgets will double.
Additionally, allocations of $4.1 mn to each “difficult” district and $165 ths to each “difficult” mahalla are envisaged.
In total, district hokimiyats (district executive administrations) and local kengashes (local representative councils) will receive an additional approximately $330 mn exclusively to support problem territories.
A key element of this model is ensuring stable energy supply for “difficult” districts and mahallas.
In 2026, each of the 903 “difficult” mahallas is expected to host the construction of a small solar power plant with a capacity of 300 kW, with a total investment of around $110 mn. These plants will be transferred to the mahallas free of charge, creating a local energy asset. Through the generation of “green” electricity, each mahalla will gain a sustainable additional income source of $33-41 ths per year.
The proceeds are intended to be used for energy-efficient renovation of housing stock, reducing utility costs, and improving quality of life. Operation of the solar plants will involve members of low-income households, simultaneously addressing employment and infrastructure sustainability objectives.
A separate emphasis is placed on supporting the most vulnerable households. An instruction has been issued to conduct targeted assessments of 6,700 families with a member having a first-degree disability and no able-bodied household members, followed by identification of needs for energy-efficient housing upgrades and the launch of “green” renovation.
Taken together, these measures form a model of territorial and energy resilience. The effectiveness of local authorities’ performance will be subject to public evaluation, reinforcing the transition to results-oriented governance.
Comparative advantages of mahallas
The President clearly defined key socio-economic targets for 2026, including the provision of permanent employment for around 1 mn people, lifting 181,000 families out of poverty, increasing the number of poverty-free mahallas by 2.5 times to 3,500, and reducing the unemployment rate to 4.5%.
Achievement of these targets is expected to be based on the comparative advantages of specific districts and mahallas in industry, agriculture, and services. This approach allows resources to be concentrated where they generate the greatest multiplier effects for employment and household incomes.
As an example of leveraging comparative advantages based on location and specialization of mahallas, the President cited Furqat District. Its advantages include, first, cooperation with neighboring economically active centers; second, deepening specialization among nearby mahallas and combining competencies; and third, increasing value added through the launch of processing activities.
Further measures were outlined within the framework of a differentiated approach to developing problem territories.
Deepening mahalla specialization
Primary attention will be focused on deepening mahalla specialization, as welfare levels are significantly higher in mahallas with deep specialization. Practice shows that in such mahallas, welfare levels are noticeably higher, while the number of recipients of social assistance is half as large, at around 7 people per 10,000 population.
Currently, the 903 “difficult” mahallas encompass around 90,000 hectares of household and leased land. To transform this resource into a source of sustainable income, a new mechanism of a “social contract” between the state and the mahalla has been proposed. Mahallas that, by leveraging residents’ skills and rational land use, manage to increase household incomes by three to four times will receive additional financing of $165 ths for the development of road, water, and irrigation infrastructure. Implementation of this model is planned to begin with “difficult” mahallas.
To support deeper specialization, banks will allocate a total of $1.4 bn in loans. For production projects, 4% of the loan will be compensated, while for processing projects the compensation will amount to 6%.
Comparative advantages of mahallas
In 2026, $11.5 bn in credit resources are earmarked for the development of small and medium-sized businesses in mahallas, compared to $10.7 bn a year earlier. At the same time, banks have been tasked with strengthening entrepreneurship financing: alongside a planned $6 bn from external sources, the total volume of funds directed to mahalla-level projects should reach $8 bn.
Not only the scale but also the principle of credit allocation is changing. The model under which loans within the “Family Entrepreneurship” programme were issued on uniform terms at a 17.5% rate across all districts and cities is giving way to territorial differentiation. In particular, for the 37 “difficult” districts, the rate is reduced to 12%. This step transforms lending into an instrument for accelerating the development of problem territories.
In parallel, programme limits and target areas are being expanded. In all districts, the maximum size of concessional loans is increased by 1.5 times, from $2.7 ths to $4.1 ths. To support this decision, an additional $165 mn is added to the planned $297 mn.
Overall, the 2026 credit policy is shaped as a targeted development mechanism, a managed conversion of credit into employment, income, and local growth.
Institutional changes in system governance
A number of institutional changes are also envisaged to enhance the effectiveness of all governance levels involved in mahalla development.
Work in mahallas is moving away from an administrative-intermediary model and is being structured around specific projects. In this framework, the hokim’s assistant acts as a territorial development manager responsible for implementing project solutions.
