Phone
Consular Issues
Phone
Uzbekistan news
We recommend
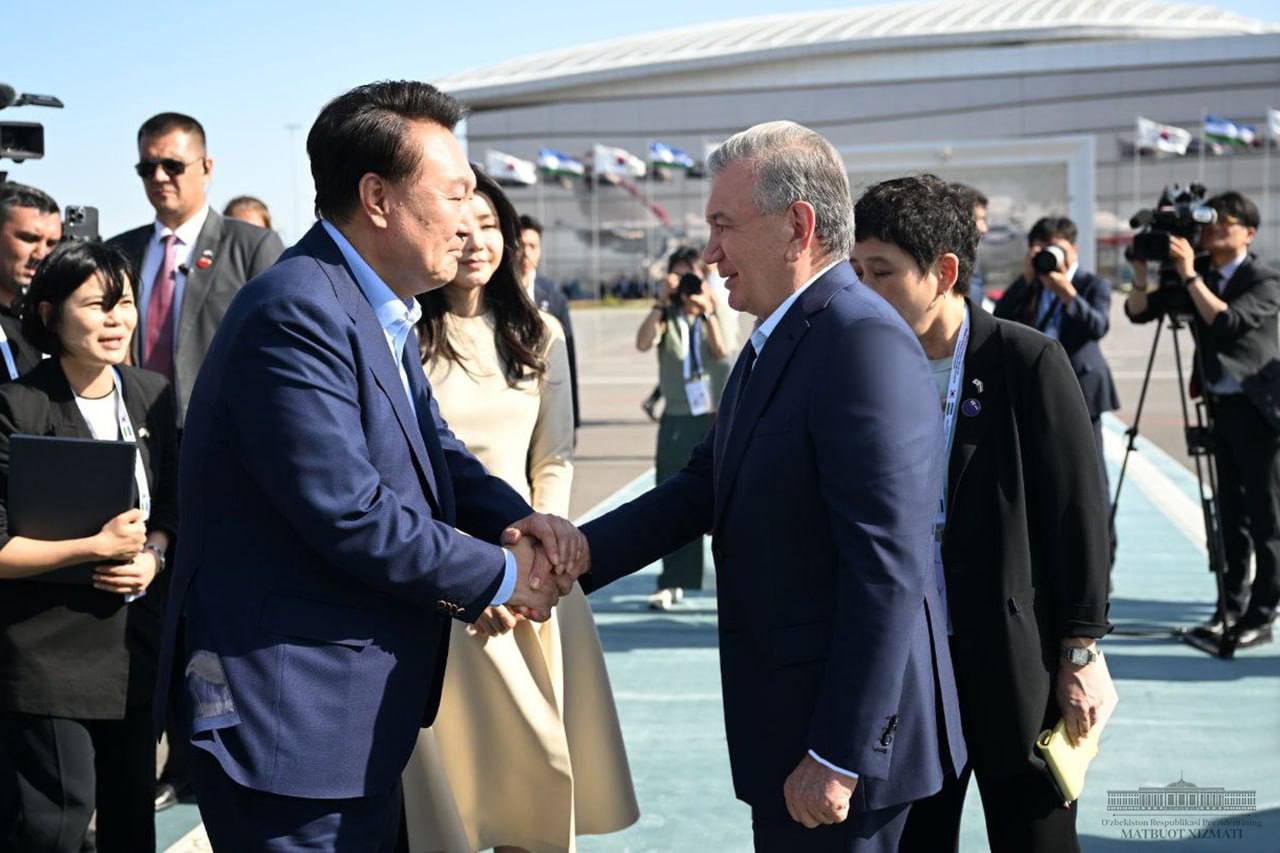
The Uzbekistan-Korea summit has ended
📅 15.06.2024
The state visit of the President of the Republic of Korea Yoon Seok-yol at the invitation of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev has ended.
During the three-day visit, high-level talks were held, at the end of which the leaders signed a joint statement on further deepening and comprehensive expansion of the Special Strategic Partnership. A bilateral set of documents was received.
The heads of state participated in a joint business forum with the participation of representatives of leading Korean companies and banking and financial institutions.
The presidents visited the Technopark in Tashkent and got acquainted with the existing potential for industrial cooperation.
Today, the dialogue between the heads of state continued in Samarkand. The presidents and their wives got acquainted with the historical and architectural masterpieces of the ancient city.
After the end of the visit, President Yun Sok Yol and his wife were escorted by President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev and his wife at the airport.
Address by the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev at the Arab-Islamic Summit
📅 12.11.2024
Bismillahir Rahmanir Rahim!
Honorable chairman!
Distinguished heads of delegations!
I would like to extend my deep gratitude to the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques, His Majesty the King of Saudi Arabia Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, and His Highness the Crown Prince and Prime Minister Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud for hosting this important summit today on the most urgent and painful issue on the global political agenda - the problem of Palestine.
Regrettably, since the historic meeting in Riyadh in 2023, the scope of this unfair and violent war has further widened.
Despite the resolute efforts and urges of the international community, flagrant violation of international norms and resolutions continues to this day.
We are all dismayed by the fact that now the flames of war encompass Lebanon as well.
As my colleagues have noted in their statements, these devastating and horrific attacks, which have caused the deaths of thousands of innocent children, women and the elderly, are turning into the darkest page of the new history of humanity.
One cannot watch without broken heart how social infrastructure facilities, schools, hospitals, mosques and even entire cities are turning into ruins, leaving millions of civilians homeless and doomed to hunger and disease.
Worst of all, as we all can see, this tragedy on the international arena is being approached through double standards.
This dramatically increases the potential for spillover of the war and poses a serious threat to international security.
Dear participants of the summit!
Uzbekistan fully supports all practical initiatives aimed at addressing the Palestinian-Israeli problem through peace and diplomacy.
In this regard, we believe that today's Summit will demonstrate common political will and unity, develop effective global and regional mechanisms and specific solutions, and swiftly put them in practice.
In first place, here we are referring to the need to drastically increase the role and influence of the United Nations and the Security Council in addressing this long-standing conflict.
Immediate cessation of military action, provision of safe humanitarian corridors and, most importantly, the initiation of peace negotiations should be at constant focus of this universal international structure.
Second. On November 15, the long suffering Palestinian people will celebrate their National Day - the Declaration of State of Palestine.
