Phone
Consular Issues
Phone
Uzbekistan news
We recommend
Founder of BMB HOLDING: Supporting entrepreneurs in the process of building New Uzbekistan has become one of the main goals of the reforms of our Head of state
📅 21.08.2024
In recent years, systematic work has been carried out to create a continuous chain of comprehensive support for the development of entrepreneurship in our country. As a result of the measures implemented and important decisions made over the last seven years, a new generation of entrepreneurs of New Uzbekistan has emerged.
In particular, BMB HOLDING is one of the major subjects of private entrepreneurship, playing an important role in the economic life of our country, and gaining strong positions not only in the domestic, but also in the international market.
On the eve of the 33rd anniversary of independence of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Dunyo information agency talked to Bekzod Mamatkulov, the founder of BMB HOLDING.
– Mr. Mamatkulov, in recent years BMB HOLDING has gained a great reputation not only in Uzbekistan, but also among the international business community. Today, the Holding effectively works in the areas of providing consulting services on investment projects, developing international business and trade relations, attracting foreign investments, export-import exchange, introducing innovative technologies, creating modern agro-industrial clusters. We would like to start our conversation with the organization of the Holding and the history of its development.
– After his election as President, Shavkat Mirziyoyev put on the agenda of our state’s policy such important issues as increasing economic potential, attracting investments and, most importantly, supporting entrepreneurs to bring the country to a new stage of development.
In this sense, the opportunities created for entrepreneurs have radically changed my life goals and made me want to test my potential in business.
We generated our first income through services. Developing business plans and providing consulting services was our first source of income. Later we bought land in Arnasay district of Jizzak region to implement our agricultural projects. We planted mung beans and peas as secondary crops here. The first attempts were successful. The agricultural products we grew gave better results than we expected. For the first time we were able to export our crops abroad. In particular, we started selling agricultural products to Pakistan, India and Afghanistan. Later, we had a plan to supply cotton and grain to the state on a contract basis, and we gradually expanded our financial capacity, making a profit from it.
In 2017, during the visit of the Head of state to Jizzakh region, our project to create a food cluster in Arnasay district was presented. At the meeting, the President emphasized that he would support us, like all businessmen, and expressed great confidence in us. Such attention and support of the President of the country gave us additional strength. After that, there was a desire to further expand our business activities, to test ourselves in new industries, to develop and implement joint projects with foreign partners.
In particular, in 2018, we were among the first to create the largest cotton cluster in the country. Thanks to the attention of the management and creation of favorable conditions for doing business, we created a cluster for growing medicinal plants, namely saffron. Later we organized a fruit and vegetable cluster. This big project, in turn, enabled us to set up a system of sorting, packing and deep processing of fruits and vegetables. Thus, having passed through various stages of business, our small project has now formed into BMB HOLDING. At present the Holding unites 30 enterprises. They employ more than six thousand people across the country.
– It is no secret that today the Holding realizes investment projects of international and national level. As an entrepreneur and a person who knows the business environment in foreign countries, how do you assess the investment environment in Uzbekistan? Are there aspects that do not satisfy you, are there factors that are obstacles for business?
– In the process of building New Uzbekistan, the creation of a favorable investment environment for entrepreneurs has become one of the main goals of the reforms of the Head of our state. The adoption by the President of Uzbekistan of a number of decrees and resolutions aimed at supporting entrepreneurs is yielding results today.
Improvement of tax legislation, creation of the possibility of free currency conversion, reforms in the sphere of private property and a number of other positive changes related to these spheres have played their important role, and entrepreneurs are now considered as the driving force of the country’s economy. In 2020-2022, despite the fact that the coronavirus pandemic worldwide had a large negative impact on the economies and the global investment environment, Uzbekistan’s economic growth rates remained stable and its investment attractiveness continued to grow.
The fact that the inflow of foreign investments into the country has increased significantly testifies to the confidence of international business in the economic reforms in our country. Active diversification of the economy is an important achievement that has opened new opportunities for investors in all sectors, starting with industry.
Now, if we talk about the factors that are obstacles for business, aspects that do not satisfy entrepreneurs, I will tell the truth openly: at the level of the government, reforms are being implemented very intensively, positive changes are taking place. But when you go to the lower level of the system, there are still cases of inattention and carelessness somewhere. I believe that such shortcomings will be eliminated.
– We know that BMB HOLDING is engaged in the production and export of a wide variety of agricultural products. In particular, the organization headed by you has achieved great success in saffron cultivation. Today saffron grown in Uzbekistan is becoming popular in many regions of the world. Tell me, when did you come up with the idea of establishing such a complex sphere as saffron cultivation in Uzbekistan and why did you choose this particular project?
– During President Shavkat Mirziyoyev’s visits to Kashkadarya region in 2017, the issue of cultivation of medicinal plants in mountainous and foothill regions, development of this sphere in our country and export of valuable medicinal plants to the world market was prioritized. The leader of our country also inquired why it is impossible to grow saffron in Uzbekistan despite all conditions, and gave a special instruction to develop this industry. During the President’s visit to Jizzakh region, we made a detailed presentation of our saffron cultivation project. Having familiarized himself with the project, the Head of state expressed his full support to it and instructed the responsible persons to implement the program as soon as possible.
However, it was not easy to realize this project at first. When implementing this business idea, first of all, we deeply studied the demand and supply in the domestic and foreign markets, opportunities and prospects for its implementation in the conditions of Uzbekistan, our own potential in this area, as well as a number of other factors. In 2020, we started to implement the project in pandemic conditions. At first, it took a lot of patience and hard work to find specialists, to bring saffron bulbs suitable for our climate from Europe and to get the desired harvest. In the first year we planted saffron bulbs on 55 hectares of land. The high demand for the harvest and the experience gained stimulated further development and expansion of the project. Today saffron is grown on 400 hectares of land. In the next three years, it is planned to increase the area of saffron plantations to 1,000 hectares and produce 20 tons of pure saffron products per year.
At the beginning of 2024, the product BMB Za’faron for the first time in our region received the USDA Organic certificate, an environmental certificate developed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, which allowed Uzbek saffron to enter the American markets. After several years of in-depth analytical research, Uzbek saffron grown in the Bakhmal district received the appropriate permission to export to Chinese markets according to the conclusion of the Uzbek-Chinese interdepartmental commission.
– Indeed, a lot of experience in saffron cultivation has been accumulated in recent years. At the same time, what countries’ experience do you think should be studied and implemented in order to grow a competitive product that meets the requirements of international standards and markets?
– In agriculture, each product is grown using a specific method. Such countries as Italy, Austria, South Korea, USA, and Saudi Arabia have enough experience in saffron cultivation. Of course, we study the experience of countries with climatic conditions close to ours and exchange experience with industry experts. I can say that we have mobilized all possibilities to get more crops and export them abroad. The increase in exports, in turn, contributes to increasing the inflow of foreign currency into Uzbekistan and ensuring economic stability.
To bring our national products to the world market and increase their competitiveness, the most important factors are, first of all, quality, then price and, of course, matching production capacity to demand. We have taken these aspects into account in our work and projects, especially in saffron cultivation.
– In Uzbekistan, on the initiative of the Head of our state, an open dialog with entrepreneurs is held annually. Tell me, what impact do these efforts have on the activities of the Holding headed by you?