To ensure integrated project governance, multi-level coordination is being introduced. Initiatives proposed by hokims’ assistants are paired with regional bankers; the first deputy hokim of the region provides operational oversight; and the “Reform Headquarters” supervises issues requiring inter-agency solutions. From February, a system of training hokims’ assistants in project management will be launched, starting with “difficult” mahallas. Each district will form a project portfolio followed by a transition to practical implementation.
One hundred “difficult” mahallas that demonstrate the best performance in job creation, income growth, and poverty reduction will receive an additional $82.5 ths each. Hokims’ assistants from these mahallas will be able to upgrade their qualifications in China, Turkiye, South Korea, and Malaysia.
In this context, work on developing mahalla master plans is being intensified. International experts are being engaged, alongside the potential of domestic universities. Final-year students in architecture programmes will be able to participate in the development of “difficult” mahallas, with the best projects being supported by state grants.
Overall, the institutional changes formalize a shift from a universal approach to a differentiated territorial policy.
Resource redistribution is justified by the structure of the economy: 62% of industrial production and 57% of services are concentrated in 50 districts and cities with high entrepreneurial potential. Growth in their budget revenues creates an opportunity to concentrate state efforts on problem territories.
This is evident from revenue dynamics: three years ago, additional local budget revenues in these 50 territories amounted to $72.2 mn, while in the current year they are expected to increase 8.5 times, to $610.5 mn.
As a result, greater attention can be directed to “difficult” districts and mahallas, where poverty and unemployment are territorially concentrated.
Conclusion
The decisions and instruments for 2026 demonstrate that Uzbekistan’s social policy is moving beyond traditional resource redistribution toward a model of managed territorial development. The new model rests on three interlinked pillars.
First, the concentration of infrastructure resources in “difficult” districts and mahallas, with the creation of long-term local assets, reduced household costs, and enhanced energy resilience.
Second, the expansion of employment based on comparative advantages and deeper territorial specialization, supported by financial incentives, access to credit, and solutions along value chains.
Third, institutional recalibration of governance, where a project-based approach and multi-level coordination align resources, responsibility, and measurable outcomes.
The essence of the current phase is that targeting becomes a technology focused on “difficult” territories. Exiting poverty is understood as an individual household trajectory, in which local conditions, skills, and infrastructure are decisive. The “Mahalla Seven” and the institution of hokims’ assistants serve as the connecting link, ensuring coordination and feedback until results are achieved.
Khurshed Asadov,
Deputy Director of Center for Economic Research and Reforms
Surkhandarya the cradle of ancient civilizations
📅 26.06.2025
5 reasons to visit Surkhandarya:
- Explore mountain and ecotourism in the region
- Explore monuments of the distant past
- Learn About Religious Monuments
and cult complex of Sultan Saodat, the Buddhist cult center of Karatepa, the Buddhist temple complex of Fayaztepa, the Jarkurgan minaret, and the Buddhist stupa of Zurmala are the oldest religious monuments of the Surkhandarya region.
- Immerse yourself in the cultural heritage of the region
The folklore festival “Boysun Bahori” (“Boysun Spring”) is held here annually, which reflects the unique rituals, traditions and special culture of the people.
- Taste the national cuisine of the region
Here meat is included in almost all dishes. One of the most delicious dishes of this region is Tandoor Gusht.
Also popular is the dish Chuponcha - shepherd's meat, which is prepared from fresh dairy lamb.
The history of the Surkhandarya region has ancient roots dating back to the beginning of great civilizations. This unique place in Uzbekistan is known for its historical monuments and beautiful nature. The region is located in the foothills of Hissar, Bobotaga, Cohitang, which are famous for their beautiful
landscapes and unique natural formations. The rich reserves of mineral water found in the region are an important source of recreation and have healing properties. A trip to Surkhandarya, will be a fascinating experience, during which you can get acquainted with the unusual landscapes of Uzbekistan, see colorful architecture, and immerse yourself in the unique culture of this region.
Canyon Kyzyl
The Canyon Kyzyl, is located in the Surkhandarya region near the village of Baysun and is translated as “Red Canyon”. The length is 30 kilometers, and the highest point is Mount Buritakht, 1218 meters high. Here, nature has created breathtaking labyrinths, stretching for several tens of kilometers, and every turn of the relief, reveals amazing landscapes. In the spring season, the appearance of the canyon differs from the usual harsh stone appearance, since the surface is completely covered with different vegetation, among which rare medicinal herbs can be found. This place is truly amazing and deserves the status of one of the wonders of Uzbekistan.