I am confident that this nation with an ancient and rich history has every right to establish an independent and free state within the borders of 1967, with East Jerusalem as its capital.
In this regard, we fully support the activities of the Global Alliance for Implementation of the Two-State Solution, organized at the initiative of Saudi Arabia.
Third. In order to prevent an unprecedented humanitarian crisis in Palestine and Lebanon, we need to expand the scope of assistance from our countries and within the framework of leading international organizations.
We support increasing the necessary assistance to the activities of UNRWA and other United Nations institutions, which have great experience.
In this regard, we express our readiness to provide free medical care to war-affected Palestinian children and women in Uzbekistan's hospitals.
We also intend to discuss the issue of extending practical assistance to the Palestinian people at the forthcoming GCC-Central Asia Summit in Samarkand next year.
Fourth. As part of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation, we should attach greater attention to ensuring the sanctity and preservation of the Holy Al-Aqsa Mosque and other unique historical and cultural sites in Jerusalem.
Dear heads of delegations!
I hope that our extraordinary meeting today will be a big step towards addressing the Middle East problem.
I pray to Allah Almighty to bestow peace and tranquility upon the world and further strengthen the unity of our Ummah.
Thank you for your kind attention.
Proposals on further development and increase of competitiveness of the jewelry industry were considered
📅 19.06.2024
President Shavkat Mirziyoyev was given a presentation on measures to further develop the jewelry industry, support jewelry production and sales, and increase exports of finished products.
Our country has a huge potential for increasing production and export of jewelry.
As the head of state noted, only 6 percent of gold mined in the country is processed, and exports of its products amount to only 78 million dollars, so it is important to create jewelry zones with special conditions for entrepreneurs, to review the provision of raw materials, training of specialists, production chain and sales system.
In this regard, the Ministry of Economy and Finance and the Chamber of Commerce and Industry have developed relevant proposals.
In particular, it is planned to improve the activity of the Uzbekzargarsanoati association, expand its powers and reorganize the management system.
In order to support manufacturers of the industry, it is proposed to apply the benefits provided for members of the Association "Uzbekzargarsanoati" to individual entrepreneurs - manufacturers of jewelry, who are members of the Association "Uzbekzargarsanoati".
The possibility of establishing a zero rate of customs duty and value added tax on equipment, packaging and marking materials that are not produced in Uzbekistan and used in the jewelry industry for the period up to October 1, 2026 is being studied.
The issues of creation of special jewelry centers including production, exhibition and trade areas were considered. Information was provided on the placement of pilot projects in Tashkent and Namangan region.
The issue of increasing the volume of jewelry exports was discussed. It was proposed to establish a zero rate of customs duty for export of jewelry made in our country to the United States of America under the GSP system.
The head of state instructed to finalize the presented measures and work out a program for the development of domestic jewelry production for the period up to 2027.
IF YOU WANT PEACE, BE FRIENDS WITH YOUR NEIGHBORS
📅 17.10.2025
Experts often use the Latin phrase “si vis pacem, para bellum”, which translates as “if you want peace, prepare for war”. They emphasis that only force can guarantee peace.
The processes observed in Central Asia in recent years suggest the opposite. Against the backdrop of geopolitical turbulence, countries in the region regularly pursue policies based primarily on the principles of dialogue and good neighborliness.
In a short period of time, the face of the region has changed dramatically, common points of growth are forming, and mutual trust is becoming an important condition for stability. Common triggers for development are being identified: the formation of a common economic space, active attraction of investment, and the strengthening of cultural and humanitarian ties. A spirit of unity and solidarity has formed in the region.
As Uzbekistan's leader Shavkat Mirziyoyev noted at the 80th session of the UN General Assembly, “Today, Central Asia is different - it is united and strong, open to dialogue and full-scale partnership”.
The political transformation of the region is underpinned by steady economic growth, demonstrating the region's growing power. In particular, over the last 10 years, Central Asia's GDP has grown by more than 6% annually — twice as fast as the global average.
Due to political will and joint efforts of the leaders of the states, significant results have been achieved in resolving border issues. An important milestone on this path was the trilateral meeting of the presidents of Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan, held on 31 March 2025 in Khujand.
As a result, an agreement was signed on the junction point of the state borders of the three countries, which is clear evidence that the governments of our states place peace and harmony above all else.
All this confirms the idea that peace can only be achieved through mutual understanding, support and cooperation, which are the basis of friendly relations. We are guided by the principle: “If you want peace, be friends with your neighbors” This approach reflects the essence of the integration processes taking place in the region and certainly deserves the attention of the international community as a “exemplary model” for resolving even the most complex conflicts of our time.
How has humanity understood the world over the centuries?
Throughout human history, peace has been regarded as one of the highest spiritual and social values. Even in ancient times, thinkers in Ancient Greece sought to understand the phenomenon of Eirene – a state of harmony, the cessation of hostility and stable order in society.
In Eastern philosophical thought, the concept of peace also occupied a special place. It was understood, first and foremost, as the inner harmony of a person with themselves and the surrounding world, as a path to spiritual balance and moral perfection.
The great thinkers of Central Asia continued to develop the idea of peace, giving it philosophical and humanistic content. Thus, Abu Nasr Farabi regarded peace and harmony as an indispensable condition for the existence of a “Virtuous City”, where justice, reason, and mutual understanding between people become the basis of social well-being. Alisher Navoi, in his poetic works, presented peace as the highest form of spiritual and moral perfection of man, the basis of creation and mutual respect between peoples.
Thus, over the centuries, the idea of peace has evolved from an understanding of it as the absence of war to an awareness of spiritual and moral harmony between people and nations.
Why was Fergana chosen as the venue for the Forum?
The choice of Fergana as the venue for the forum is no coincidence.
The Fergana Valley is a unique geographical area where peoples speaking different languages and practicing different religions have coexisted peacefully for centuries. The Great Silk Road passed through the valley, and its inhabitants were engaged in crafts, trade and science, always striving for mutual understanding and dialogue. Conflict is a foreign concept to the region.
Today, the Fergana Valley unites the territories of three independent states, whose relations are based on the principles of good neighborliness, mutual respect, sovereignty and territorial integrity.
The Fergana Valley is the most populous region in Central Asia. According to data, the Andijan, Namangan and Fergana regions of Uzbekistan alone are home to about 11 million people, which is almost a third of the country's population. If we take into account the population of the territories of neighboring states that are geographically part of the region, the total figure is about 17 million.