– It would not be an exaggeration to say that the adoption of a number of resolutions and decrees on creation of favorable business environment and healthy competition in our country, comprehensive support for entrepreneurs, further liberalization of tax policy have served to eliminate the problems that have arisen for many years and hindered the free activity of entrepreneurs.
Thanks to the political will of the President of Uzbekistan, the organizational and legal foundations for the development of the industry have been strengthened, and the attention to entrepreneurs has changed dramatically. Most importantly, all this has already started to yield positive results.
In addition, an open dialog between the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan and entrepreneurs has been established. In my opinion, there is no other country in the world that has such a format.
I can confidently say that the open communication of the Head of state with the business community, which has now become a tradition and is held annually, serves as an important factor in the formation of a new competitive class of entrepreneurs in New Uzbekistan.
I visit many countries for work. In particular, my friends-partners in Italy, Germany, the United States, Austria and other countries highly appreciate the annual dialog of the President of Uzbekistan with entrepreneurs. It is no secret that people look at us with envy when they see the personal attention of the Head of state to the development of business in our country. In fact, it is a great achievement for both sides — the President meets with businessmen, listens to their systemic problems, finds solutions and solves them. Therefore, today all businessmen are looking forward to meeting with the President. This meeting has also become an important forum for businessmen to assess their activities for the year and determine plans for the future. The speeches of our country’s leader at the meeting and important initiatives aimed at further development of the industry, removal of existing obstacles, provision of benefits to entrepreneurs serve as a program for further expansion of businessmen’s activities.
I would like to give an example based on my experience. Before dialoguing with the President, I note in my notebook the issues we face in our work. Listening to the President, I always get comprehensive answers to all my questions based on deep analysis.
– In August 2022, by the decree of the President of Uzbekistan, you were awarded the “Faol Tadbirkor” sign, and in 2023 — the “Dustlik” order. Recall those moments when your entrepreneurial activity was highly appreciated by the leadership of our country.
– Before answering, I have to say one thing. Before coming to business, I worked in state and public organizations for more than 15 years. I never received even a certificate of honor, let alone a state award. Today, the leader’s focus is on people who have sincerely worked for the development of our dear country — Uzbekistan. In recognition of our work, in 2022, I was awarded the “Faol Tadbirkor” sign. In 2023, I had the honor to receive the “Dustlik” Order from the esteemed President. These are not just awards given to me, they are recognition of the work of thousands of dedicated people working in the Holding’s system. Such a high appreciation gives our team more confidence and motivation, and gives us great strength to realize the goals we have set for ourselves.
– The direction of economic diplomacy is becoming increasingly important in attracting foreign investment to Uzbekistan, finding new partners and exporting national products abroad. In this regard, does the Holding, which you head, use the opportunities of diplomatic missions of our country in foreign countries? How satisfied are you with the work of our country's embassies in this direction?
– Frankly speaking, it used to be impossible to meet with diplomats. If you went abroad and wanted to meet with the Ambassador of our country, he would not accept businessmen. This is an open statement. The Ambassador only dealt with politics. Thanks very much to our President, he brought the diplomats’ attention to the economy as well. This, of course, has opened wonderful conditions and opportunities for entrepreneurs. Openness in this sphere, in turn, has become an important step for entrepreneurs in finding foreign partners and attracting investment.
Today, the diplomatic missions of Uzbekistan in foreign countries play a very important role in the activities of the Holding Company, and we feel their support at every stage of realization of our numerous projects. The introduction of the position of Advisor to the Ambassadors of Uzbekistan on economic issues has been very useful for us entrepreneurs. It should be noted that BMB HOLDING has established close relations of economic cooperation with embassies of foreign countries in Uzbekistan, in particular with diplomatic missions of Russia, China, USA and a number of European countries such as Poland, Austria and Latvia.
In a word, the role of diplomatic missions of Uzbekistan and foreign countries in our country is very important in effective realization of the company’s projects.
– Today BMB HOLDING operates in the field of cultivation and production of agricultural products. Our readers are also interested in the future plans of the Holding.
– Our plans for the near future are huge. In particular, the work on establishment of deep processing of agricultural and fruit and vegetable products, and the launching of textile factories in Syrdarya region is in full swing. We also want to implement projects in the field of medicine. Our first project in this direction will be the creation of a health center in Navoi region in 2025. Also, a chain of restaurants and hotels “Zafaron” will be launched in Tashkent city and Tashkent region.
Along with this, we plan to implement the project “Energy-efficient technologies and equipment for production, mining and processing of natural decorative stone” worth 50 million US dollars together with the organization Toksel Makina from Turkey.
– Our last question may be off-topic, but many people are also very interested in this area. We would like to ask about your projects in sports, especially in soccer. What are your goals in soccer and futsal? Also, please, provide information about BMB HOLDING brand ambassadors in the sphere of chess.
– This is an interesting question. BMB HOLDING considers the development of sports in our country, especially soccer and futsal, as one of the main directions of its activity. The Holding was one of the sponsors of Sogdiana soccer club in 2021 and Lokomotiv soccer club in 2022. Since 2023, our Holding has been one of the sponsors of the professional soccer league of Uzbekistan.
At the same time, the BMB PROFESSIONAL FUTSAL CLUB team started its activity in the system of the Holding. A number of famous local and Brazilian futsal players were invited to the team. For the last two years the team won the Cup of Uzbekistan and the Super Cup of Uzbekistan. Today the basis of our team is made up of futsal players playing in the national team of Uzbekistan on mini-football.
On June 30, on the occasion of Youth Day in Uzbekistan together with the Agency for Youth Affairs within the framework of the project of the brand ORRO ROSSO in Milan (this brand is currently the official partner of the Italian soccer club Milan and Monza) we organized a trip to our country of four famous former players of the soccer club Milan, world and European champions Dida, Sergino, Panucci and Zaccardo. I believe that the visit of famous soccer players to Uzbekistan has served to increase the interest and activity of our youth in sports.
As you know, the Futsal World Cup will be held in our country from September 14 to October 6 this year. BMB HOLDING as the main partner organization is preparing for this futsal holiday.
Besides, BMB HOLDING actively supports talented young chess players. Recognizing them as the face and ambassadors of the Holding, we call them brand ambassadors. In particular, FIDE Master of Sports Humoyun Bekmurodov won a silver medal at the X Chessable Sunway Sitges International Chess Festival 2023 held in Barcelona (Spain), and also won the Dubai Police Global Chess Challenge tournament held in Dubai (United Arab Emirates) on May 3-13 this year.
Another of our young chess players is Umida Omonova, a student of the International Chess School, world champion in blitz and rapid, FIDE Master of Sport, member of the Uzbekistan national team, holder of the state award named after Zulfiya, brand ambassador of BMB HOLDING. She also won the 18th round of the Uzbekistan Championship held in April this year.
Another thing is that BMB HOLDING mobilizes all its capabilities and potential in the direction of further prosperity of New Uzbekistan, which is being built under the leadership of the Head of state, improvement of welfare of our people and development of the Motherland.
- Thank you for taking the time to talk to us.
- Thank you.
Dunyo IA
Uzbekistan and Finland: Similar Approaches to Building Good-Neighborly Regional Relations
📅 06.11.2025
In an era characterized by growing disunity among global powers, the strategies employed by so-called “middle” states in forging stable regional relations present promising solutions for achieving international peace and cooperation. Uzbekistan, a Central Asian nation situated at the heart of the historic Silk Road, and Finland, a Nordic state with a unique experience as a neutral border state during the Cold War, exemplify how a consistent commitment to dialogue can contribute to regional stability amidst the complexities of global relations.