Cave Boy-Bulok
In the Chul-Bair Mountain range, located in the Surkhandarya region, there is an amazing cave, called Boy-Bulok. It is considered the deepest in the entire Asian continent and reaches a depth of an impressive 1415 meters. Boy-Bulok is located 60 kilometers from the regional center of Baysun, and is a technically complex facility classified as the fifth complexity category.
In 1985, the first study of this unique place was carried out. Various obstacles were found inside the cave, including vertical bends, narrow vertical shafts up to 180 meters deep, and water-filled passages called half-siphons and siphons. Boy-Bulok has an impressive size that extends both down to a depth of minus 1158 meters, where the impenetrable siphon is located, and up to 359 meters. The very impressive amplitude – is 1517 meters.
Boy-Bulok, located at a depth of 1283 meters, is connected with Vishnevsky Cave. These two caves have a potential connection that is 2033 meters deep and extends for about 30 kilometers. This makes Boy-Bulok the third deepest cave in the world.
Massif Khoja Gur Gur ota
In translation, Khoja Gur Gur ota means “Father of all caves”. At an altitude of 3700 meters above sea level, there is a remote region of harsh and very wild nature. The gigantic, sloping peak of the mountain range ends with an impressive 500-meter-high cliff on one side, and deep canyons with cracks tearing the plateau on the other. Here can be seen fossilized traces of dinosaurs, fragments of basalt and crushed stone of the most bizarre shapes, as well as the burial place of the holy righteous man Khumajoy-ota. The slope of Khoja Gur Gur ota extends vertically and has entrances to many caves, many of which have not yet been explored. In addition, upon reaching the highest point of the massif, you will feel like you are standing on a huge wall separating one world from another.
Machay Cave
Machay Cave is another settlement of primitive people, which is located in the Baysun district of the Surkhandarya region. It is located near Mount Cohitang, on the right bank of the Machay River. The cave is 3.4 to 4 meters high, about 8 meters long and about 10 meters wide. It consists of two cultural layers: the upper layer belongs to the Mesolithic, and the lower layer belongs to the late Mesolithic and early Neolithic. Inside the cave, bones of a man and a woman were discovered that date back to the Mesolithic period. It is of great interest to the scientific community is the availability of material evidence of how people lived in the Stone Age. As a result of research, an abundance of artifacts was discovered in Machay Cave, which indicates the way of life of those times. The finds included 87 different stones, hundreds of weapons made from the bones of 15 different animal species, as well as stone knives, axes, handles, sawtooth weapons, arrowheads, bows and spears. The inhabitants of Machay Cave used these various weapons to skin domestic and wild animals and then use them to make clothing for themselves. These findings are of great value to the scientific community, as they allow us to better understand the lifestyle of people of that time. Surkhandarya – the cradle of ancient civilizations.
Sangardak Waterfall
The Sangardak Waterfall is located among the gorges of the Surkhandarya Mountains, being one of the wonders of the country's natural world. The waterfall is situated in the Sariasi region, 205 kilometers from Termez and 30 kilometers from Denau. Sangardak Waterfall is formed from karst waters flowing inside caves, rather than from a mountain river. As a result, people have created various legends about the waterfall and believe that it has healing properties. Moreover, it is worth noting that even ancient Arabs, Greeks, rulers of Transoxiana, and other peoples came to admire the waterfall.
The Teshik-Tash Cave
The Teshik-Tash Cave is located on the slopes of the Baysuntau mountains. In 1938, during excavations, archaeologists discovered an ancient burial there. Scientists discovered five cultural layers 1.5 meters thick. Clay layers and crushed stones separated the layers. The remains of a Neanderthal child are the most famous finding in the cave, which became famous throughout the world and made the site well-known. Soviet archaeologist A.P. Okladnikov, who discovered these remains, subsequently received the Stalin Prize.
Zarautsay Gorge
The gorge is located in the Kugitang mountains in the Surkhandarya region. These are the southwestern spurs of the Hissar ridge. The discovered cave paintings are rare examples of primitive art. All rock paintings in Zarautsay are written in red ocher, unlike other petroglyphs in Uzbekistan. Impressive hunting scenes with running bulls, goitered gazelles, saigas, arrows, chasing dogs and people with bows and axes, as well as mysterious hooded figures who clearly carry out rituals associated with hunting, can arouse interest and surprise among viewers of this unique ancient art person. Of the 200 images found in 1940, only 40 have now survived in the Zarautsay grottoes.