With this in mind, the countries of Central Asia are striving to deepen regional integration, viewing it as an important condition for sustainable development. Strengthening mutual trust and partnership is becoming one of the key areas of their foreign policy. To discuss specific steps and exchange experiences, platforms are needed that promote open dialogue and coordination of positions.
One such platform will be the Fergana Peace Forum, which will be held on 15–16 October at Fergana State University. It will be attended by representatives of government agencies and business circles of Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, experts from scientific, analytical and research centers, as well as delegates from the CIS, SCO, OSCE, UNDP, EU and other international organizations.
In addition, the Fergana Valley is a multinational region where representatives of all peoples and ethnic groups live in peace and harmony.
In this regard, the attention that the government pays to strengthening interethnic friendship and creating conditions for all citizens to receive education in their native language and study their national culture is of great importance.
Today, there are more than 250 schools in the Fergana, Namangan and Andijan regions where instruction is conducted in Kyrgyz, Russian and Tajik.
It is important to emphasize the important role of regional branches of national cultural centers, which are involved in ensuring inter-ethnic harmony, developing intercultural dialogue and tolerance, and strengthening good-neighborly relations with neighboring states.
Various activities are carried out in this area by 17 national cultural centers (8 in Fergana, 5 in Andijan and 4 in Namangan regions), including Russian, Slavic, Korean, Jewish, German, Tatar, Kyrgyz, Uyghur, Tajik and Turkish.
Special mention should be made of the activities of public associations, foundations and NGOs implementing socially significant projects, both with funding from domestic donors and with the support of international organizations and foreign partners such as the World Bank, UNDP, the United Nations Population Fund, the UN Women, the European Union, the International Organization for Migration, Saferworld, DVV International, Fair and Sustainable Development Solutions, DIA International and others.
The implementation of such projects contributes to ensuring access to social protection, developing entrepreneurial skills, increasing the participation of women and young people in public affairs, and strengthening mutual understanding and friendship between residents of border areas.
Overall, the first Fergana Peace Forum opens a new page in the development of good neighborly relations and partnership between the countries of the region.
In this case, the choice of the Fergana Valley as the venue reflects its historical role as a space for mutual understanding and harmony. Undoubtedly, this forum will provide an additional stimulus for further strengthening stability and expanding cooperation in Central Asia.
Abror Yusupov,
PhD in Political Science,
Associate Professor,
Deputy Director of the
Center for Analysis of Democratic Processes
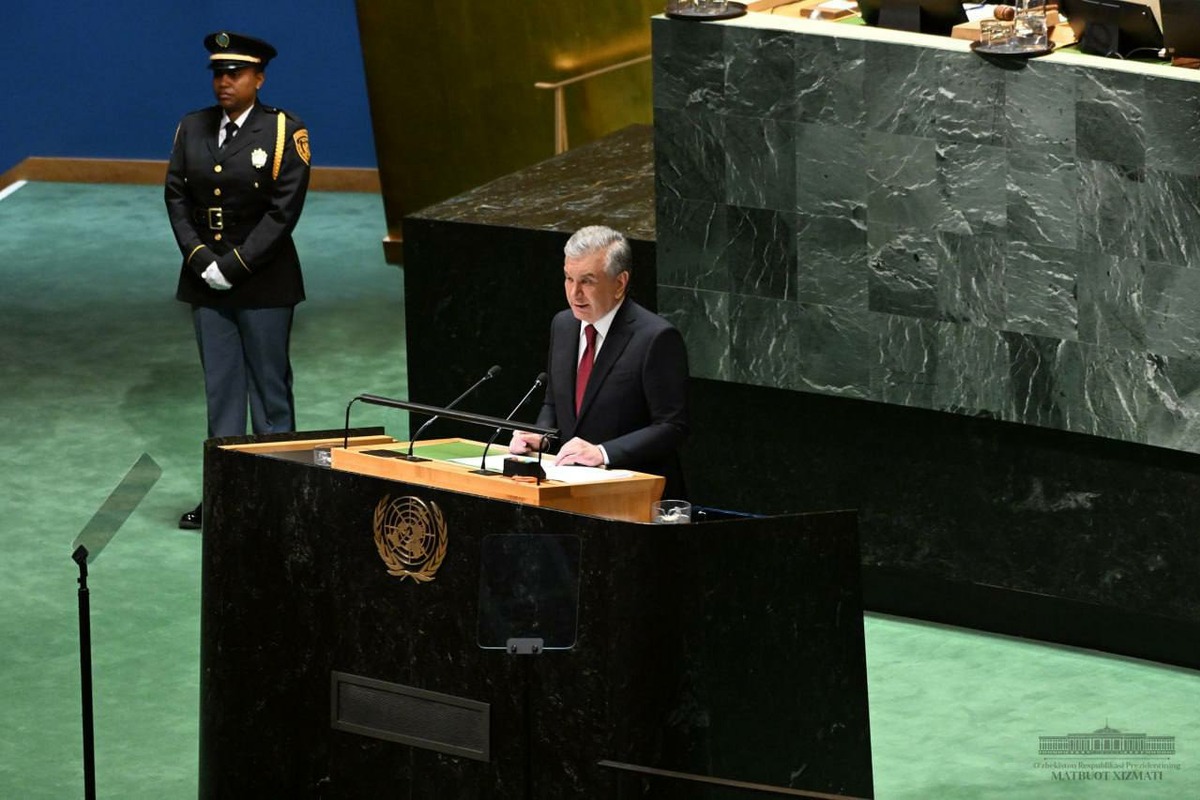
President of Uzbekistan to participate in the 80th session of the United Nations General Assembly in New York
📅 22.09.2025
On September 20-24, President of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev will pay a working visit to the city of New York to attend the events of the 80th jubilee session of the United Nations General Assembly.
According to the press service of the Head of our state, President of Uzbekistan will deliver a keynote address on the first day of organizing the general debate of the UN General Assembly plenary session.
It’s noteworthy that during the current jubilee session of the UNGA topical issues of ensuring global security and stability, achieving Sustainable Development Goals, reforming the system of the UN and international financial architecture, combatting the consequences of climate change and other modern challenges, will be reviewed.