Geographically separated, these countries have developed strikingly similar approaches to ensuring sustainable development, peace, and stability in their regions. They address key regional security challenges by strengthening multifaceted and mutually beneficial good-neighborly relations with their neighbors. Additionally, they engage in multilateral, long-term partnerships with interested countries and organizations.
While Uzbekistan and Finland have been shaped by different historical contexts, these experiences have contributed to the development of a shared diplomatic philosophy centered around stability, cooperation, sovereign equality, mutual respect, and multilateral interaction.
Central Asia, a region steeped in ancient history, has long been a cultural and historical hub. Centuries ago, it was a unified space where politics, economics, and culture intertwined seamlessly. As one of the cradles of human civilization, Central Asia boasts a rich tapestry of history and a vibrant cultural heritage that has shaped universal values. These values emphasize cooperation over confrontation, tolerance over imposition, and the belief that the well-being of neighbors is intrinsically linked to one’s own.
Since gaining independence in 1991, Uzbekistan has consistently championed a policy of regional interaction. This policy, which gained prominence under President Shavkat Mirziyoyev in 2016, became a cornerstone of Uzbekistan’s foreign policy. Tashkent’s “diplomatic offensive” to enhance intra-regional cooperation became one of the most significant policy changes that transformed relations in modern Central Asia.
Tashkent’s unprecedented focus on dialogue and building trust with neighboring states has transformed Uzbekistan into the primary organizer of cooperation in the region. It has advocated for the development of multilateral interaction mechanisms, spanning various domains such as water resource management, transport corridor expansion, industrial cooperation, border demarcation, and regional security.
The positive impact of these policy changes has reverberated throughout the entire region. After 2016, economic cooperation witnessed a remarkable surge, leading to a nearly doubling of the total GDP of Central Asian states from $273 billion to $520 billion. Trust and strengthened ties between countries have facilitated a 4.5-fold increase in intra-regional trade, soaring from $2.4 billion to $11 billion. Moreover, the number of tourists visiting the region has doubled, further boosting its appeal.
The collective openness and enhanced stability have become attractive factors for third countries, resulting in a significant increase in the region’s foreign trade. This growth has seen a remarkable rise of over 200 percent, from $112 billion to $253 billion.
Finland’s diplomatic traditions were shaped by its unique position at the crossroads of Eastern and Western “spheres of influence.” Its vulnerable geographical location drove its pursuit of interaction and stability.
Finland consistently advocates for strengthening friendly relations with all countries, particularly its neighbors, and fostering ties within Nordic cooperation structures like the Nordic Council, the Council of Ministers of the Nordic Countries, and the Nordic Investment Bank.
This approach is reflected in Finland’s active involvement in the OSCE with aims to enhance dialogue and trust.
Finland’s 2025 OSCE chairmanship, coinciding with the 50th anniversary of the Helsinki Final Act, holds symbolic significance. It exemplifies Finland’s commitment to building bridges, fostering dialogue, and cultivating trust, aligning with its dialogue-based foreign policy. Finnish diplomacy consistently emphasizes the importance of strengthening common positions and approaches among states, reflecting Finland’s consensus-oriented diplomatic style, which Uzbekistan shares as well.
It’s worth noting that both countries adhere to the same fundamental principles of international law. Respect for national sovereignty, non-interference in internal affairs, and the inviolability of borders serve as practical guidelines shaping Uzbekistan and Finland’s foreign policy, regional behavior, and international positioning.
Tashkent’s approaches to regional interaction resonate with Helsinki’s priorities for cooperation with the Nordic and Baltic countries. Uzbekistan’s efforts in resolving border disputes and collaborating on water resources in the region mirror Finland’s approach to peacebuilding and fostering cooperation.
Furthermore, both countries have established themselves as advocates of results-oriented cooperation. They are pragmatic architects of projects that create mutual benefits and strengthen regional stability and interregional connectivity.
Under the leadership of President Sh. Mirziyoyev, Uzbekistan is actively promoting the development of transport infrastructure within Central Asia and with neighboring regions, including the West, East, and South. For instance, the development of the “Middle Corridor” (Trans-Caspian International Transport Route) has led to a remarkable six-fold increase in cargo shipments along it over four years, from 2020 to 2024, reaching a substantial volume of 4.5 million tons. Tashkent is also actively involved in the construction of the China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan railway and is promoting connectivity between Central and South Asia.
Economic cooperation and environmental protection are additional pillars of Uzbekistan’s regional strategy. These aspects play a crucial role in Uzbekistan’s environmental programs, particularly in mitigating the consequences of the Aral Sea disaster.
Finland, following a similar pattern of project-oriented cooperation, has been an active participant in initiatives of the Nordic Council and the Barents Euro-Arctic Council. These initiatives encompass cross-border cooperation in environmental protection, innovation, and people-to-people contacts. Finland also promotes initiatives of the Trans-European Transport Network and Arctic connectivity.
Known for its leadership in environmental protection, Finland actively participates in cross-border economic projects with partners from the Nordic and Baltic countries.
Alongside their close cooperation with countries in their respective regions, Uzbekistan and Finland pursue a policy of strategic multilateralism. Both countries actively participate in various regional and global institutions, reflecting their shared views that modern challenges require collective responses. They believe that “middle powers” can exert effective influence through institutional engagement.
Since 2016, Uzbekistan has significantly increased its involvement in regional organizations, primarily the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), the Organization of Turkic States (OTS), and various United Nations bodies.
Additionally, the “Central Asia +” (C5+1) platform, now comprising over 10 partner countries and organizations, actively promotes interregional cooperation. Notably, the inaugural “Central Asia – European Union” summit held in April 2025 resulted in an agreement on “deep and comprehensive cooperation” between the two regions.
Finland’s international engagement, while having a longer history, also follows a similar pattern of active institutional participation. As a member of the European Union since 1995 and multiple international organizations, Finland maintains its traditional interactions with regional structures in Northern and Baltic Europe.
As the international landscape becomes increasingly intricate, Uzbekistan and Finland encounter similar challenges that test their historically established unique diplomatic approaches.
Uzbekistan faces the primary challenge of sustaining the momentum for deepening regional partnership and intensifying cooperation with external actors amidst escalating geopolitical tensions, environmental threats, and economic shocks.
From Uzbekistan’s perspective, responding to the changing geopolitical landscape and the economic transformation needs of Central Asia requires strengthened cooperation, both among Central Asian countries and between regions.
Finland’s challenge lies in finding a balance between its commitments within the EU and NATO and its traditional role as a mediator in building consensus and dialogue, particularly in organizations like the OSCE, where it continues to promote “strengthening dialogue and trust.”
Overall, Uzbekistan and Finland exemplify successful regional cooperation based on a consistent commitment to dialogue and interaction. Despite their distinct geographical and historical contexts, both countries have adopted similar foreign policy approaches focused on conflict prevention, institutional engagement, and pragmatic regionalism.
In an interconnected world characterized by great power rivalry, the diplomatic approaches of Uzbekistan and Finland serve as a reminder that sustainable security and prosperity are achieved through dialogue, cooperation, and practical collaboration, rather than diktat, isolation, or empty rhetoric.