Dinosaur tracks
Traces of hoofed dinosaurs were discovered in the limestones of the Cretaceous period in the village of Gumatak. The footprints are on a stone slab, which is easily accessible from a car after walking only 300 meters.
Speleologists have also discovered traces of other large dinosaurs in Surkhandarya, but to see them you will need to make a separate trip.
Karyshoto Gorges
In the Surkhandarya region, there is another unusual place, the Karyshoto Gorges. The gorges have karst waterfalls along their walls despite the fact that they are located in hot and dry areas.
As a result, you feel as if you have entered a picturesque oasis. The gorge in several places prevents passage due to the rather high waterfalls. However, when you overcome them, you can see how the gorge continues in two directions.
Canyon Kaptarhona
Several thousand doves have been nesting in this canyon for a long time, which is why this place received the name Kaptarhona, which is translated from Uzbek as “dovecote”.
Once upon a time, the canyon was completely deserted, and its only inhabitants were doves, which were so numerous that one could safely call this place the kingdom of these birds.
Kaptarhona is a winding road along a narrow gorge. Various boulders are scattered along the path. Many attractive and exciting turns hide amazing views.
Khojaikon Salt Cave
In 1989, the Khojaikon Salt Cave was opened, which since then, thanks to the concentration of salt and light negative air ions in the air, has helped people cope with various ailments, such as asthma, respiratory diseases, chronic bronchitis, complications of pneumonia, as well as various skin problems.
The cave is 155 meters long and is a salt monolith inside of which there are treatment room chambers, each of which differs in temperature, humidity, pressure and trace element content. The healing procedure takes only 2-2.5 hours a day.
Meteor Lake Kanbeshbulak
Lake Kanbeshbulak is located in the Khaman tract in the west of Surkhandarya region. The lake is an exceptional natural monument.
According to scientists, this lake was formed as a result of a meteorite fall. In their opinion, it was a meteorite crater that filled with water and became known as Kanbeshbulak. The explosive red sandstones that make up the slopes of the lake indicate the origin of the bowl.
Panjob Gorge
The Panjob Gorge is located in the foothills of the Kugitang Tau ridge in the Surkhandarya region of Uzbekistan, 125 km northwest of Termez. This is a very beautiful gorge in which the small river Gazak, in the Karyshoto mountain range, cuts its way through limestone, gypsum and rock salt, creating a powerful picturesque canyon with vertical cliffs more than 200 meters high.
In some places the width of the gorges can be no more than two meters. In the narrow passages of the gorge, the most beautiful place is a 30-meter section on the right side of the canyon. In this place, water is knocked out of a rock covered with bright green moss, either as a curtain of water or in separate streams, forming a multiple rainbow under the sun's rays.
Surkhan State Reserve
The Surkhan State Nature Reserve is located in the Surkhandarya region of Uzbekistan, just 60 kilometers from the city of Termez. The reserve was created in 1986 by combining the Kugitang and Aral-Paigambar reserves. The purpose of its creation was the preservation and restoration of rare species of plants and animals.
The reserve consists of two separate parts, located in the Sherabad and Termez districts of the Surkhandarya region. The reserve occupies 24,554 hectares and is located in the southwestern spurs of the Hissar ridge at an altitude of up to 3,157 meters above sea level. The Surkhan Reserve currently has more than 130 species of birds, as well as more than 25 species of mammals, 27 species of reptiles, and 2 species of amphibians and fish.
Kampyrtepa Fortress
Kampyrtepa is an ancient archaeological site on the territory of Uzbekistan, which is an ancient port city located on the banks of the Amu Darya River (formerly known as the Oxus). It was founded at the end of the 4th century BC and existed until the beginning of the 1st century AD. The main purpose of this settlement was to serve the crossing of the Burdaguy River, as well as to serve as a hotel and customs office. Kampyrtepa served as a transit point for traders traveling along the Silk Road, where they could rest, reload their goods, pray and continue their journey.
After decades of excavations and studying written sources, it was decided that the site of Kampyrtepa is the mysterious Alexandria Oxiana, a port city that Alexander the Great built on the Amu Darya.
Topalang Reservoir
Uzbekistan is famous for the presence of two significant rivers - the Amudarya and the Syr Darya, which flow through its territory and flow into neighboring countries. The Hissar mountain ranges serve as a source for the Topalang River, which originates on the southern slope. It should be noted that the most abundant right tributary of the Surkhandarya has a length of 117 kilometers. The main source of water replenishment in the Topalang River is seasonal snow and glacial water. It is thanks to this that the river supplies water to the Denaus, Shurchin and Kumkurgan districts of the Surkhandarya region.