On the sidelines of the summit, the Leader of Uzbekistan will hold talks with the UN Secretary-General António Guterres, heads of foreign states and governments, leaders of authoritative international financial institutions.
In the framework of the business program in the United States, it’s planned to hold meetings and events with participation of the leading American companies and financial-investment structures. It’s planned to sign a package of new agreements and contracts.
Dunyo IA
Proposals for the development of environmental protection and tourism were considered
📅 20.09.2024
Prezident Shavkat Mirziyoyev 19-sentabr kuni atrof-muhitni muhofaza qilish va turizm sohalaridagi takliflar taqdimoti bilan tanishdi.
Hozirgi kunda havoni musaffo saqlash, ekologik hodisalarning ta'sirini kamaytirish tobora dolzarb bo'lib bormoqda. Shu bois bu borada ikkita dastur ishlab chiqildi.
Birinchisi - Chang bo'ronlariga qarshi kurashish va ularning oqibatlarini yumshatish bo'yicha 2024-2030-yillarga mo'ljallangan milliy dasturdir. Bu hujjatda “Yevro-4” standartidan past toifadagi yoqilg'ini sotish va undan foydalanishni bosqichma-bosqich to'liq taqiqlash nazarda tutiladi. Buning uchun Buxoro va Farg'ona neftni qayta ishlash zavodlari yuqori sifatli yoqilg'i ishlab chiqarish bo'yicha modernizatsiya qilinadi.
Ikkinchisi - Toshkent shahrida atmosfera havosi sifatini yaxshilashga qaratilgan chora-tadbirlar dasturi bo'lib, unga ko'ra, kelgusi 5 yilda poytaxtimiz va unga tutash Toshkent viloyati tumanlarida 441 gektar “yashil belbog'” va bog'lar tashkil qilinadi.
Sanitar tozalash ishlarini tartibga solish maqsadida mavjud markaz negizida Chiqindilarni boshqarish va sirkulyar iqtisodiyotni rivojlantirish agentligini tuzish taklif etilmoqda. Sanitar tozalash korxonalarining samaradorlik ko'rsatkichlariga qarab, uchta toifaga ajratgan holda reyting tizimi joriy qilinadi.
Yangi quriladigan, balandligi 12 metrdan yoki umumiy maydoni 500 kvadrat metrdan ortiq bo'lgan binolarni loyihalashtirishda unga tutash hududlarning kamida 25 foizini ko'kalamzorlashtirish talabi qo'yiladi. Shuningdek, atrof-muhitga zarari ko'p sanoat korxonalari ham “yashil belbog'”lar barpo etish majburiyatini oladi.
Ekologik huquqqbuzarliklarning oldini olish, bu borada jamoatchilik nazoratini kuchaytirish masalalariga ham e'tibor qaratildi. Faol va jonkuyar insonlarni rag'batlantirish maqsadida “O'zbekiston Respublikasida xizmat ko'rsatgan ekolog” faxriy unvonini ta'sis etish taklifi bildirildi.
Atrof-muhit bilan bog'liq bo'lgan masalalar bo'yicha qarorlar qabul qilish jarayonida jamoatchilikning axborot olish imkoniyati, ishtiroki va odil sudlovga erishishish imkoniyati to'g'risidagi Orxus konvensiyasiga qo'shilish masalasi ko'rib chiqildi.
Ma'muriy javobgarlik to'g'risidagi kodeksga qurilish maydonlarida atmosfera havosini muhofaza qilish talablariga rioya qilmaslik bo'yicha modda kiritish maqsadga muvofiqligi aytildi. Shuningdek, daraxtlarni kesish va qasddan quritish, daryo o'zanlaridan noqonuniy qum-shag'al qazib olish, chiqindilarni belgilanmagan joylarga tashlash kabilar uchun jarimalarni oshirish va qat'iylashtirish choralari ko'riladi.
Vazirlar Mahkamasining 2019-yil 27-maydagi qarori bilan respublikada ekologik markirovkalash tizimi joriy etilgan. Endi ISO 14024 xalqaro standartiga muvofiq, “Yashil belgi” nomi ostida mahsulot va xizmatlarni ixtiyoriy ekologik markirovkalash yo'lga qo'yiladi. 2 ming 336 ta xo'jalik yurituvchi subyektlarda avtomatik monitoring stansiyalari, chang-gaz tozalash uskunalari va suv tozalash inshootlarini o'rnatish bo'yicha tarmoq jadvallari tasdiqlanadi.
Ekologiya vazirligi huzurida jamoatchilik nazorati ostida boshqariladigan va yuridik shaxs maqomiga ega bo'lmagan “Yashil xayriya jamg'armasi” tashkil etiladi. Elektron xarid ilovalarida “Yashil to'lov” ixtiyoriy ustama turi ochiladi.
Sohadagi yana bir muammo yovvoyi hayvonlarni asrash bilan bog'liq. Ularni xonadonlarda boqish huquqiy jihatdan tartibga solinmagan. Shu bois endi yovvoyi hayvonlarni uy sharoitida, sirk va shapitolarda saqlash hamda tomoshalarda foydalanish taqiqlanadi. Jismoniy shaxslar ixtiyoridagi hamda sirklarda saqlanuvchi bunday jonzotlar hayvonot bog'laridagi reabilitatsiya markazlariga, okeanariumlar, pitomnik va ilmiy-tadqiqot muassasalariga topshirilishi belgilanmoqda.
Taqdimotda tibbiy turizmni rivojlantirish chora-tadbirlari ham muhokama qilindi.
Shu maqsadda O'zbekiston bu yo'nalishda Markaziy Osiyoning “chorlovchi nuqtasi” sifatida targ'ib qilinadi. “Tibbiy xizmatlar mehmondo'stligi” dasturi amalga oshiriladi. Tibbiy va sog'lomlashtirish muassasalari faoliyati rag'batlantirilib, ularning yagona reyestri ishga tushiriladi. Mehmonxonalar kabi yulduzli sanatoriylar faoliyati yo'lga qo'yiladi.
Davlatimiz rahbari bular bo'yicha hujjat loyihalarini puxta ishlab chiqish va ijrosini samarali tashkil etish bo'yicha ko'rsatmalar berdi.