And unsurprisingly, these foreign policy approaches positively impact the lives of their citizens. It’s not a coincidence that Finland consistently ranks as the “happiest country in the world” for the eighth consecutive year in the World Happiness Report. Similarly, Uzbekistan leads in the level of happiness among Central Asian countries in the same ranking.
Sharif Akhmedov,
Chief Researcher at the Institute for Strategic and Regional Studies under the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan
President of the Republic of Uzbekistan departs to the United Arab Emirates
📅 14.01.2025
At the invitation of the of President of the United Arab Emirates Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, on January 13 President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev departed to this country with an official visit.
In accordance with the program negotiations at the highest level, as well as bilateral meetings with the heads of leading organizations, companies and banks of the UAE will be conducted in the Emirates’ capital of Abu Dhabi.
President of Uzbekistan will also participate in the activities of the international summit “Abu Dhabi Sustainability Week”.
In the framework of the visit, the Head of our state will visit Dubai, where he will hold a meeting with Vice President, Prime Minister of the United Arab Emirates, Emir of Dubai Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum.
Address by President Shavkat Mirziyoyev at the ceremony dedicated to the 33rd anniversary of independence of the Republic of Uzbekistan
📅 01.09.2024The text of the article is in Uzbek!
Strengthening Peace in Gaza and Expanding Economic Ties with the U.S.
📅 27.02.2026
On the Inaugural Meeting of the Peace Council in Washington
At the invitation of the President of the United States Donald Trump, President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev paid a working visit to Washington on February 17–19 to participate in the inaugural meeting of the Peace Council. The visit combined a substantive political agenda with an extensive economic program and resulted in a number of agreements aimed at further strengthening Uzbek-American strategic partnership and expanding bilateral cooperation across key sectors.
Expanding Participation in Addressing Global Challenges
The Peace Council is an intergovernmental initiative put forward by President Trump within the framework of the Gaza peace plan endorsed by the UN Security Council in November 2025. The establishment of this platform is intended not only to coordinate humanitarian assistance but also to create institutional mechanisms for long-term stabilization, reconstruction, and socio-economic recovery of the Gaza Strip, while reducing the risks of renewed escalation in the Middle East.
The Charter of the Peace Council was signed on January 22, 2026, on the sidelines of the World Economic Forum in Davos. Signatories included leaders and representatives of Azerbaijan, Argentina, Armenia, Bahrain, Bulgaria, Hungary, Indonesia, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Qatar, Morocco, Mongolia, the United Arab Emirates, Pakistan, Paraguay, Saudi Arabia, Türkiye, Uzbekistan, and Kosovo. Subsequently, Belarus, Albania, Cambodia, Egypt, El Salvador, Jordan, and Kuwait officially joined the group of founding states, expanding the Council’s geographic and political representation.
By joining the founding members at the invitation of the U.S. President, Uzbekistan reaffirmed its commitment to peaceful diplomacy, respect for international law, and shared responsibility for maintaining global stability. Uzbekistan recognized Palestine in 1994 and consistently supports the right of the Palestinian people to establish an independent state in accordance with international legal norms and UN resolutions.
Uzbekistan’s policy toward Gaza combines principled political positioning with practical humanitarian engagement. In 2023, Uzbekistan allocated $1.5 mln through UNRWA. In December 2023, 100 wounded Palestinian women and children were evacuated and provided with medical treatment and rehabilitation services. In 2025, Uzbekistan developed a comprehensive state support mechanism for Palestinian citizens received in the country, including asylum procedures, access to healthcare, education for children, and employment assistance. A dedicated fund under the National Agency for Social Protection was established to finance these measures through budgetary and charitable resources.
The inaugural meeting of the Peace Council held on February 19 in Washington brought together leaders and representatives of more than 40 countries. Discussions focused on humanitarian relief, infrastructure restoration, and ensuring the sustainability of the post-conflict recovery process. At the opening of the session, President Trump announced that nine countries – Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, the UAE, Morocco, Bahrain, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Uzbekistan, and Kuwait – had jointly pledged $7 bn in assistance to Gaza, while the United States committed an additional $10 bn to support the Council’s activities.
In his address, President Mirziyoyev expressed full support for the peace initiative and confirmed Uzbekistan’s readiness to participate practically in its implementation. Particular emphasis was placed on the principle that any external governance framework for Gaza must rely on internal public support in order to ensure legitimacy, stability, and long-term effectiveness.
Highlighting the importance of coordinated international efforts, the President noted that joint actions would help secure the sustainability of the post-conflict process and accelerate socio-economic recovery. Uzbekistan also declared its readiness to contribute to the construction of residential housing, schools, kindergartens, and healthcare facilities in Gaza, thereby supporting both humanitarian and development objectives.
The Palestinian and Gaza issue has remained on the international agenda for decades without a comprehensive solution. In this context, the creation of the Peace Council represents one of the most structured multilateral attempts in recent years to address the crisis, while Uzbekistan’s participation among the founding states reflects the growing recognition of its constructive diplomatic role.
Expanding Trade and Economic Cooperation
Alongside political dialogue, the economic dimension of the visit formed a central pillar of bilateral engagement. In recent years, Uzbekistan and the United States have steadily restored institutional mechanisms of strategic partnership and expanded practical cooperation.
Cooperation with the U.S. Export-Import Bank resumed in 2017 after a 13-year hiatus. Agreements were concluded between Amazon and Uztrade, while science, technology, and economic modernization were identified among priority cooperation areas. In 2018, a $100 mln memorandum on trade financing was signed between Eximbank and Uzbekistan’s National Bank for Foreign Economic Activity. Cooperation with Openbucks supported the development of e-commerce and digital payment infrastructure.
A major milestone was reached in September 2025 during the 80th UN General Assembly in New York, where negotiations between the two presidents resulted in the formation of a portfolio of contracts and prospective projects exceeding $100 bn. The agreements covered aviation, mining and chemicals, energy, finance, and innovation. Specific arrangements included cooperation with Denali Exploration Group on rare earth elements, Re Element Technologies in rare earth metals, Flowserve on modernization of pumping stations, Valmont Industries on water-saving technologies, and Palo Alto Networks in artificial intelligence.
During the Washington visit, President Mirziyoyev held meetings with U.S. Secretary of Commerce Howard Lutnick, Eximbank President John Jovanovic, DFC CEO Ben Black, and U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer. Discussions focused on expanding financing for major industrial and infrastructure projects, supporting high-tech equipment exports, launching a bilateral Investment Platform, advancing Uzbekistan’s WTO accession, and strengthening regional trade cooperation under TIFA. The agreement establishing the Investment Platform was formally signed during the visit.
Additional bilateral documents were concluded covering construction of fuel station networks, sprinkler irrigation technologies, extraction and supply of critical minerals, development of poultry clusters, agro-industrial cooperation, financial market development, and investment climate reforms. The economic agenda was identified as one of the key pillars of Uzbek-American strategic partnership, with priority cooperation areas including critical raw materials, petrochemicals, energy, agriculture, and industrial modernization.
Trade and Investment Dynamics
The intensification of bilateral cooperation has already produced tangible economic results. Between 2017 and 2025, trade turnover increased 4.7-fold from $215 mln to $1 bn. Exports grew 9.1-fold to $291.7 mln, while imports rose 3.9-fold to $712.3 mln.