Hospital “Khojaipok”
Khojaipok Hospital specializes in the treatment of various diseases, including gynecological problems, cardiovascular disorders, general therapy and neurological disorders. To achieve a positive result, various methods are used, such as hydrotherapy (including mineral baths and circular showers), heat therapy, mud therapy, physiotherapy, electrotherapy and ozone therapy.
Upon completion of the procedures, visitors can visit the natural beauty, swim in the resort's pool, play tennis or engage in other outdoor activities in the sports club.
Sanatorium “Omonkhona”
The Omonkhona Balneological Sanatorium, located in the mountains near the city of Baysun, and the Khojaipok Hospital, located at the foot of Mount Kenagi, are the most famous health complexes in the Surkhandarya region.
The thermal water in the Omonkhona sanatorium has healing properties and is part of the health programs of the sanatorium. Using magnetic therapy, laser therapy, acupuncture, water procedures, massages, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis and other diseases are treated.
Hissar Mountains
The Hissar Mountains are a mountain range that stretches 200 kilometers from east to west across the Hissar region of Tajikistan. It is the western part of the Pamir-Alai system. The highest point in Uzbekistan, Khazret-Sultan, is 4643 meters, located on the border of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. The ridge is a place of unique geological outcrops in Eurasia. The structure consists of sandstones and crystalline rocks interspersed with granite intrusions. In addition, all ecosystems and climates of the Pamir-Alai are represented here. At the highest places there are glaciers and rocky wastelands. A famous natural attraction of the Hissar Ridge, located in the southern part of the mountains, is the cave of Amir Temur. This natural formation, stretching for 860 meters, is considered the largest underground lake in Uzbekistan. It is important to note that the cave was inhabited back in the Greco-Bactrian period (IV-III centuries BC).
Archaeological Museum of Termez
To celebrate the 2500th anniversary of the city of Termez in 2002, the Termez Archaeological Museum was built and opened. Today it is the only archaeological museum in Central Asia, and many of its unique exhibits date back more than 100 thousand years BC. These include 624 museum relics of global significance, displayed using the latest information and communication technologies.
Karatepa Complex
Located in the northwestern part of old Termez, Karatepa is a place of worship associated with Buddhism. On the three hills of this place there are various temples and monasteries that were built in the 2nd century AD. The architecture of Karatepa is remarkable for its unique combination of caves carved into sandstone and buildings made of pakhsa and adobe.
Zurmala Stupa
Northeast of the ruins of the ancient settlement of Termez is Zurmala, a 12-meter-tall Buddhist stupa. It was built during the Kushan period, around the 1st and 2nd centuries AD, while Buddhism was spreading in Central Asia. The modern city of Termez is located 10 kilometers west of the ancient settlement of Termez. On its outskirts one can see the remains of entire complexes of ancient Buddhist buildings, which in the Middle Ages covered agricultural fields. Over time, the Buddhist stupa turned into a clay mound, which was difficult to recognize as a ritual structure.
Mausoleum of Al-Hakim At-Tirmizi
Al-Hakim At-Tirmizi is a sacred place of worship for Muslims and an architectural monument. The mausoleum is one of the holy places of the Surkhandarya regional center. The architectural monument is located approximately 60 kilometers from the current center, northwest of old Termez. Abu Abdulloh ibn Hassan ibn Bashir Al-Hakim At-Tirmizi is an outstanding Islamic figure, author of various philosophical and religious works and founder of the order of Dervishes. About 80 works were written by the eminent At-Tirmizi who received the name Al-Hakim, which means the wise one, due to his deep knowledge and broad vision.
Mausoleum of Ak-Astana-baba
In the village of Telpek-Chinar, Sariasi district, Surkhandarya region, there is the Mausoleum of Ak-Astana-baba. Scientists believe that the mausoleum was built on the grave of the companion of the Prophet Muhammad (SAW), Saint Abu Hurair. The mausoleum has four rooms called “Chorsi Khona,” in which bricks are laid in batches, and the north-eastern part of the complex can be accessed through the roof. At the entrance to the mausoleum, there are two complex signs, about half a meter in diameter. It is still not possible to correctly interpret the semantics of these signs.