Human dignity and the benefits of the people in New Uzbekistan – high values
📅 12.07.2024
It is not an exaggeration to say that in the historical conditions where humanity is going through a difficult period, where contradictions and conflicts are intensifying and seriously undermining stability, in the multi-ethnic New Uzbekistan, human dignity and the interests of the people are recognized as the highest values, and in this regard, it is becoming an example and model for many countries of the world.
Because sustainable development can be achieved first of all by valuing and honoring people, creating conditions for the population to live well today, and realizing the high trust and responsibility of the population for the future.
Abdulla Awlani, the famous modern enlightener, defined man in such a way: “...the purpose of the creation of the universe is man. Man is the glory and honor of all existence. All creation must serve man: man is its master. Because man has a mind. He acquires knowledge with the help of this mind, and rules the world thanks to his knowledge”.
Therefore, measures aimed at the development of citizen's activity and participation in state management are being systematically implemented in Uzbekistan today, with comprehensive support for human rights and interests.
In recent years, the reforms implemented in Uzbekistan and the active participation and involvement of citizens in the state administration have been observed, which is especially important in the adoption of documents that will be the criteria for the future fate of our country.
In particular, in 2023, the "people's constitution" adopted for the first time in the history of Uzbekistan on the basis of the will of the people is a program for creating the foundation of the country's future destiny and happy future. More than 220,000 proposals have been received from different layers of the population, and this is also an example of the people's interest in state management and fate.
For this reason, first of all, the proposals received from the population, as well as the experiences and norms of constitution – making of 190 countries were thoroughly studied, and the articles of the updated constitution increased from 128 to 155, and the number of norms increased from 275 to 434.
In a situation where modern threats and problems are becoming increasingly rooted, the issues of ensuring a stable economy, effective governance, a safe state and social guarantees in Uzbekistan in the future have been deeply analyzed, 65% of the basic law has been updated based on people's proposals, and new norms based on national and universal values and modern opportunities have been introduced.
In the words of the President of Uzbekistan, "Our Basic Law, which is literally a public dictionary, serves as a strong legal guarantee that our large-scale reforms aimed at establishing New Uzbekistan will not go back."
Another proof of the active participation of citizens in the sphere of public administration in Uzbekistan is the launch of the portal for the discussion of projects of regulatory legal documents (https://regulation.gov.uz/) to receive proposals from citizens for drafts of state programs, laws and legal documents. During the year, 77,731 proposals were received from the population for 25,283 draft documents.
Another important point is that in recent years, the share of women in state management in Uzbekistan has increased from 27% to 35%. In particular, 32% of the deputies of the Legislative Chamber of the country's parliament (Supreme Assembly) and 25% of the members of the Senate are women. The number of businesswomen doubled, and the number of women who started their own business exceeded 205,000.
It is of particular importance that Uzbekistan is listed among the 5 fastest developing countries in the world in the field of gender equality in the World Bank index, and is among the top 20 countries in the open gender data index.
First of all, the conceptual basis of the reforms was created in Uzbekistan, and a number of strategic decisions were made for its systematic operation.
In order to further increase the effectiveness of the ongoing reforms, create conditions for comprehensive and rapid development of the state and society, implement priority directions for modernization of our country and liberalization of all spheres of life, the Strategy of Actions on five priority directions for the development of the Republic of Uzbekistan in 2017-2021 is consistently implemented increased.
Strategy 5 – Improvement of the system of state and community building, ensuring the rule of law and further reforming the judicial system, developing and liberalizing the economy, developing the social sphere and ensuring security, inter-ethnic harmony and religious tolerance, as well as a well-thought-out, mutually beneficial and practical foreign policy reforms worthy of universal recognition took place in the field of priority directions.
The economic growth in the country alone was ensured to grow by 4.4% in 2017, 5.4% in 2018, and 5.7% in 2019.
On September 11, 2023, the "Uzbekistan-2030" strategy was adopted based on the experience gained during the implementation of the development strategy of New Uzbekistan and the discussions of the general public, and the strategic tasks that we must achieve in the next 7 years were defined. The importance of this strategy, consisting of 100 points, is that in this document, specific goals and targets are set, which are expected to be achieved in all areas, and the reforms continue consistently.
The important thing is that this document sets the future priority goals, in particular, to use all the possibilities to increase the size of the country's gross domestic product from the current 80 billion dollars to 160 billion dollars, thereby doubling the size of the economy by 2030 and "countries with an income above the average". Bold steps are being taken to enter the ranks.
In Uzbekistan, great attention is being paid to this area, which is directly related to the quality of life. In the last 7 years, the amount of funds allocated to the healthcare system has increased from 5.9 trillion soums to 33.5 trillion soums, that is, it has increased 6 times. Hospitals are equipped with modern equipment and new ones are being built.
In Uzbekistan, systematic measures are being taken to provide social support to the population, to identify the root causes of the problems of each of its strata, and to provide targeted assistance, especially to reduce poverty.
"Temir daftar" (Iron book), "Ayollar daftari" (Women`s book), "Yoshlar Daftar" (Youth book), "Mahallababay" (Neighbourhood) and "Khonadonbay" (House work) work methods are being introduced for this purpose. On this basis, not abstract indicators of the problem, but the problems of every family and citizen, women, and youth who need help and support are clearly studied on the spot, and they are solved in a timely and effective manner.
Today, the noble traditions of supporting the elderly, disabled people, people in a difficult situation, and showing them love and kindness are being enriched and improved with new meaning and practical actions. In this regard, programs such as "Prosperous village", "Prosperous neighborhood", "Five important initiatives", "Every family is an entrepreneur", and "Youth are our future" are giving positive results.
At this point, it should be noted that since 2017 Virtual and Public receptions of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan have been established. In 2017-2021, the President's virtual lobby and People's lobby received 5 million. More than 780,000 appeals were considered, of which 3 mln. More than 288 thousand were satisfied. As a result of complete, timely and legal investigation of appeals, the level of their satisfaction is also increasing year by year. In particular, this indicator was 47.5 percent in 2017, 53.9 percent in 2018, 60.9 percent in 2019, 60.4 percent in 2020, and 86.7 percent in 2021.
Another consideration is that in recent years, the intensity and scope of the globalization process has increased in the intellectual world in the complex conditions where the struggle for the hearts and minds of the young generation is intensifying, the role and importance of education in the spirit of patriotism is increasing more and more, and the need to educate our youth as true patriots is growing stronger than ever. In the world, the number and scale of ideological struggles and conflicts are increasing, and new threats are emerging that cannot be predicted in advance.