Exports to the United States are dominated by services (81%), including programming, financial, information, and transport services. Petroleum products account for 8.6%, machinery and equipment 3.7%, food products 3.5%, and industrial goods 3.3%.
Imports from the United States are led by machinery and equipment (59%), including aircraft, vehicles, computing equipment, engines, pumps, and industrial installations. Services account for 20.5%, chemicals 9.7%, industrial goods 3.8%, food products 3.2%, and manufactured goods 2.2%.
Investment cooperation has expanded dynamically. U.S. FDI and loans increased nearly 64-fold from $8.6 mln in 2017 to $383.2 mln in 2025, with cumulative inflows exceeding $2.9 bn. As of February 2026, 346 enterprises with U.S. capital operate in Uzbekistan, including 146 joint ventures and 200 wholly foreign-owned firms. Investments are concentrated in manufacturing, mining, construction, services, and agriculture.
Prospects for Deeper Economic Partnership
Recent dynamics indicate a transition from trade expansion toward long-term technological and industrial partnership. While services dominate exports, significant untapped potential remains in agro-processing, textiles, non-ferrous metallurgy, and higher value-added manufacturing.
Given annual U.S. imports of $118 bn in textiles and apparel, $539 bn in food products, and $213 bn in pharmaceuticals, even limited market penetration could significantly expand Uzbek exports and rebalance their structure.
Technology cooperation represents a separate strategic track. The United States accounts for 45% of Uzbekistan’s IT exports, with 448 of 800 exporters supplying digital services to the U.S. market. The next phase may involve joint industrial production in electronics and microelectronics with companies such as NVIDIA, Intel, and Qualcomm, enabling integration into global value chains.
Energy cooperation could support infrastructure modernization and renewable energy deployment, while pharmaceutical localization and joint R&D with companies such as Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck offer additional avenues for technology transfer and investment.
Privatization and PPP initiatives create further opportunities. By 2030, the private sector share in Uzbekistan’s economy is projected to reach 85%, with stakes in 2,000 enterprises planned for sale and $30 bn in PPP projects to be launched. Cooperation with U.S. capital markets, including the NYSE and Nasdaq, may further support the development of Uzbekistan’s financial infrastructure.
Conclusion
President Mirziyoyev’s visit to Washington and participation in the inaugural Peace Council meeting carry both diplomatic and economic significance.
Uzbekistan’s engagement in the Council strengthens its international standing and expands its contribution to addressing global challenges. At the same time, the agreements reached and the expanding portfolio of joint projects elevate Uzbek-American relations to a new stage characterized by deeper institutional cooperation, industrial integration, and long-term strategic trust.
Viktor Abaturov,
Center for Economic Research and Reforms
Uzbekistan: New reforms to improve the penal enforcement legislation and their practical results
📅 24.06.2024
In recent years, taking into account international standards and advanced foreign experience, ensuring the protection of the rights of convicts, respect for their honor and dignity, education of morality and conscientious work for further social adaptation in society upon release, a fundamental improvement of the penal enforcement legislation in the Republic of Uzbekistan has been carried out with the introduction of effective legal mechanisms.
Currently, there are a number of international conventions and provisions aimed at protecting the rights of convicts, which are regulated by the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. (1966), "Convention against torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment" (1984), "Declaration on the protection of all persons from torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment" (1975), "Standard minimum rules for the treatment of convicts (Nelson Mandela rules)" (2015), "UN rules for the protection of minor children deprived of liberty " (1990), "Basic principles of the treatment of convicts" (1990).
Based on the norms of these international documents developed and adopted by the international community on standards for the treatment of convicts, systematic work is underway in the country to humanize execution and reduce negative consequences during their execution, as well as strengthen the legislative, organizational and legal framework for the protection of human rights, the implementation of international human rights standards into national legislation and other important norms human life activities that have been accepted for implementation by the Republic of Uzbekistan as a subject of the above-mentioned and other international treaties.
It is important to note that "Standard minimum rules for the treatment of prisoners" of UN 1955 are generally recognized minimum standards for the detention of prisoners and have great importance and influence on the improvement of legislation, criminal law policy and the practice of penitentiary institutions around the world.
The revised text of these standard minimum rules of December 17, 2015 at the 70th session of the UN General Assembly № A/RES/70/175 was unanimously adopted in the form of a resolution. These Rules became known as the "Nelson Mandela rules" as a sign of respect for his memory after the death of the famous statesman, the President of South Africa, who outlined these rules based on the experience of spending a long part of his life in prison.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the fact that, following the visit to Uzbekistan of the Special Rapporteur of the UN Human Rights Council, the topic "Promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the fight against terrorism" recommendations were made to bring the legislation of the Republic of Uzbekistan into line with the minimum standard rules for the treatment of prisoners (Nelson Mandela rules), in order to improve the conditions of detention of convicts in penal institutions, to ensure the rights to freedom of religion, which formed the basis of the “Road maps”, developed in accordance with the National Action Plan of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
In order to ensure the fulfillment of these tasks, the conditions of detention of convicts in penal institutions of the Republic of Uzbekistan are considered on the basis of the requirements of the standard minimum rules for the treatment of prisoners (Mandela rules), which are gradually being implemented in accordance with these rules.
On the basis of international standards of the rights and duties of convicts, taking into account the best practices of foreign countries, the system of execution of punishments is being radically improved, the problems that have accumulated over the years are being solved.
In the new version of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan the right to life is an inalienable right of every person and is protected by law. The most serious crime is an attempt on a person's life. The death penalty is prohibited in the Republic of Uzbekistan. Essence is that no one can be intentionally deprived of life. This norm is in line with the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms, as well as the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. The human right to life is recognized as a natural and inviolable right arising from the moment of his birth, and belongs to a person regardless of the existence of statehood and laws.
In recent years, as part of the work to bring national legislation into line with international standards, for the first time the right to be elected was granted to convicts, except for persons who committed serious and especially serious crimes (Part 6 of Article 128 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan). The number of convicts held in institutions of general, strict, special, prison and educational regime has doubled, for correspondence, receiving visits, parcels, transfers and parcels, conducting telephone conversations.
In addition, those sentenced to imprisonment are guaranteed psychological assistance and non-application of disciplinary measures for violations committed at the time of mental disorder, and the right to a pension is established for those serving sentences in penal colonies.
Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan June 30, 2020 introduced a new norm into the Penal Enforcement Code defining the procedure for the application of incentive measures for persons serving sentences, expanded measures aimed at ensuring the personal safety of convicts while serving their sentences.
At the request of the convicts, long-term visits can be replaced by short-term visits or remote video calls or telephone conversations, and short-term visits are replaced by remote video calls or telephone conversations. Persons serving sentences from low-income families are employed in high-paying jobs.
In the process of ongoing reforms, special attention was paid to creating decent conditions for convicts, for this purpose, the pre-trial detention facility -64/1, which had a negative character and was popularly nicknamed "Tashturma", was closed in Tashkent. Instead, a new pre-trial detention facility №1 has been built and is functioning in Zangiata district of the Tashkent region, fully meeting international standards. Similarly, the institution "Jaslyk" in Karakalpakstan was abolished, and the convicts held in it were transferred to other colonies of the republic.