Kirk Kiz Fortress
One of the most interesting ancient places is the Kirk Kiz Fortress. Although the fortress is almost completely destroyed at present, even the ruins allow us to see the former size of the structure and marvel at the skill of the ancient architects. The symmetry of Kirk Kiz makes it unique; each archway and corridor have a counterpart located on the opposite side.
Two passages cross the building crosswise and divide it into four equal parts. There are versions that it was a country aristocratic palace, a women's madrasah, a khanaka, or a caravanserai.
Dzharkurgan Minaret
The minaret is located 5 kilometers from the city of Jarkurgan and 40 kilometers from Termez, near the village of Minor. Thanks to the deciphered inscription on the building, it was established that this architectural monument dates back to the 12th century. The inscription states that construction took place from 1108 to 1109 AD, but some scholars believe the date reads differently and construction was completed in 1110.
This building is unique with its decorative elements. At that time, mosaics were often used to decorate minarets; in the case of this minaret, we see vertical decorative corrugations that were made using a specially baked brick masonry, which was cut in a herringbone pattern from top to bottom.
Dalverzintepe Settlement
Dalverzintepe, the main city of the powerful Kushan Empire, has so far been the subject of careful study by many historians and archaeologists. With its secrets and many valuable objects found, the site attracts attention. The largest treasure in history was found here; about 36 kilograms of gold were discovered in this place in 1972.
Archaeological excavations have revealed a lot of new things about the architecture, culture and fortifications of Northern Bactria. Finds such as sculptures, paintings and figurines show the high level of culture of the people of the Kushan Era. According to many researchers, Dalverzintepe is considered the most ancient Buddhist building.
Ensemble Sultan-Saodat
On the outskirts of the city of Termez in the center of the Surkhandarya region of Uzbekistan there is the architectural ensemble of Sultan-Saodat. The memorial complex consists of tombs of the Termez Seyyids, who were considered direct descendants of the Prophet Muhammad. The complex contains various memorial and religious buildings built from the 11th to the 17th centuries. All buildings have a common architectural concept despite the fact that they were built at different times.
Hanaka Kukildor-ota
Khanaka Kukildor-ota in Termez is a holy monastery that has become one of the most revered among Muslims. Khanaka Kukildor-ota was built in the mid-1100s. It stands out among other monasteries due to its unique architecture, history and significance in the Muslim world.
The building contains numerous tombstones, as well as the burial place of the Muslim Saint Kukildor-ota. This prominent religious figure was known for his great righteousness. The monastery was built in memory of him.
After the restoration of the Khanaka, Kukildor-ota acquired a unique appearance, which is characteristic of all architectural monuments of the Timurid era.
Fayaztepa Complex
Fayaztepa is located at a distance of 4 kilometers from modern Termez, Surkhandarya region. The monastery complex consists of 13 rooms and an inner courtyard with an ivan where a refectory was attached to the monastery on the left side. In some places of the complex there are cooking fires, as well as skulls with inscriptions in Bactrian and other ancient languages. Coins of Heliocles (the Greco-Bactrian king) and Kanishki (the ruler of the Kushan Empire) were also found there. According to archaeological excavations, monks used to live in the monastery, and they also provided housing for pilgrims.
In the IV century, Fayaztepa was captured by the Sassanid army (the dynasty of Persian rulers), due to which the complex stopped functioning. Previously, the complex was called Khaya-Vihara, which translates as "the monastery of horsemen". The current name of the complex was given in honor of the director of the Surkhandarya Museum of Local Lore R.F. Fayazov, who participated in the excavations of the Buddha complex.
Neighborhoods of Derbent
The Derbent mountain village is located on an important trade route along the Sherabad River, connecting the southern regions of modern Uzbekistan, Northern Afghanistan and Tajikistan with the central cities of Samarkand, Bukhara and Tashkent, which were known at the time as Shash. The land around Derbent looks heavily damaged — high rocks either form a majestic gate, or almost merge overhead, reminding us of the bloodshed here while defending the borders of different empires.
Also, travelers can expect places that surprise with their power, strength and pristine beauty. Here you will find gorges including the famous Iron Gate, which was besieged by Alexander the Great.
The Church of Alexander Nevsky
In 1901, a temple was erected in the city of Termez in honor of the Holy Prince Alexander Nevsky. Currently, the temple is in excellent condition. The sanctuary is impressive in its scale: the bell tower and iconostasis occupy a significant space. Inside the temple there is a room measuring 24 by 16 meters. In addition, the temple is rich in icons and church objects.