In such a situation, education of young people in the spirit of loyalty to the Motherland, national identity and values, and concern for national interests is gaining urgent importance.
When one of the scholars said that "the happiness of every nation, the peace and happiness of the states depends on the good education of the youth", there are many real truths.
Based on the opinion of the head of Uzbekistan in his speech at the extended session of the Council of Spirituality and Enlightenment of the Republic that "it is natural that the legacy of our enlightened ancestors serves as a foundation for the legal democratic state and civil society that we are building today", it is clear as day that the development of national spirituality should be one step ahead.
In this regard, specific measures have been defined in 9 directions in the country, in particular, spirituality should be ten steps ahead of other fields, popularization of the heritage of the ancients, addition of an additional "Spiritual sector" to 4 sectors, enrichment of the activities and contents of theaters, cultural centers, priority issues such as the development of Uzbek cultural diplomacy, film, visual and applied arts in the international arena are among these.
The concept of the President of Uzbekistan, "If the economy is the body of society's life, then its soul is spirituality" has already become a vital principle for all of us. Strong spirituality based on the rich heritage of our ancestors and national values serves as a strong pillar for the country that decided to build the new Uzbekistan.
In recent years, "Man-Society-State" has become an irrevocable strategic principle in Uzbekistan, fundamental reforms have been carried out to pay attention to people and protect their rights and interests.
It is necessary to recognize one fact: reforms in accordance with international standards are being implemented in all areas related to people and their activities. At the same time, the critical analysis of our activities by the head of the country, using the existing freedom of speech, encourages us to constantly examine ourselves and improve our measures regularly in order to reach new goals in the future.
For example, more than 2,200,000 families are in need of social assistance, among them there are many young people. In this regard, specific measures have been determined this year, and in the updated Constitution, the state's social obligations have been tripled, and an additional 30-40 trillion soums will be allocated annually from the state budget.
The principle of "man-society-state" is of particular importance for the future development of our country, and constitutional guarantees have been strengthened in this regard.
The international community of Uzbekistan is paying special attention to strengthening friendly relations with neighboring countries on the basis of cooperation, mutual support, peace and harmony, and the legal basis for further deepening of the reforms implemented in foreign policy in recent years is also being strengthened.
For example, due to the resolution of the 30-year-old border problem with neighboring Kyrgyzstan, more than 2 million inhabitants of the valley were able to move freely with their relatives and friends.
The directions of strengthening peace and stability of Uzbekistan in our region, expanding the potential of our country in the international arena and developing comprehensive and mutually beneficial relations with foreign countries are confirmed in the "Concept of Foreign Political Activities" approved by law.
Today, Uzbekistan has established diplomatic relations with 131 countries of the world, we have 37 embassies in 38 countries, consulates in 17 cities, permanent representative offices in the UN and other international organizations.
In a word, as the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Shavkat Mirziyoyev, said, "From now on, we will focus on strengthening multifaceted and mutually beneficial cooperation with all the neighboring countries in Central Asia and the countries and international organizations that are our strategic partners in the world."
Ensuring decent life of citizens in Uzbekistan, inter-ethnic and inter-confessional harmony, well-being and prosperity of our multi-ethnic country of Uzbekistan is also one of the most important directions.
In order to support our compatriots in many countries of the world and further strengthen our relations with them, the "Compatriots" fund was established.
Our work aimed at strengthening the environment of inter-ethnic harmony and tolerance in our society is reaching a new level in terms of quality. July 30, which is widely celebrated as the International Friendship Day, has been announced as the "International Friendship Day" in Uzbekistan. This year, this holiday was widely celebrated for the first time in our country. It can also be considered as a common phenomenon where internal and external political factors converge.
It will be necessary to mobilize all our strength and capabilities to further strengthen the atmosphere of inter-civilian harmony, inter-ethnic friendship and tolerance.
The future strategic tasks in the foreign policy have already been defined, which will serve as a consistent continuation of the actions in the field of foreign policy and economic diplomacy.
In this regard, first of all, it is necessary to further strengthen close friendship, good neighborliness and strategic partnership relations with the countries of the region, to expand mutually beneficial and multilateral relations with the countries of the far and near countries of the world, especially to continue providing assistance to the Afghan people to restore a peaceful and peaceful life in neighboring Afghanistan. It is appropriate to carry out priority tasks such as the implementation of large transport and communication projects together with the country at a qualitative level. In this regard, it is time to raise multilateral relations with international regional organizations and financial institutions to a new level.
In a word, the so-called New Uzbekistan is boldly marching towards sustainable development with systematic reforms, hard work and the will of the creative people. Systematic reforms implemented today in our country, which realizes its high responsibility to present and future generations to build a humane democratic state, an open and fair society, where human life, freedom, honor and dignity are considered the highest value, are a thing of the ages.
Khudoyberdi Khaknazarov
Doctor of History
Public Diplomacy in Uzbek-Turkish Relations: The Factor of Trust and Cooperation
📅 28.01.2026
In the modern system of international relations, stable and long-term cooperation between states is based, above all, on political will and trust at the highest level. Relations between the Republic of Uzbekistan and the Republic of Turkey have consistently developed based on an open, sincere, and trusting dialogue established between the heads of state. This political trust creates a solid foundation for public diplomacy, including deepening fraternal ties between the cities.
In recent years, high-level meetings, regular political dialogue, and strategic agreements between the presidents of Uzbekistan and Turkey have elevated relations between the two countries to the level of a comprehensive strategic partnership. Mutual trust and political support from the heads of state have resulted in concrete and practical results in trade, economic, investment, cultural, humanitarian, and educational spheres.
From this perspective, public diplomacy is becoming an important component of Uzbek-Turkish relations. It strengthens official interstate agreements at the public level and deepens trust and mutual understanding between peoples. Particularly between two fraternal nations with shared historical roots, a common language, and spiritual values, public diplomacy is a natural and indispensable process.
In this context, the Uzbekistan-Turkey Friendship Society functions as an important institutional platform for the development of public diplomacy. Cultural events, scientific and educational conferences, youth and women’s initiatives organized by the society contribute to strengthening mutual trust and friendship between the two peoples. This activity promotes public support for priority areas established at the level of heads of state.