In recent years, there has been a tendency in our country to use alternative, non-custodial measures, which has reduced the number of convicts sent to penal institutions. This situation has made it possible over the past four years to reduce three penal colonies of the general regime, one each in Navoi, Kashkadarya and Tashkent regions.
In the Republic, the legislative, executive, and departmental authorities constantly monitor compliance with the rule of law and ensure the rights and legitimate interests of persons serving sentences in places of deprivation of liberty.
Thus, with the introduction of the post of Commissioner of the Oliy Majlis of the Republic of Uzbekistan for Human Rights (Ombudsman) He was granted the right to freely visit penal institutions. The Ombudsman and the Prosecutor have separate mailboxes designed for applications and complaints from these persons. The Prosecutor's Office and the Ombudsman regularly examine the observance of laws in penal institutions. The management of the Department for the Execution of Punishment constantly carries out field visits to places of deprivation of liberty in order to study the complaints and statements of convicts and make an appropriate decision and its immediate execution.
It should be added that, according to the recommendations of the UN charter bodies and treaty committees, the national preventive mechanism is being improved on the basis of the "Ombudsman Plus" model. The Ombudsman, and the Children's Ombudsman, the National Center for Human Rights and the Business Ombudsman have also been given the authority to monitor penal institutions.
As a result of the ongoing reforms, completely new priorities of the State penal enforcement policy have been developed and put into practice, providing for the following main aspects.
In particular, the Penal Enforcement Code has been supplemented with a new Article 102 "Procedure for the application of incentive measures", which abolished restrictions on visits of juvenile convicts with their parents or persons replacing them; convicted pregnant women with children are granted additional rights to long visits with minor children lasting up to five days - four times a year as well as long - term visits with the possibility of living outside the territory of the institution, the application of incentive measures to convicts - at least twice a year; if there is a threat to the safety of a person sentenced to imprisonment, it is established that he can apply, verbally or in writing, to any employee of the institution for the execution of punishment in order to ensure the declared safety, while the requirement is defined – upon receipt of such a statement about the need for immediate action, measures should be taken immediately to ensure his safety. An important requirement is also to prevent the unjustified use of rudeness, physical force and special means by employees and military personnel during the search of convicts; timely and appropriate conduct of long and short-term visits, telephone conversations, remote video communication, short-term remote video communication or telephone conversation.
It should be noted that such measures of encouragement for convicts are also enshrined in the penal codes of Spain, Turkiye, Japan and some other countries.
In accordance with the norms of the Penal Enforcement Code of the Republic of Uzbekistan, penitentiary institutions provide measures to protect the health of convicts, ensure their education, free use of libraries and other authorized sources of information (radio, television, movies and video films, etc.).
The "Import model" of prison management in Norway with a developed penal enforcement system is of interest. To implement this model, work is underway to establish a system of providing services (education, library use, health care) in places of detention.
It is also necessary to mention the Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan dated December 7, 2021, which, in order to humanize minors in the Penal Enforcement Code, provides for a norm defining the placement of persons in educational colonies not from the age of 13, but from 14. This has become one of the important steps towards reliable protection of the rights and legitimate interests of minors in the process of criminal and judicial proceedings in our country.
In order to further deepen the large-scale reforms being implemented in the system of Ministry of Internal Affairs, decree of March 26 and Resolution of April 2, 2021, the Main Directorate for the Execution of Punishment was transformed into the Department for the Execution of Punishment under the Ministry of Internal Affairs, it defines the legal basis for the department's activities to ensure the order of serving punishment by digitalizing the penal enforcement system, which will eliminate errors related to the human factor.
In addition, the law of the Republic of Uzbekistan dated February 15, 2023 "On State pension provision for citizens" provides that any work performed by persons sentenced to imprisonment while serving their sentence in penal institutions may be envisaged that the convicted person will be included in the work record in case of tax payment. This procedure is now defined in Article 96 of the Penal Enforcement Code of the Republic of Uzbekistan in a new edition, which has been renamed as "Payment of social tax and pension provision for convicts." Its first part defines "The expenses of institutions for the execution of punishment for the payment of labor sentenced to imprisonment that are subject to social tax", along with this, convicts have the right to transfer funds and use other services provided to convicts.
An important legislative decision is the prohibition of the use of a punishment measure with the use of a "straitjacket". This provision is based on Article 26 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan, which states: "No one may be subjected to torture, violence, or other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment" directly acts to prevent the use of torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment in penal institutions.
As a result of the ongoing reforms in the system of state penal enforcement policy, it is stipulated that common living quarters for persons with disabilities of groups I and II sentenced to imprisonment should be equipped with special means and devices; it is allowed to watch films, television and radio broadcasts, except for the time allotted for night rest; criteria for treatment are defined convicts.
In addition, it is important to eliminate corruption factors in assessing the behavior of convicts by including the length of service in the institution in the total length of service for their further retirement and, most importantly, by establishing strict criteria that determine the way to correct convicts.
The above allows us to conclude that the reforms carried out in this area are yielding positive results. In particular, recently the offenses of convicts in places of deprivation of liberty and after their release have been reduced; to a greater extent, the conditions of serving a sentence in the form of imprisonment comply with international standards, the incentive mechanisms applied to convicts serving sentences and those who have embarked on the path of correction are being improved, they ensure the protection of the rights, freedoms and legitimate interests of convicts, allowing them not to violate their interests; Public groups and citizens' self-government bodies are actively involved in the educational process of correcting convicts; offenses by law enforcement agencies have significantly decreased.
Mirzayusup Rustambayev,
Head of the University of Public Safety of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Doctor of Law, Professor
The text of the article is in Uzbek!
📅 25.07.2024The text of the article is in Uzbek!
UN Secretary-General to visit Uzbekistan
📅 30.06.2024
At the invitation of President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres will pay an official visit to our country from June 30 to July 1.
The program of the high-ranking guest's stay in Tashkent envisages talks at the highest level.
The agenda includes issues of further expansion and strengthening of Uzbekistan's multifaceted cooperation with the UN and its institutions, as well as topical aspects of global policy and regional interaction. Special attention will be paid to supporting measures to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals in our country.
During the visit, the UN Secretary-General will also visit a number of industrial and social sites, hold bilateral meetings and events.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
Congratulations to the people of Uzbekistan on Kurban Hayit holiday
📅 15.06.2024
Dear compatriots!
Sincerely, from the bottom of my heart, I congratulate you, all our people on the holiday of Kurban Hayit, which has come in our country, which is being transformed and illuminated with the light of peace, kindness and harmony every day.
In these blessed moments we all deeply feel the spirit and joy of the great holiday and give immense gratitude to the Almighty for the fact that we meet such bright days together with our people.
Today, Kurban Hayit, firmly established in people's lives as a symbol of mercy, generosity and humanism, is gaining more and more significance, consonant with the content of large-scale reforms in the New Uzbekistan, in which respect for human honor and dignity comes to the fore in all spheres.
It should be especially noted that our sacred religion and this bright holiday, which embodies its humanistic essence, serves as a source of strength and inspiration for us in all good deeds aimed at strengthening the atmosphere of peace and tranquility, friendship and cohesion in mahallas and families, caring for the older generation, youth and women, low-income families, and making sure that no one is left behind.
Dear friends!
In these bright days, when our hearts are filled with joy, we talk about the great work carried out in recent years to revive the original spiritual values, to improve the sacred places, to create favorable conditions for the Muslims of the country to freely perform religious rites, including hajj and umrah.