Kurganzol Fortress
The Kurganzol Fortress is an impregnable structure built in 328 BC by Alexander the Great, located on a cliff near Baysun at an altitude of 900 meters. Archaeological excavations of Kurganzol began in 2003 and revealed that it belongs to the Hellenistic era. The fortress dates back to the 4th century BC and is believed to have housed about fifty soldiers, with six towers protecting the entrance. Construction took a long time to complete, as nomadic tribes frequently attacked and destroyed parts of the building during those years.
Inside the fortress, parts of residential and utility rooms, a water pool with a drain to prevent overflow, and defensive structures were discovered. Built of mud bricks, the fortress has an outstanding appearance, with walls averaging more than 2.5 meters thick.
Uzundara Fortress
Uzundara, the oldest fortress dating back to the 3rd–4th centuries BC, is located in the foothills of Baysun. The fortress featured powerful defensive structures, including double walls reinforced with 13 towers, and outer walls stretching nearly 1 kilometer in length. The fortress walls, lined with clay bricks, have almost retained their original appearance and rise up to 5 meters high.
Among the main finds discovered during the expedition are unique coins from the Hellenistic period depicting Alexander the Great, Antiochus I (king of the Seleucid state), and all rulers of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom from Diodotus to Heliocles. The fortress existed for about 150 years before being destroyed by the nomadic tribes of the Saks and Yuejs during the reign of one of the last Greco-Bactrian kings between 171 and 166 BC
Uzbekistan’s electoral transformation: embracing technology for a stronger democracy
📅 30.07.2024
Uzbekistan's upcoming elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis (Parliament) and the Councils of People's Deputies, scheduled for October 27th, are not just a routine event. They mark a significant milestone in the nation's democratic journey, introducing groundbreaking changes that promise to transform the electoral landscape. The recent meeting of the Central Election Commission unveiled several key innovations that will ensure greater efficiency, transparency, and inclusivity, making these elections a matter of global interest.
For the first time in the nation's history, the Legislative Chamber elections will employ a mixed electoral system, combining majoritarian and proportional representation. This change means that voters will elect seventy-five deputies directly, while another seventy-five will be chosen based on party votes. This system aims to create a more balanced and representative legislature, enhancing democratic legitimacy and ensuring a broader spectrum of political voices.
One of the most notable advancements in Uzbekistan's electoral system is the full digitization of election commission activities. The introduction of the 'E-Saylov' information system is a significant leap forward, revolutionizing the election process. This digital platform not only streamlines the process, reducing bureaucracy and document handling, but also ensures a smoother, more efficient, and transparent electoral experience. It automates interactions between election commissions, political parties, candidates, observers, and the media, providing real-time statistical data, candidate information, and interactive maps. This technological leap empowers voters with unprecedented access to essential election-related information, making the electoral process more inclusive and transparent.
Inclusivity is another cornerstone of these elections. New election legislation requires political parties to ensure that at least 40% of their candidates are women, a progressive move towards gender equality in political representation. This requirement not only aligns Uzbekistan with advanced democratic standards but also enriches the political discourse by incorporating diverse perspectives.
The elections are taking place in a context where the updated Constitution has significantly enhanced the powers of parliament and representative bodies. The Legislative Chamber's powers have increased from 5 to 12, and the Senate's from 12 to 18. Parliament's oversight functions over executive, judicial, law enforcement, and special services have also been expanded. Additionally, the leadership of local Councils of People's Deputies by hokims (governors) has been abolished, transferring 33 powers previously held by hokims to local Councils to increase their role in resolving critical state issues.
The slogan "My Choice—My Prosperous Homeland" not only captures the spirit of these elections but also reflects the unwavering commitment of Uzbekistan's leadership to democratic state-building and citizen empowerment. With over 120,000 election commission members, 70,000 citizens, and numerous international observers participating, the elections are set to be a transparent and inclusive process, further demonstrating this commitment.
In conclusion, Uzbekistan is setting a remarkable precedent with its upcoming elections by embracing technological innovation and inclusivity. These initiatives will undoubtedly pave the way for a more prosperous and democratic future, showcasing Uzbekistan’s dedication to advancing democratic principles and practices.
Eldor Tulyakov,
The Executive Director,
Development Strategy Centre (Uzbekistan)
18 new energy facilities commissioned, 6 facilities are launched for construction
📅 16.12.2024
President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev on December 13 took part in a solemn ceremony dedicated to the launch of new energy capacities and the beginning of construction of a number of facilities.