At the same time, fraternal relations between cities are one of the most effective and practical forms of public diplomacy. Fraternal relations established between the cities of Uzbekistan and Turkey strengthen political trust at the local level and create a favorable environment for economic and cultural cooperation. The Brother Cities Alliance and the Union of Municipalities of the Turkic World participate in this process as important international structures coordinating and systematically developing relations between cities.
Brother cities cooperation, which has historical significance in Uzbek-Turkish relations, includes ties between the cities as Bukhara – Izmir, Bukhara – Malatya, Samarkand – Sakarya, Tashkent – Ankara, and Khiva – Bolu. Cultural and humanitarian projects, educational and tourism programs, as well as investment initiatives implemented within the framework of this cooperation serve to achieve the strategic goals set by the leaders of the two countries at the local level.
It should be noted that cooperation between cities has not only cultural or economic significance but also an important political content. Trust and cooperation established at the local level ensure the stability and continuity of interstate relations. This demonstrates the significant role of public diplomacy in strengthening the strategic partnership between Uzbekistan and Turkey.
In conclusion, public diplomacy in Uzbek-Turkish relations is an important factor that builds on, complements, and strengthens the trusting political dialogue between the heads of state. Within the framework of the priority areas identified by the heads of state, work carried out at the city level in cooperation with the Brother Cities Alliance and the Union of Municipalities of the Turkic World will contribute to the further strengthening of friendship, trust, and cooperation between the two fraternal peoples.
Zokir Abidov,
Chairman of the Brother Cities Alliance
Investments’ implementation, poverty and unemployment reduction set as priority tasks in Bukhara
📅 02.12.2024
On November 29, President Shavkat Mirziyoyev convened a meeting dedicated to identifying additional opportunities, increasing investments and jobs in Bukhara region.
Previously, the economy of this region was mainly linked to agriculture. However, over the past seven years, the region has attracted more than $4 billion investments, enabling development of such industries as energy, electrical engineering, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, textiles and leather. In the past period of the current year, 1.5 million foreign tourists visited Bukhara.
The visit of the Head of State to the region on May 31-June 1 gave a new impetus to its development. All the tasks outlined during the visit will be fully accomplished by the end of the year.
At the same time, it is important to ensure further growth of economic indicators in 2025, increase employment and well-being of the population. To this end, the working group studied additional opportunities of the region and factors hindering entrepreneurship development.
The critical meeting emphasized that the region's economic performance does not correspond to its potential. Work on investment absorption, poverty and unemployment reduction was recognized as unsatisfactory.
In this regard, the hokims, their deputies and sector heads will be put on emergency duty for a period of six months. The entire focus will be on improving these three areas. Special attention will be paid to implementing 70 driver projects based on the experience of Saikhunobad, Uychi, Zarbdar and Gijduvan. They will provide income to 150 thousand people and lift 40 thousand people out of poverty.
As it was mentioned, each district of the region can be specialized for a certain industry. For example, Peshku and Shafirkan - for production of construction materials and textiles, Kagan city, Alat and Jondor districts - for food industry, Gijduvan and Romitan - for chemical industry. This will make it possible to implement projects of entrepreneurs worth $150 million, create 411 small enterprises and provide 12 thousand jobs.
Four textile factories are planned to be built in Vabkent, Karakul, Jondor and Alat at a total cost of $320 million. This will double the volume of finished knitwear and textile products and create 5,000 jobs.
Next year, the number of foreign tourists is expected to reach 2.2 million and tourism exports are expected to reach $600 million. This will be supported by opening 69 new hotels and 2 thousand handicraft stores.
It is planned to develop additional 20 thousand hectares of land, which will allow to grow additional 100 thousand tons of agricultural products and provide employment for 2 thousand people. Trees and food crops will be planted on vacant homestead land, along canals and field edges.
Another opportunity is pastures. In Bukhara region their area exceeds 2 million hectares. As part of the decisions made at a recent meeting on horticultural development, it is planned to grow pistachios on unused pastures.
Hokim of Bukhara region presented plans to utilize these opportunities. In general, next year 106 projects will be implemented, 105 thousand permanent jobs will be created, exports will be increased by $350 million due to foreign investments worth $2 billion.
The Head of State pointed out the insufficiency of these plans and instructed to intensify efforts and improve results. He tasked to revise the proposals again and draft a relevant resolution.
9 projects with a total value of 2 billion dollars
📅 15.10.2024The text of the article is in Uzbek!
Do you know Uzbekistan?
📅 11.07.2024The text of the article is in Uzbek language!
FERGHANA VALLEY: A COMMON VISION OF A STRATEGY FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND PROSPERITY
📅 13.10.2025
Annotation. The Ferghana Valley is the historical heart of Central Asia, where a new model of regional cooperation based on trust, good neighbourliness and sustainable development is currently taking shape. The initiative
of the President of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev to hold the Ferghana Peace Forum reflects a common desire among the countries of the region to strengthen mutual understanding and create the area of peace, stability, and shared prosperity.
INTRODUCTION
Historically, the Fergana Valley was a shared space where countries used common resources and people kept close ties. For centuries, the valley was
at the crossroads of key trade routes connecting the West and the East.
The establishment of an atmosphere of good neighbourliness
in the Ferghana Valley reflects positive developments throughout Central Asia. Essentially, this is the result of political will, a concentrated expression
of the joint efforts of the leaders of all five countries to maintain security
and stability in the region.
Holding the Fergana Peace Forum in Fergana on October 15–16, 2025, confirms the statement made by the President of Uzbekistan at the 80th session of the UN General Assembly about the transformation of Central Asia into
an area of peace, friendly relations and partnership.
FROM A ZONE OF TENSION TO A SPACE OF TRUST
In the early years of independence, unresolved border issues and
the existence of numerous ethno-territorial enclaves served as grounds
for viewing the region as a conflict zone.
However, today, thanks to the political will and joint efforts of the leaders
of states, the Fergana Valley, previously perceived as a “powder keg,”
“Achilles' heel,” and “hot spot,” is becoming a symbol of peace, sustainable development, and a space of opportunity.
In recent years, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan have made significant progress in diplomacy and establishing stable political contacts.
The visits of the countries' leaders and their participation in regional forums and organizations such as the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
and the Consultative Meeting of the Heads of Central Asian States contribute
to the deepening of political and economic ties. The development of bilateral
and multilateral relations in the political sphere has helped to create a solid foundation for regional integration and mutual support.