In a short period of time, international scientific centers of Imam Bukhari, Imam Termezi and Imam Maturidi have been organized. The memorial complexes of Abu Iso Termezi, Abu Muin Nasafi, Sulton Uwais Karani and Suzuk Ota have been radically transformed. Work on the construction and equipping of the Imam Bukhari memorial complex and the Centre for Islamic Civilization is continuing apace. Majestic mosques are being built in many towns and villages.
Over the past seven years, more than 60 thousand Muslims of the country have made the Hajj. These days 15 thousand more of our compatriots are making pilgrimage to two sacred cities - Mecca and Medina, having realized their most cherished dream.
In such blessed moments, when good thoughts come true, we wish them with all our heart to fully perform the rites of Hajj and safely return to their homeland.
On the eve of the celebration of Hayyit, during our telephone conversation with the Chairman of the Muslims' Board, the Honorable Mufti Sheikh Nuriddin Kholiknazar, who is staying in the holy Mecca, he emphasized the created conditions necessary for our compatriots to perform the rites of Hajj. We hope that, having returned home, our pilgrims will become an example in further strengthening the atmosphere of kindness and mutual assistance in the society, in the struggle of enlightenment against ignorance, strengthening the education of youth and establishing harmony in families.
Dear compatriots!
Today we sincerely congratulate our compatriots abroad on this holiday, wish them health, happiness and success.
We convey warm congratulations to believing Muslims in the states of near and far abroad and sincere wishes of peace and progress to their peoples and countries.
May the ongoing wars and conflicts in different regions cease! May peace reign on the Earth forever!
Dear friends!
Today, together with our multinational people, we are building a new Uzbekistan. The new Uzbekistan is a new life, a new development, a happy future.
If we unite more firmly and continue the initiated reforms with even greater determination, we will undoubtedly achieve this great goal.
We will surely raise our children to be a generation of true patriots, highly educated, possessing modern knowledge and professions.
I wish you happiness and success on this path.
May the Almighty protect our nation!
I once again congratulate you on the holy holiday of Kurban Hayit, wish you health, peace and prosperity to your families.
Shavkat Mirziyoyev,
President of the Republic of Uzbekistan
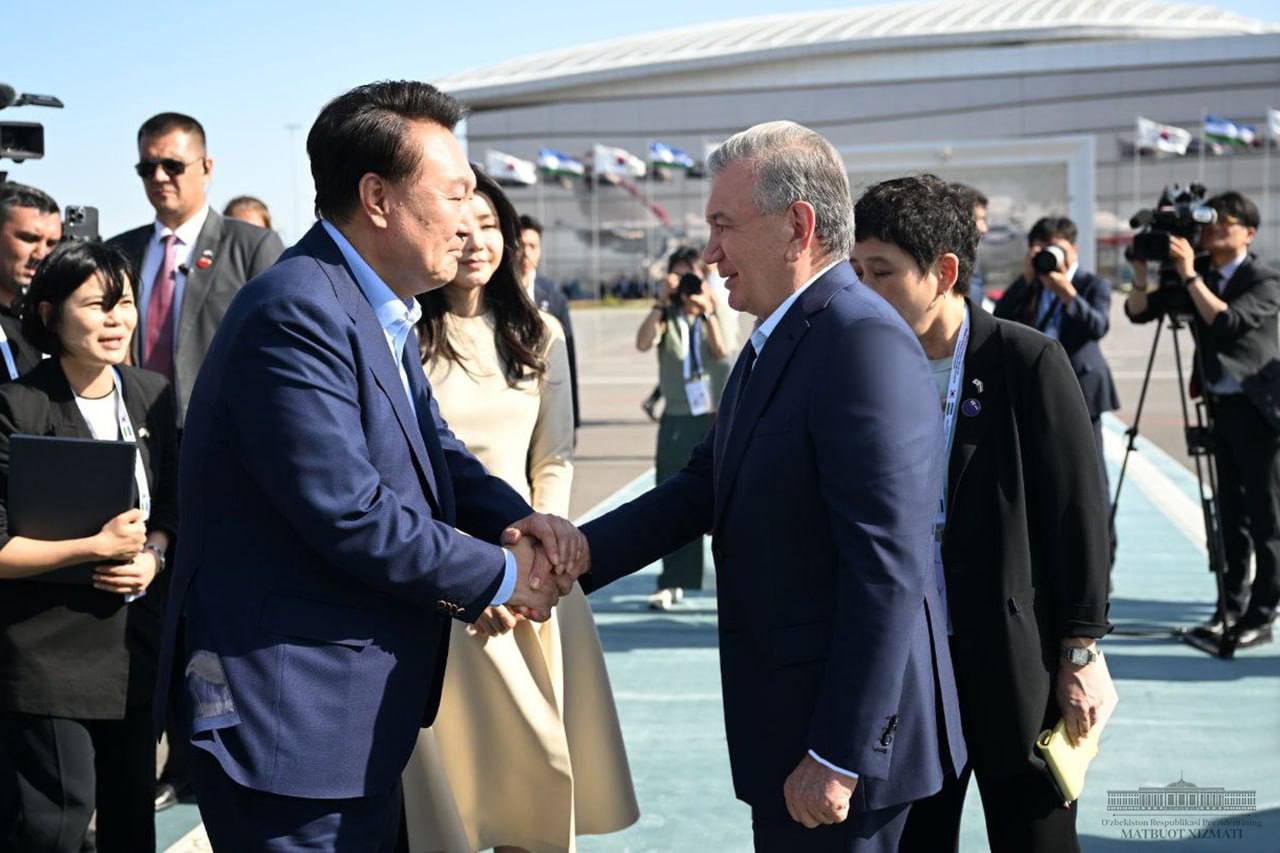
The Uzbekistan-Korea summit has ended
📅 15.06.2024
The state visit of the President of the Republic of Korea Yoon Seok-yol at the invitation of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev has ended.
During the three-day visit, high-level talks were held, at the end of which the leaders signed a joint statement on further deepening and comprehensive expansion of the Special Strategic Partnership. A bilateral set of documents was received.
The heads of state participated in a joint business forum with the participation of representatives of leading Korean companies and banking and financial institutions.
The presidents visited the Technopark in Tashkent and got acquainted with the existing potential for industrial cooperation.
Today, the dialogue between the heads of state continued in Samarkand. The presidents and their wives got acquainted with the historical and architectural masterpieces of the ancient city.
After the end of the visit, President Yun Sok Yol and his wife were escorted by President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Shavkat Mirziyoyev and his wife at the airport.