These projects are part of a large-scale work aimed at strengthening the potential of the country's energy system. Last December, five solar and one wind power plants were put into operation. Many new projects were launched during the Head of State's visits to the regions.
Today, 24 projects worth more than $7 billion have been launched. In particular, in Bukhara, Navoi, Namangan and Tashkent regions, 5 solar and wind power plants with a total capacity of about 2.3 thousand megawatts, as well as 5 high-voltage substations have been connected to the network.
For the first time in Uzbekistan, an energy storage system with a capacity of 300 megawatts was created in Andijan and Fergana. A 400 megawatt power plant was put into operation in Kashkadarya, and a modern cogeneration plant was put into operation in Tashkent, and in Andijan, Surkhandarya and Tashkent regions - four small hydroelectric power plants.
In addition, construction of 6 energy facilities with a total capacity of 2.5 gigawatts has started in Fergana, Samarkand, Navoi, Tashkent regions and Tashkent city.
These new projects will generate an additional 9.5 billion kilowatt hours of electricity, save 2.5 billion cubic meters of natural gas and prevent the emission of 4.6 million tons of harmful gases in the coming years.
Most importantly, over 4 million households will be provided with uninterrupted and clean energy.
This will also set the stage for $4 billion worth of value creation in other sectors of the economy.
In total, in 2025, our country will produce 84 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity, which is 25 billion kilowatt hours or 1.5 times more compared to 2016.
Speaking at the ceremony, President Shavkat Mirziyoyev emphasized that all these projects are implemented through foreign direct investment. Gratitude was expressed to companies from the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Türkiye, China and Germany, as well as international institutions such as the Asian Development Bank, the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, the Islamic Development Bank, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and the World Bank for their fruitful cooperation.
Thanks to the open access of the private sector, Uzbekistan's energy sector has attracted about $20 billion of foreign direct investment over the past five years.
Twenty-four independent energy producers have started to operate in the sector, where previously only the state was present.
In particular, large solar and wind power plants with a total capacity of 3,500 megawatts, equivalent to 10 billion kilowatt-hours, were launched in the green energy sector. This increased the share of “green energy” in the energy system to 16 percent.
As is known, last year the country's GDP reached the historic figure of $100 billion for the first time. By 2030, Uzbekistan's economy should grow to $200 billion.
This will increase the demand for electricity by 1.5 times over the next five years. In addition, under the Paris Agreement, it is planned to reduce harmful gas emissions by 35 percent by 2030.
The President outlined the priority areas of work in the energy sector.
First, 19 thousand megawatts of additional “green capacity” will be built by 2030, and the share of renewable energy will be increased to 54 percent. Already by 2025, 18 solar and wind power plants with a capacity of 3.4 thousand megawatts and energy storage systems with a capacity of 1.8 thousand megawatts are planned. This will increase green energy production to 12 billion kilowatt-hours next year. Also within two years, a large-scale project will be implemented in cooperation with private partners to create more than 2,000 small and micro-hydroelectric power plants.
Second, liberalization of the electricity market will continue. By the end of next year, it is planned to create a competitive wholesale electricity market. Public-private partnership will be introduced in the sphere of energy distribution, and $4 billion of investments will be attracted for the modernization of networks. The first project of transferring the management of regional power grids to the private sector has been developed in Samarkand region, and an international tender has been announced.
Third, the expansion of international cooperation in the field of “green energy”. Within COP-29, agreements were signed with Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan and Saudi Arabia on joint export of “green energy” to Europe. Jointly with neighboring countries a single platform has been launched to ensure the stability of the regional energy system.
Fourth, development of “green energy” as a new driver for other sectors of the economy and improvement of living standards of the population.
Solar panels with a total capacity of 1,000 megawatts have already been installed, which makes it possible to produce 1.5 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity annually. Support for “green” initiatives will continue with the introduction of dual education for the training of specialists.
- Today's event opens a new page in the history of our country's energy sector. These projects will not only ensure economic growth, but also will create an environmentally friendly and sustainable future for our descendants - said Shavkat Mirziyoyev.
The ceremony was addressed by Minister of Energy and Infrastructure of the United Arab Emirates Suhail Mohamed Al Mazrouei, Minister of Energy and Natural Resources of Türkiye Alparslan Bayraktar and Minister of Energy of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman Al Saud.
By pressing a symbolic switch, President Shavkat Mirziyoyev launched the operation of 18 energy facilities and construction of 6 new projects.
Uzbekistan and Azerbaijan: stable friendship and reliable partnership
📅 02.07.2025