Moreover, all five Central Asian countries contribute to the sustainable development of the Ferghana Valley. Joint water and energy projects are being implemented. In January 2023, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan signed
a “”Road Map” for the implementation of the Kambarata HPS-1 construction project, and in June 2024, an interdepartmental agreement on preparations
for the implementation of the project.
A new phase of regional diplomacy began in 2017 with the election
of Shavkat Mirziyoyev as the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Relations
with neighbouring countries reached a qualitatively new level. Dialogue based on the principles of openness, respect, and equality laid the foundation
for long-term friendly coexistence.
Thanks to the political will of the leaders of the three states—Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan—historic agreements were reached in 2025
with the signing of the Treaty on the Junction Point of the State Borders
of Three States and the Khujand Declaration on Eternal Friendship.
These documents became a symbol of a new era of trust and creative partnership. The treaty legally established the borders of the three states
at a concrete point in the Ferghana Valley.
This breakthrough did not come unexpectedly, without preparatory work. In the preceding months, on March 13, 2025, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan signed an important agreement on the demarcation of their common border—the final stage of their long negotiations.
Kyrgyz President Sadyr Zhaparov noted that regional integration continues to develop actively, and the strengthening of cooperation
in all spheres will be the key to sustainable development and prosperity throughout Central Asia.
In turn, Tajikistan President Emomali Rahmon called the development
of relations between the three countries based on the principles of good neighborliness, equality, and mutual respect one of the priorities of Tajikistan's foreign policy.
The international community particularly highlights the indispensable role of Uzbekistan's President Shavkat Mirziyoyev, who initiated a new diplomatic line: "Borders should not divide, but unite our peoples."
This approach creates a model for peaceful transformation, where internal rather than external factors shape the architecture of trust, friendship, and good neighbourliness.
The formation of the area of stability and cooperation in Ferghana Valley was achieved without external involvement, solely through the strong political will of the leaders of the three states, combined with the desire of the peoples
of the region for peaceful coexistence, creating a solid foundation for lasting peace and prosperity.
Ferghana Valley – an “exemplary model” for building inter-state relations in other regions
The Ferghana Valley is one of Central Asia's unique oases – a place where the destinies of the peoples of Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan have intertwined. More than 17 million people live here, accounting for 20%
of the total population of Central Asia, which is around 83 million.
Today, the valley is gradually becoming a symbol of the new Central Asia – a region where borders are not barriers, but bridges of interaction.
The development of transport, trade, and humanitarian ties between Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan paves the way for the formation of a single space
for interaction in the name of common prosperity.
Joint infrastructure and economic projects, the restoration of roads
and railways, the development of border logistics hubs, and the modernization of checkpoints are creating conditions for the free movement of people, goods, and ideas.
Communications between the Ferghana Valley and the outside world are actively developing. Today, it is being integrated into international multimodal transport corridors and is gradually regaining its status as an interregional transit hub connecting East and West.
In this regard, the China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan railway project is of great importance. If implemented, it will have a multiplier effect on the economies
of all countries in the region.
The railway will provide access to the ports of the Persian Gulf
and the Pacific Ocean, open up new markets, thereby diversifying the economy and creating new jobs.
Visa regimes are being simplified and the throughput capacity at border crossing points is being improved, which will encourage more mutual travel
by citizens.
Uzbekistan maintains a visa-free regime with all Central Asian countries except Turkmenistan. In particular, there are currently 17 border crossing points between Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and 25 between Uzbekistan
and Kyrgyzstan. In 2016, there were only 13 between Uzbekistan
and Kyrgyzstan, and all of them operated with restrictions. For example, currently, up to 20,000 people pass through the Dustlik checkpoint
on the Uzbek-Kyrgyz border every day, which is 100 times more than in 2016.
At the same time, the number of vehicles passing through has increased tenfold, reaching 700 per day.
The Mingtepa and Khanabad border checkpoints were opened in 2023, and the Uchkurgan and Karasu checkpoints in 2024. These points had been closed since 2009-2010.
Today, citizens of Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan can travel to each other's countries for up to 30 days without registration. A visa-free regime
for up to 60 days has been established between Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan,
and since September 1, 2023, it has been possible to use ID cards
(instead of foreign passports) for mutual travel between the two countries.
The time required for goods and people to cross the border has been reduced to an unprecedented eight minutes. In turn, citizens of Tajikistan
and Uzbekistan can stay in each other's territory for up to 30 days
without a visa. This, in turn, contributes to the intensification of cooperation
and improved mutual understanding between the peoples of the Fergana Valley.
On the whole, a common space is forming in the Ferghana Valley, as it has throughout history. The restoration of the valley's interconnectedness contributes to the stability and sustainable development of the entire region.
The international community's keen interest in these processes confirms that Central Asia is becoming an important center for the formation of a culture of peace. The initiatives put forward by Uzbekistan have received support
from the UN, OSCE, EU, and other international partners, which strengthens
the legitimacy and sustainability of regional efforts.
The Ferghana Peace Forum has a special place in this process—it's not just a diplomatic meeting, but a platform for developing a new philosophy
of regional cooperation. This forum brings together political leaders, experts, and public figures, offering an open dialogue on strengthening peace, trust,
and sustainable development in Central Asia.
The event will enable the countries of the region to independently shape their own architecture of stability and sustainable development, based
on mutual respect and the desire for a better future for new generations.
CONCLUSION
The Ferghana Valley is gradually transforming into a space of peace
and harmony, where peoples find common ground and jointly strengthen
the region's stability.
The establishment of the atmosphere of friendship and
amicable relations in the Ferghana Valley shows that, even in today's turbulent global environment, ensuring stability in the region is an achievable goal.
This process requires patience, wisdom, and willingness to make reasonable compromises. Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan have demonstrated these qualities and their ability, despite complex challenges,
to unite for common goals such as strengthening security and sustainable development.
In turn, the Fergana Peace Forum is called to become a permanent platform aimed at strengthening dialogue and trust, ensuring sustainable development of the Ferghana Valley, unlocking economic potential,
and strengthening cultural and humanitarian ties. This meeting reflects the unity of the countries in the region, which are determined to build a common future together.
Authors: Diloram Mukhsinova and Bekhzod Alimjanov,
senior researchers at the Center for Foreign Policy Studies
(Uzbekistan)