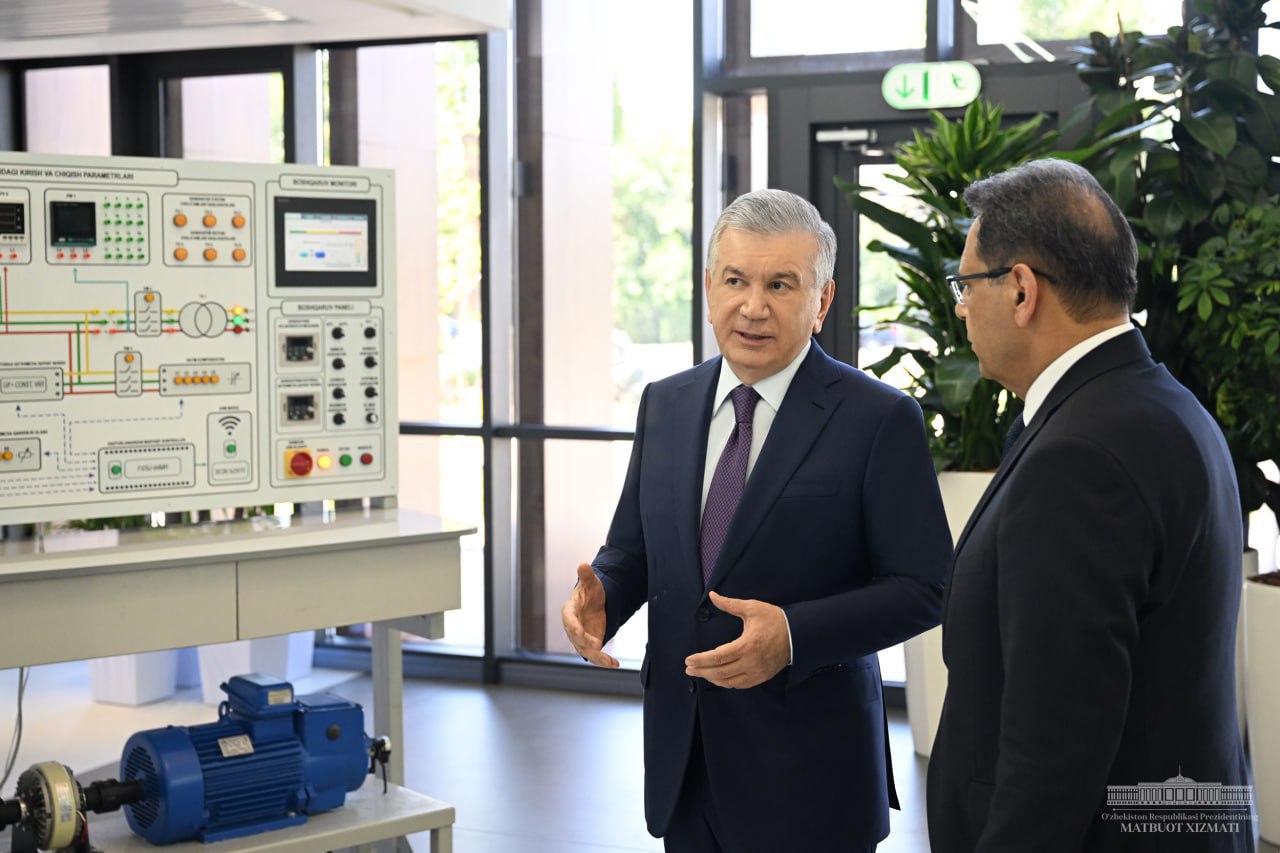
Proposals for the development of engineering education were considered
📅 20.06.2024
President Shavkat Mirziyoyev visited the Inno innovative training and production technopark in Almazar district of the capital.
This technopark was established three years ago. Innovative ideas and inventions for the development of industrial sectors are developed here. In order to train young people in modern professions, cooperation with higher educational institutions has been established. Every year seminars and workshops are held with the participation of about 15 thousand students and pupils.
There are more and more such innovation centers in our country. Industry, energy and information technologies are developing, new complexes are being launched. They require engineers and technicians with up-to-date knowledge and qualifications.
The activity of higher engineering schools established at Tashkent State Technical University, Bukhara Institute of Engineering and Technology, Tashkent State Transport University, Fergana Polytechnic Institute, Tashkent Architecture and Construction University and Tashkent University of Information Technologies has been presented to the President.
The decree of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan dated February 2, 2024 sets a number of tasks in this direction. In particular, according to the decree, the organizational and managerial activities of higher education institutions that train personnel in engineering and technology are being improved. The existing training programs are being studied and fundamentally changed in accordance with modern technologies and the requirements of employers.
The head of our state was informed about it.
At the first stage, higher engineering schools will be opened at 10 institutions of higher education. The supervisory board of the schools will include not only scientists, but also representatives of partner enterprises.
Two-year master's degree programs will be implemented in these schools, candidates will be selected on the basis of manufacturers' orders. In the first year, students will design new products on the orders of enterprises, conduct scientific research and study in in-depth modular programs. In the second year, they will test at enterprises technological processes related to the creation of prototypes of new products.
The President paid attention to the practical applicability and effectiveness of scientific research in higher educational institutions. It was noted that the attention paid to the education system should be really embodied in scientific achievements.
The head of state also familiarized himself with the inventions and advanced developments of researchers. In particular, energy-efficient devices, a cooling system protecting transformers from overheating under load, chemical reagents important for the oil and gas industry, modern approaches in construction, including road construction, engineering projects for hydraulic structures and modern solutions in the field of information technologies were presented.
Members of the Uzbekistan national chess team
📅 24.09.2024
I cordially congratulate you on your worthy participation in the 45th World Chess Olympiad held in Budapest, the capital of Hungary. You have opened another bright page in the history of Uzbek chess, taking the honorable third place among representatives of about 200 countries.
In very sharp and uncompromising chess duels, you, having demonstrated high intellectual potential, unwavering will and steadfastness, outperformed the teams of such countries as China, Serbia, Armenia, Germany, Azerbaijan, Slovenia, Spain, which is truly admirable.
By your example, we have seen that the youth of New Uzbekistan is capable of achieving truly high standards in competitions of mind and thinking, and this has filled our hearts with a sense of joy and pride.
The results achieved by Nodirbek Abdusattorov, Zhavohir Sindorov, Shamsiddin Vokhidov, Nodirbek Yokubboyev and Zhakhongir Vokhidov, who displayed outstanding intellectual abilities, are very valuable and dear to us.
It should be especially noted that Shamsiddin Vokhidov, having won a gold medal and Nodirbek Abdusattorov a silver medal in the board section, proved again what true masters of chess game they are.
Along with courageous and brave young men, our purposeful chess players such as Afruza Hamdamova, Nilufar Yokubboeva, Umida Omonova, Marjona Malikova, Nodira Nodirjonova, who directed all their strength and energy, skill and professionalism to worthily defend the honor of the Motherland, also took part in the competition.
It is undoubtedly noteworthy that they improved their results from the last Olympiad, taking the 12th place among the
170 countries. It is gratifying that our chess player Nodira Nodirjonova won the 2nd place in the board section and was awarded a silver medal. I sincerely congratulate them all, wish them to reach even higher milestones and take prizes at future competitions.
Undoubtedly, the tremendous success of our chess players is a practical result of the enormous attention paid to the youth in New Uzbekistan, the ongoing large-scale reforms to develop sports, including the most intellectual one - chess.
Undoubtedly, such bright achievements further unite our people on the way to noble goals, serve as a source of inspiration for thousands of young men and women.
Taking this opportunity, on behalf of all our people and on my own behalf I express my sincere gratitude to you, my dear ones, to your experienced mentors and coaches who made a great contribution to your success, to all members of the national team, to your parents who supported you and to all chess fans.
May you have good luck in conquering the highest peaks at the next World Chess Olympiad, which will be hosted by our native Uzbekistan for the first time in 2026!
I wish you all health, happiness and well-being, great success in your studies and subsequent activities. May your path to victory be steadfast, my dear ones!